AI Overview:
This blog delivers a practical, step-by-step cybersecurity checklist designed specifically for small and mid-sized businesses. It explains why SMBs are frequent targets and outlines 10 essential security controls—from multi-factor authentication, patch management, and endpoint protection to backups, incident response, and employee training. Rather than abstract advice, the guide focuses on clear implementation steps that reduce risk, protect data, and improve resilience. Overall, it positions cybersecurity as an ongoing business function and provides a roadmap to move from reactive defenses to a proactive, layered security posture.
Cyber threats pose a significant risk to small and mid-sized businesses, where a single breach can have devastating financial and reputational consequences. Many business owners mistakenly believe they are too small to be a target, yet attackers often view them as accessible entry points into larger supply chains. Lacking enterprise-level resources does not mean you have to accept enterprise-level risks. A structured, proactive approach to security is not just achievable; it’s essential for survival and growth.
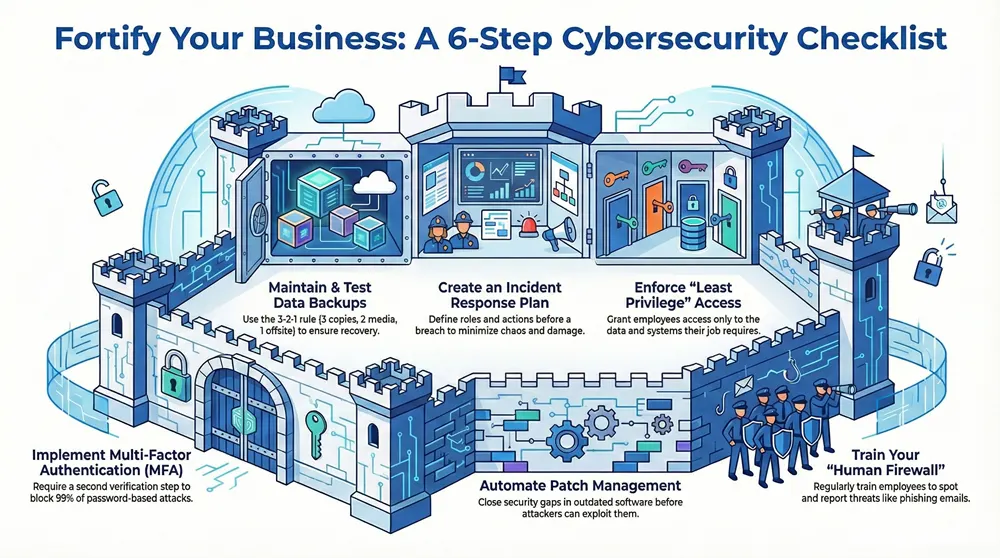
This article provides a definitive small business cybersecurity checklist, moving beyond generic advice to offer a prioritized, actionable framework. You will learn the 10 critical security controls needed to build a resilient defense, protect your sensitive data, and ensure business continuity. We will detail specific implementation steps for everything from multi-factor authentication and patch management to incident response planning and user training. At the core of any robust cybersecurity strategy are foundational data security principles that every small business must uphold, and this guide puts those principles into practice.
Each item on this checklist is designed to be a clear, manageable step that directly reduces your organization’s attack surface. Instead of abstract concepts, you’ll find practical guidance on what to do, why it matters, and how to get it done. By following these steps, you can systematically fortify your defenses, safeguard client and company information, and transform your security posture from reactive to proactive. Let’s begin building a more secure future for your business.
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to protect your business assets. A single compromised password can give an attacker complete access to your sensitive data. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) acts as a powerful security barrier, requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access, drastically reducing the risk of unauthorized entry.
MFA works by combining independent categories of credentials. This means a user must present proof from at least two of the following: something they know (a password), something they have (a security token or a code from a mobile app), or something they are (a fingerprint or facial scan). For example, a global technology firm thwarted a sophisticated phishing attack because the attackers, despite having stolen passwords, could not bypass the mandatory MFA prompt, saving the company from a significant breach. To understand the nuances between different approaches, you can learn more about 2-step and 2-factor authentication here.
How to Implement MFA
Implementing MFA is a critical first step in any small business cybersecurity checklist. Start by identifying your most critical systems and data.
- Prioritize Critical Accounts: Begin your MFA rollout with high-value targets. This includes all administrative accounts, email systems (like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace), financial software, and any cloud service storing sensitive customer data.
- Choose the Right Method: While SMS-based codes are better than nothing, authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator are more secure as they are not vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. Hardware tokens offer an even higher level of security.
- Communicate and Train: Prepare your team for the change. Provide clear instructions, support documentation, and training on how to set up and use MFA. Explain why it is essential for protecting both company and personal information.
- Secure Backup Codes: When users enroll in MFA, they are often given one-time backup codes. Instruct them to store these codes in a secure, offline location, such as a physical safe or an encrypted password manager.
2. Patch Management and Vulnerability Scanning
Running outdated software is like leaving your business’s front door unlocked. Every day, vendors like Microsoft and Apple release security patches to fix newly discovered vulnerabilities. Failing to apply these updates provides attackers with a clear and easy path into your network. A structured patch management and vulnerability scanning program is fundamental, ensuring you find and fix these security gaps before they can be exploited.
This two-part strategy is a cornerstone of any effective small business cybersecurity checklist. Patch management involves applying vendor updates to software, firmware, and operating systems in a timely manner. Vulnerability scanning is the proactive process of using tools to identify potential weaknesses across your systems. Together, they create a powerful defensive cycle that significantly hardens your security posture.
How to Implement Patch and Vulnerability Management
A consistent and repeatable process is key to keeping your systems secure. This involves not just applying updates, but also testing them and prioritizing the most critical fixes first.
- Create a Patch Management Policy: Define clear timelines for applying updates based on their severity. For example, mandate that critical patches identified in vendor security advisories, like a major Windows vulnerability, are deployed within 72 hours, while less severe ones can be scheduled for a monthly maintenance window.
- Automate and Centralize: Use automated tools to streamline patch deployment. For Windows environments, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) can manage updates across your network. For Apple devices, solutions like Jamf or Kandji provide centralized control. Automation reduces manual effort and ensures no system is missed.
- Schedule Regular Vulnerability Scans: Implement a routine scanning schedule using tools like Nessus or Qualys. Start with at least quarterly scans of all internet-facing systems and internal networks; monthly is even better. These scans will generate reports detailing weaknesses and their severity.
- Prioritize and Remediate: Not all vulnerabilities are equal. Use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score from your scan reports to prioritize remediation. Focus on fixing critical and high-severity vulnerabilities first, especially those known to be actively exploited by attackers. Track your progress with metrics like Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR).
3. Enforce Strong Password Policies and Management
Relying on weak or reused passwords is one of the most common ways businesses expose themselves to cyberattacks. A single compromised credential can grant an attacker access to your entire network. Strong password policies, combined with effective password management tools, create a formidable defense against credential-based breaches by ensuring that every access point is secured with a unique, complex key.
This approach works by establishing clear rules for password creation and lifecycle, then providing employees with the tools they need to adhere to those rules without friction. A modern policy, guided by standards like NIST SP 800-63B, emphasizes length and uniqueness over forced, frequent rotations. This reduces user frustration and discourages the unsafe practice of writing passwords down or making minor, predictable changes.
How to Implement Strong Password Policies
Integrating robust password management is a foundational element of any small business cybersecurity checklist and directly hardens your defenses against unauthorized access.
- Set Modern Password Standards: Mandate a minimum password length of 14 characters, including a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. More importantly, educate your team that a longer passphrase (e.g.,
Correct-Horse-Battery-Staple) is more secure and easier to remember than a short, complex password (e.g.,P@ssw0rd1!). - Deploy a Business Password Manager: Implement an enterprise-grade password manager like 1Password, LastPass, or Dashlane across your organization. These tools securely store credentials, generate strong, unique passwords for every service, and facilitate secure sharing among team members. You can find the right solution by reviewing a guide to the best password managers for business.
- Monitor for Compromised Credentials: Use tools that check employee passwords against databases of known breaches. Many password managers have this feature built-in, alerting users if their credentials have appeared in a public data leak so they can be changed immediately.
- Train Your Team: Conduct regular training on the importance of password hygiene. Teach employees how to use the password manager effectively, how to identify phishing attempts designed to steal credentials, and why they should never reuse passwords across personal and work accounts.
4. Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Technology and tools are only part of the solution; your employees are the first and most critical line of defense against cyber threats. Security awareness training educates your team about common attack vectors, cybersecurity best practices, and their specific role in protecting organizational data. Since human error is a factor in the vast majority of breaches, empowering your employees with knowledge is one of the most effective security investments you can make.
Effective training transforms your workforce from a potential vulnerability into a “human firewall.” It moves beyond a simple annual presentation to become an ongoing program that reinforces secure behaviors. By regularly simulating real-world threats like phishing, you can measure and improve your team’s ability to spot and report malicious activity, significantly reducing your organization’s risk profile. To learn more about this approach, you can explore how to build a human firewall as your first line of cyber defence.
How to Implement Security Awareness Training
Building a culture of security is a vital part of any small business cybersecurity checklist. A successful program is engaging, consistent, and relevant to your employees’ daily tasks.
- Make Training Role-Specific: Tailor content to different departments. Your finance team needs specific training on invoice fraud and business email compromise, while your IT staff requires more technical instruction.
- Run Simulated Phishing Campaigns: Use services like KnowBe4 or Cofense to send safe, simulated phishing emails to your staff monthly. This provides invaluable, real-world practice in a controlled environment and delivers clear metrics on your team’s progress.
- Keep It Short and Frequent: Instead of one long annual session, opt for short, engaging training modules (15-20 minutes) delivered quarterly or semi-annually. This “micro-learning” approach dramatically improves knowledge retention.
- Focus on Education, Not Punishment: When an employee clicks on a simulated phish, use it as a teaching moment. Punitive measures can discourage reporting. To ensure your security awareness programs are truly effective and engaging, consider adopting principles from actionable compliance training best practices.
- Track and Document Everything: Maintain records of who has completed training and when. This documentation is crucial for demonstrating due diligence and meeting compliance requirements.
5. Maintain Comprehensive Data Backups with Testing
A single event, such as a ransomware attack, hardware failure, or even a simple human error, can wipe out your most critical business data. Comprehensive data backups serve as your digital insurance policy, creating copies of your information that can be restored to get you back up and running. Without a reliable and tested backup strategy, your business is one disaster away from a potential shutdown.
The core principle behind effective backups is the 3-2-1 rule: maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep at least one copy offsite or “air-gapped.” This layered approach ensures that even if one backup is compromised, others remain safe and accessible. For instance, businesses that had offline backups were able to recover from the WannaCry ransomware attack with minimal data loss, while others without them were forced to pay ransoms or cease operations.
How to Implement Data Backups
Effective implementation goes beyond just creating copies; it involves a robust, automated, and tested process. Integrating this into your small business cybersecurity checklist is non-negotiable for resilience.
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Implement a clear strategy to have three total copies of your data. This could be your live data, a local backup on a network-attached storage (NAS) device, and a third copy with a cloud backup provider like Backblaze or AWS Backup.
- Automate and Isolate: Backups should run automatically on a daily schedule with zero manual intervention required. Ensure at least one backup copy is stored offline or on an isolated network segment (air-gapped) so that a network-wide attack cannot infect it.
- Test Your Restores: A backup is useless if it can’t be restored. Schedule quarterly tests where you attempt to restore files, servers, or entire systems from your backups. This practice validates your data integrity and familiarizes your team with the recovery process.
- Encrypt Everything: All backup data, whether at rest on a storage device or in transit to the cloud, must be encrypted using strong, modern encryption standards like AES-256. This prevents unauthorized access if a backup device is stolen or compromised.
6. Deploy and Maintain Endpoint Protection (EDR/XDR)
Traditional antivirus software is no longer enough to defend against sophisticated cyberattacks. Modern threats often bypass signature-based detection, making advanced endpoint protection a non-negotiable part of your security strategy. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions provide comprehensive, real-time protection by monitoring and responding to threats across all your company devices.
Unlike basic antivirus that only scans for known threats, EDR and XDR tools actively hunt for suspicious behavior patterns. For example, a solution like SentinelOne or CrowdStrike can detect when a common application like Microsoft Word suddenly tries to encrypt files—a classic sign of a ransomware attack—and can automatically stop the process and isolate the device. This proactive approach significantly reduces the time an attacker has to cause damage. For a deeper understanding of these technologies, Gartner offers extensive research on the EDR and XDR frameworks.
How to Implement Endpoint Protection
Rolling out an effective EDR or XDR solution is a foundational element in any modern small business cybersecurity checklist. It hardens the devices where your team works and your data resides.
- Cover All Endpoints: Ensure your chosen EDR solution is deployed on every device connecting to your network. This includes not just laptops and desktops but also servers and company-owned mobile devices. A single unprotected endpoint can be a gateway for an attacker.
- Configure Automated Responses: A key benefit of EDR/XDR is its ability to react instantly. Configure automated response rules to handle common threats, such as quarantining infected files, blocking malicious network connections, and isolating a compromised device from the rest of the network to prevent an attack from spreading.
- Ensure Continuous Monitoring: Effective protection requires constant vigilance. Verify that your EDR platform is configured for 24/7 logging and alerting. Regularly review these alerts to identify potential threats and tune your detection rules to reduce false positives and improve accuracy over time.
- Keep Intelligence Updated: EDR solutions rely on up-to-date threat intelligence to recognize the latest attack techniques. Ensure that your system is set to automatically update its threat signatures, behavioral models, and intelligence feeds. This keeps your defenses aligned with the evolving threat landscape.
7. Implement Network Security and Firewall Controls
Your network is the central nervous system of your business operations, making it a prime target for cyberattacks. A single breach can allow an attacker to move freely, accessing sensitive files and critical systems. Network firewalls and segmentation act as digital gatekeepers, controlling the flow of traffic to and from your network and between different internal segments, effectively containing threats.
Modern next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) go beyond simple traffic blocking. They provide advanced capabilities like intrusion prevention, application awareness, and integrated threat intelligence to identify and stop sophisticated attacks before they can cause damage. By creating secure zones, you can isolate critical assets, such as financial servers, from general-use areas, limiting the potential impact of a compromise.
How to Implement Network Security
Properly configured network security is a cornerstone of any effective small business cybersecurity checklist. Start by establishing a strong perimeter and then work inward to protect your most valuable assets.
- Deploy a Perimeter Firewall: Your first line of defense is a robust firewall between your internal network and the internet. Configure it with a “default-deny” rule, which means all traffic is blocked unless it is explicitly permitted. This ensures only necessary communication is allowed.
- Segment Your Network: Divide your network into smaller, isolated zones. For example, create separate segments for your guest Wi-Fi, internal servers, and point-of-sale systems. This prevents an intruder who compromises a less secure zone, like guest Wi-Fi, from accessing your critical business data.
- Monitor and Update Rules: Your business needs will change, and so should your firewall rules. Regularly review firewall logs for suspicious activity and update your rule sets to remove outdated permissions. Keeping your firewall’s firmware and threat intelligence feeds current is also critical.
- Filter Outgoing Traffic: Egress filtering controls what data can leave your network. This is a powerful technique to block malware from “phoning home” to its command-and-control server or to prevent an unauthorized user from exfiltrating sensitive company data.
8. Establish an Incident Response Plan and Testing
Despite the best preventative measures, a security incident is not a matter of if, but when. An Incident Response (IR) plan is a documented, pre-agreed-upon strategy for how your business will handle a security breach or cyberattack. Having a clear plan minimizes chaos, reduces damage, contains the threat efficiently, and significantly shortens recovery time.
An IR plan acts as a playbook for chaos. It outlines specific procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from incidents like ransomware attacks, data breaches, or denial-of-service attacks. Without one, teams are forced to make high-stakes decisions under extreme pressure, often leading to costly mistakes. Organizations like the SANS Institute and NIST provide frameworks that help businesses prepare for these inevitable events.
How to Create and Test an Incident Response Plan
Developing a functional IR plan is a foundational element of any complete small business cybersecurity checklist. The goal is to ensure a coordinated and effective response when an incident occurs.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Assign specific roles before an incident happens. Key roles include an Incident Commander to lead the effort, a Technical Lead to manage the IT response, and a Communications Lead to handle internal and external messaging. Maintain an up-to-date contact list for this team.
- Create Response Playbooks: You don’t need a single plan for every possibility. Instead, develop specific playbooks for the most likely threats to your business, such as phishing attacks, malware infections, or lost devices. Outline the step-by-step actions for each scenario.
- Establish Communication Protocols: Determine how, when, and what you will communicate to employees, customers, suppliers, and potentially law enforcement or regulatory bodies. Having pre-drafted communication templates can save critical time.
- Conduct Regular Tabletop Exercises: A plan is useless if it’s not tested. At least quarterly, run tabletop exercises where you simulate a security incident. This allows your team to walk through the plan, identify gaps, and practice their roles in a low-stress environment. After each exercise, update the plan with lessons learned.
9. Secure Remote Access and Work-From-Home Infrastructure
As hybrid and remote work models become standard, the boundaries of your office network have dissolved. Each remote employee’s connection is a potential entry point for attackers. Securing your remote access infrastructure is essential to protect your business from data breaches and prevent unauthorized access to your core systems. A robust strategy involves using technologies like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and zero-trust principles to create a secure, encrypted tunnel between remote workers and company resources.
This approach ensures that all data transmitted over public networks, such as home Wi-Fi or coffee shop internet, remains confidential and protected. By treating every connection attempt with scrutiny, regardless of its origin, you build a resilient defense against threats targeting your distributed workforce. Implementing these controls is a non-negotiable part of a modern small business cybersecurity checklist.
How to Secure Remote Access
Securing your work-from-home infrastructure requires a multi-layered approach that combines strong authentication, device compliance, and continuous monitoring.
- Implement a Business-Grade VPN with MFA: Deploy a reliable VPN solution like Cisco AnyConnect or Fortinet FortiClient. Critically, you must enforce multi-factor authentication for every VPN connection to verify user identities and prevent access via stolen credentials.
- Enforce Endpoint Security: Do not allow any device to connect to your network that does not meet your security standards. Use endpoint protection software to verify that devices have active antivirus, up-to-date patches, and a firewall enabled before granting access.
- Adopt Zero-Trust Principles: Move away from the old model of trusting everyone inside the network. Verify every connection attempt, every time. Implement conditional access policies, for example, using Microsoft Azure AD to block access from unmanaged devices or high-risk locations.
- Disable Split Tunneling: Configure your VPN to route all of the user’s internet traffic through the corporate network. This prevents employees from bypassing your security controls (like web filtering and threat detection) and ensures all activity is monitored and protected.
10. Establish Access Control and Least Privilege Principles
Giving every employee broad access to your company’s digital assets is a significant security risk. A single compromised account could expose your entire network. The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) is a foundational cybersecurity concept that ensures users and systems have only the minimum levels of access, or permissions, needed to perform their job functions, drastically limiting potential damage from a breach or insider threat.
Adopting this principle means that if an employee’s account is compromised, the attacker’s movement is restricted to only what that user could access. This containment strategy is essential for protecting sensitive data and critical systems. Leading frameworks like the NIST Zero Trust Architecture are built upon this core idea, moving away from a model of inherent trust to one that requires verification for every access request.
How to Implement Access Control
Implementing a least privilege model is a key part of any small business cybersecurity checklist and involves creating a structured, role-based system for permissions.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Group users based on their job roles and responsibilities (e.g., “Sales,” “Finance,” “IT Admin”). Assign permissions to these roles rather than to individual users. This simplifies management and ensures consistency.
- Separate Standard and Administrative Accounts: No user should use an administrative account for daily tasks like checking email. Provide a separate, standard user account for routine work and require a switch to a privileged account only when necessary.
- Conduct Regular Access Reviews: At least quarterly, review who has access to what. This process helps identify and remove unnecessary permissions, especially for employees who have changed roles or left the company. Immediately revoke all access for terminated employees.
- Use Privileged Access Management (PAM): For your most critical systems, consider a PAM solution. These tools add layers of security, such as monitoring, logging, and requiring approval workflows for any use of administrative credentials.
- Establish Clear Third-Party Access Rules: Create and enforce strict access policies for contractors, vendors, and partners. Grant them temporary, role-based access only to the specific systems required for their work and deactivate it as soon as the project is complete.
Turn Your Checklist into an Action Plan
Completing this small business cybersecurity checklist is a critical first step toward building a resilient defense. The ten fundamental controls we’ve detailed—from implementing MFA to establishing an incident response plan—are not isolated tasks. They are interconnected components of a dynamic security program designed to protect your most valuable assets. Think of security not as a one-time project, but as an ongoing business function as essential as finance or marketing.
Your goal is to build layers of defense that make your organization a much less attractive target. By prioritizing foundational elements like patch management and endpoint protection, you close the most common entry points. By investing in regular security awareness training, you empower your employees to become your first line of defense. And by maintaining and testing your data backups, you create a safety net that ensures business continuity.
Ultimately, mastering these concepts is about more than just avoiding a data breach. It’s about building trust with your clients, protecting your reputation, and ensuring the long-term viability of your business. Use this checklist not as a finish line, but as your roadmap for a continuous journey toward digital resilience.
Navigating the complexities of cybersecurity can be overwhelming, but you don’t have to do it alone. 1-800 Office Solutions offers comprehensive Managed IT and Cybersecurity services designed to help you implement this checklist and build a defense-in-depth security strategy. Partner with our experts to gain 24/7 protection and the peace of mind to focus on growing your business.