Insider Threats: Human Error Remains a Significant Cause of Data Breaches
Insider Threats
Data breaches have been a growing concern for businesses and organizations around the world due to the potential financial and reputational damage they can cause. A particular area of attention has been the role of insider threats, which can be divided into two main categories: malicious insiders and human error. This article focuses on the latter, examining the role of human error in data breaches and the measures that can be taken to prevent them.
The issue of human error remains a significant factor in data breaches, with the potential to leave organizations vulnerable to malicious actors. From accidental misconfigurations to careless sharing of sensitive data, human error can occur at multiple stages of the security process. In addition, the complexity of modern systems can also lead to errors that can have catastrophic consequences. As such, organizations need to create a comprehensive security strategy that takes into account the risk of human error and the potential for insider threats.
Understanding Insider Threats
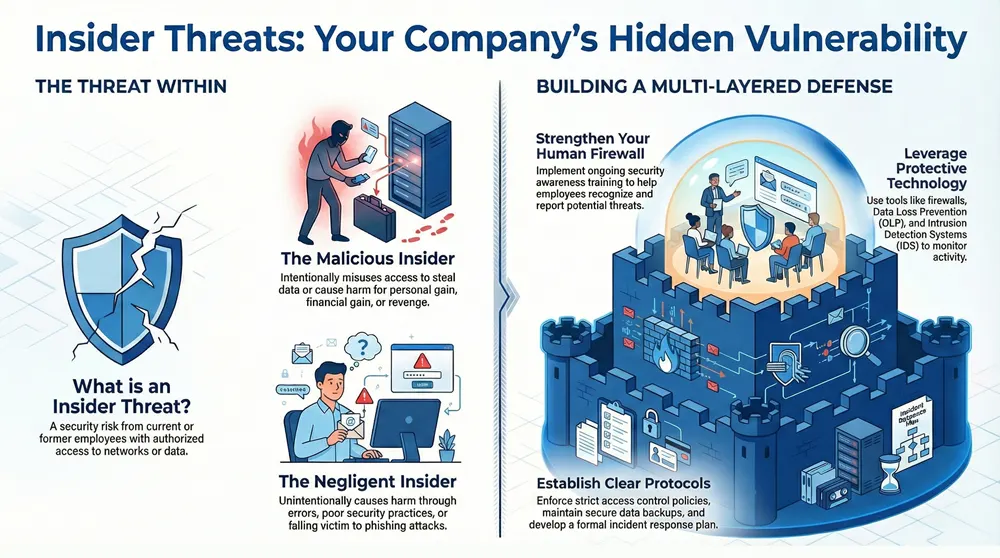
Insider threats are a complex security risk that originates from within an organization. Malicious insider threats are intentional and malicious actions taken by employees, contractors, or other insiders who have authorized access to an organization’s network, confidential information, or critical assets. Unintentional insider threats are associated with negligence or lack of security awareness and include cases of data loss caused by incorrect data management practices.
Insider threat indicators include a change in user behavior, privileged access to data, accessing large quantities of data, or a former employee attempting to access an organization’s network.
Types of Insider Threats
With the rise of technology, it is increasingly important to understand the risk of Insider Threats. Insider Threats can come in many forms, from malicious actors to negligent behavior. This section will focus on the different types of Insider Threats, and how to mitigate them.
Below are the various types of Insider Threats that organizations must be aware of:
- Malicious Insider Threats: These threats arise from malicious intent of an insider, and can come in the form of a malicious attack or a data breach. Examples of malicious insider threats include theft of intellectual property, or trade secrets.
- Unintentional Insider Threats: These threats are typically caused by negligence or lack of knowledge. Examples of unintentional insider threats include user error, or mistakenly sending confidential information to an unauthorized party.
Organizations must be prepared to recognize the risk of insider threats, and take measures to mitigate them. This can be done by implementing security measures such as regular user behavior monitoring, threat management, and security policies and procedures. Additionally, security teams should focus on both external threats, as well as potential insider threats.
Organizations should also employ security solutions such as data loss prevention, firewall and intrusion detection systems, best practices for cyber security, and security awareness training.
Examples of Insider Threats
It is a sad and sobering truth that the potential for insider threats to cause irreparable damage to an organization’s network is very real. As much as organizations may like to focus on external threats, malicious insiders can be just as damaging. Examples of insider threats include malicious insiders, negligent insiders, and former employees.
- Malicious Insiders: These are individuals with malicious intent, such as employees or contractors who misuse their access privileges to steal confidential information or intellectual property. They may also use their privileged access to launch a cyber attack on the organization’s network or damage its critical assets. These type of insider threats could be driven by personal gain, financial gain, or revenge.
- Negligent Insiders: These are individuals who unintentionally compromise the organization’s network and sensitive data. They may fall victim to social engineering, phishing emails, and other malicious attacks. These individuals may also be unaware of the organization’s security policies and procedures, resulting in them unknowingly exposing the organization to security threats.
- Former Employees: Former employees can still pose a threat to an organization’s network, especially if they still have access to the organization’s confidential information or proprietary data.
Impact of Insider Threats
Transitioning from the previous section, the impact of insider threats should not be underestimated. Insider threats are a major security risk that can have disastrous results for organizations. A malicious insider threat can cost organizations in lost intellectual property, confidential information, trade secrets, customer information, and financial losses. Not to mention, an organization’s reputation and brand can also be damaged by a malicious insider attack.
The potential for an insider threat to use their authorized access to exploit an organization’s network and steal confidential information makes insider threats more difficult to detect and prevent than external threats. Organizations must focus on both external and internal threats, to secure their networks and protect their critical assets.
To mitigate the risk of insider threats, organizations must have effective security measures and threat management solutions in place. Security professionals must be familiar with security policies and procedures, insider threat indicators, and best practices for insider threat detection and prevention.
- Security Measures:
- Security awareness training for employees
- Monitor insider behavior, user activity, and credentials
- Security policies and procedures
- Firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Data loss prevention solutions
- Intrusion detection systems
- Advanced threats
Identifying Potential Insider Threats
Identifying potential insider threats requires identifying risk factors, monitoring employee activity and implementing security protocols. Threats can come from malicious insiders, external sources and negligence. Common types of insider threats include stealing intellectual property, trade secrets, customer information, and accessing confidential information.

Organizations must focus on both external and internal threats, and use cyber security measures like phishing attack prevention, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention. Security teams must also monitor user behavior and behavior from current and former employees to detect malicious behavior. Insider threat indicators include over privileged access, credential sharing, large quantities of data transferred, and the use of multiple data sources.
Identifying Risk Factors
Transitioning from the previous section, understanding the various types of insider threats, it is important to be able to identify potential insider threats. One of the most effective ways to do this is by first understanding the risk factors associated with insider threats and then systematically monitoring employee activity and implementing security protocols to mitigate the risk.
When it comes to identifying risk factors associated with insider threats, it is important to note that this type of security risk can originate from both malicious and unintentional threats. Malicious insiders are typically employees or former employees who intentionally use their privileged access to resources and confidential information to steal intellectual property, trade secrets, or customer information. Unintentional insider threats, or negligent insiders, are typically caused by employees accidentally introducing malicious actors, malware, or phishing attacks into the organization’s network.
It is important to note that insider threats are usually more difficult to detect than external threats. When focusing on external threats, cybersecurity teams can utilize various security solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention to mitigate and prevent security incidents. However, when it comes to mitigating insider threats, security teams must be more proactive in monitoring user behavior and insider access and focus on implementing best practices and security measures to detect insider threat indicators.
Monitoring Employee Activity
Transitioning from the previous section, in order to properly identify and mitigate potential insider threats, it is necessary to monitor employee activities. By doing so, organizations can identify risk factors, observe insider behavior, and detect malicious insiders.
Using data sources such as access logs, user activity log, and audit reports, cybersecurity professionals can track any suspicious activity within the organization’s network. It also allows them to pinpoint any potential security risks that originate from within. This can be done through a process of monitoring user behavior, privilege access, credential usage, and potential malicious actions. Furthermore, security professionals can also observe the activity of both current and former employees to identify any malicious insider attack.
In order to effectively monitor insider behavior, organizations should focus on implementing security protocols such as data loss prevention systems, intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and security awareness. These measures, in combination with best practices such as threat management and security solutions, can be used to mitigate potential insider threats, as well as cyber security risks.
Therefore, by monitoring employee activity, organizations can identify risk factors, observe insider behavior, and detect malicious insiders. This, in turn, can help them protect their critical assets and confidential information, as well as reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Implementing Security Protocols
While the external threats to an organization’s cyber security are numerous and often difficult to detect, the potential for an insider to use their authorized privileges to maliciously or negligently cause harm is often overlooked. Insider threats are typically more difficult to detect and can have catastrophic outcomes, making it essential to focus on mitigating insider threats.
Organizations should take steps to prevent insider threats by implementing the following security measures:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection: Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are essential for preventing malicious actors from infiltrating an organization’s network and stealing confidential information. Such systems should be regularly monitored to detect any suspicious activity.
- Security Awareness: Organizations should create security awareness programs to educate employees on the risks of insider threats and how to identify or prevent them. Security teams should also put in place security policies and procedures for all employees to protect the organization’s critical assets, such as its proprietary information or large quantities of data containing sensitive information.
- User Behavior Monitoring: Security professionals should also monitor user behavior to detect any malicious insider behavior, such as a malicious insider attack, a phishing attack, or a data breach. By monitoring user behavior, organizations can quickly identify any potential insider threats and take steps to protect their network security.
The Role of Human Error
The role of human error is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, with causes ranging from malicious and external threats to negligence and insider access. Malicious and external threats such as phishing attacks, malware, and other cybersecurity risks can lead to data breaches, loss of proprietary information, and security incidents.
Negligent or unintentional insiders can also cause errors, making it easier for threat actors to access confidential and sensitive data. Organizations must be aware of the potential for an insider to use their authorized access to cause harm, either intentionally or unintentionally.
Causes of Human Error
The potential for an insider to unintentionally or maliciously cause harm to an organization’s network and its sensitive data is a unique and serious security risk that often goes overlooked. Common causes of human error in insider threats include:
- Poor Security Practices:
- Failing to keep up with security patches or other security measures
- Improperly disposing of confidential information
- Not properly training users in security policies
- Accidental Mishaps:
- Unintentionally sending sensitive information to the wrong recipient
- Failing to delete copies of sensitive information
- Losing devices containing proprietary information
These are only a few examples of how human error can contribute to insider threats. Unfortunately, insider threats are typically more difficult to detect since the perpetrator is already familiar with the company’s security measures and protocols.
In addition, insider threats pose a higher risk since the perpetrator already has access to the company’s critical assets and can steal large quantities of data from multiple sources before anyone notices. Security teams must be mindful of both malicious and unintentional threats when monitoring insider behavior and developing security measures.
Impact of Human Error
The impact of human error can be disastrous for an organization. A malicious insider or external threat actor can easily exploit the negligence of an employee to gain access to confidential, sensitive, or proprietary information. This could lead to a data breach, theft of intellectual property, or the disruption of critical assets.
It is not just malicious insiders that can cause a significant risk; oftentimes, employees can unintentionally cause damage to the organization’s network, critical assets, or proprietary data. By failing to follow security policies and procedures, or through unknowingly downloading malicious software or malware, employees can make insider threats easier to exploit.
Organizations must focus on mitigating both intentional and unintentional insider threats. Security teams must monitor user behavior and insider access to quickly identify and prevent potential malicious insider threats.
Additionally, security awareness programs and security solutions, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, should be implemented to protect against cyber security threats and reduce the cost of insider threats.
Though cybersecurity professionals should focus on external threats, dealing with insider threats is a priority for any organization. By understanding the potential risks associated with insider threats and implementing proper security measures, organizations can better protect their critical information and prevent potential malicious insider attacks.
Strategies to Reduce Human Error
The strategies to reduce human error are essential in preventing insider threats. With the right tools and knowledge, organizations can mitigate the risk of insider attacks and protect their confidential information, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Security teams can look at user behavior and monitor for potential insider threats, such as suspicious credential use, malicious behavior, and data exfiltration attempts.
By leveraging data sources, security professionals can identify and detect insider threats and advanced threats, providing multiple layers of security.
Organizations should focus on implementing security measures to protect critical assets and prevent access to proprietary data. Security solutions, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can help to protect the organization’s network against malicious actors. Security teams should also implement data loss prevention solutions to prevent the accidental or malicious leakage of sensitive data.
Security awareness and training are also essential in mitigating insider threats. Organizations should educate their employees on the potential insider threats, the cost of insider threats, and the best practices such as monitoring user behavior, avoiding clicking on phishing links, and avoiding the sharing of confidential information. Security teams should also create security policies and procedures to protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of insider threats.
Securing Data Access
Securing data access means limiting access to data, ensuring secure authentication, and implementing access control policies. To protect against insider threats, organizations need to be aware of the malicious insider threat, which is an external threat that can come from within the organization.

Malicious insiders can steal confidential information, intellectual property, or trade secrets, or even disrupt operations. To prevent this, organizations should use threat management solutions to monitor user behavior and detect insider threat indicators. Additionally, security teams should focus on potential external threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, and social engineering.
Limiting Access to Data
In order to ensure cyber security, it is important to limit access to data. Insider threats, whether malicious or negligent, can be some of the most difficult to detect and prevent. Malicious insider threats can involve cyber attacks from within an organization’s network and can include activities such as stealing intellectual property or customer information. Negligent insider threats might involve unauthorized access to data or the accidental introduction of malware to the organization’s network. Organizations must focus on both external threats and internal threats in order to mitigate the risk of insider threats.
Organizations need to protect their critical assets and confidential information, as well as their customers’ information, from malicious insider threats. They must also protect their trade secrets and intellectual property from competitors. Security professionals must focus on mitigating insider threats by developing security policies and procedures, monitoring user behavior and access to critical data sources, and implementing security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Organizations should also focus on preventing insider threats by educating employees on best practices and security awareness. Security teams must be familiar with security threats and indicators of insider behavior in order to identify or prevent malicious insider attacks. Security teams should also be aware of the potential for an insider to unintentionally or unintentionally breach the organization’s network.
Ensuring Secure Authentication
The potential for an insider to use their authorized access to critical assets, proprietary information, and large quantities of data for malicious purposes is a security risk that originates from within an organization and must be addressed in order to protect customer information, trade secrets, and intellectual property.
Focusing on external threats, such as malware and phishing attack, can leave an organization unprepared to detect, identify, or prevent malicious insider behavior that can lead to a data breach. Insider threats pose a unique challenge to security professionals, as threats occur both intentionally and unintentionally, making it more difficult to mitigate potential insider threats.
When it comes to ensuring secure authentication, there are several best practices that a security team must implement in order to protect against insider threats. Organizations must focus on insider threat prevention and detection by monitoring insider behavior and identifying insider threat indicators such as privileged access, risk of insider threats, and user behavior. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are also critical in mitigating insider threats as they can detect malicious behavior from both current and former employees, as well as from external threats.
Additionally, organizations should also establish security policies and procedures, and create security awareness training programs to help employees understand the cost of insider threats and the importance of data security. With these measures in place, organizations can protect their confidential information and prevent data loss.
Implementing Access Control Policies
Having discussed the role of human error in compromising the security of data access, the next step is to discuss the measures that can be taken to ensure secure data access. In particular, we will focus on implementing access control policies to mitigate the risks of insider threats.
Insider threats are malicious or negligent acts committed by a current or former employee, contractor, or business partner who has access to an organization’s network, confidential information, intellectual property, or trade secrets. Insiders may intentionally or unintentionally steal information, disrupt operations, or damage the organization’s reputation due to malicious, negligent, or careless behavior. Furthermore, insider threats are more difficult to detect than external threats, as the threat actor is familiar with the organization’s security measures.
Organizations must focus on mitigating insider threats by implementing security policies and procedures, and monitoring insider behavior. Security teams can obtain insight into an organization’s potential insider threats through insider threat indicators, such as changes in user behavior, privileged access, and large quantities of data being transferred. To mitigate the risk of insider threats, organizations should take measures to protect critical assets, such as applying firewalls and intrusion detection systems to detect malicious behavior.
Minimizing Data Loss
Minimizing data loss requires strategies to protect against all threats, both internal and external. Insider threats, caused by malicious or negligent insiders, are of particular concern as they are notoriously difficult to detect and mitigate. To protect against these threats, organizations must focus on implementing data backup strategies, limiting data storage and sharing, and encrypting data and communications.
Insider threats are most commonly caused by malicious insiders, such as a current or former employee, competitor, or another threat actor with privileged access and intent to steal confidential information. Organizations must monitor insider behavior and activity to identify potential insider threats and prevent data breaches.
Implementing Data Backup Strategies
With malicious outsiders often taking the focus of cybersecurity professionals, many organizations fail to recognize the risk posed by insider threats. From malicious actors to negligent employees, the potential for an insider to use their authorized access to steal or damage sensitive information cannot be ignored. Fortunately, implementing the right data backup strategies can help mitigate this risk.
Organizations must take measures to protect their critical assets and confidential information from both malicious and unintentional threats. This may include:
- Network Security: Utilizing firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent external attacks and limit access to sensitive data.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing security policies and procedures to help contain sensitive information from unauthorized users.
- Security Awareness: Training employees on cyber threats and best practices to help protect against potential insider threats.
- Monitoring Insider Behavior: Utilizing user behavior analytics and privileged access management to monitor and identify malicious insider behavior.
Data backup strategies are essential to mitigating the risk of insider threats. By focusing on both external and internal threats, organizations can protect their intellectual property, customer information, and other proprietary data. Security teams should also focus on mitigating insider threats through security solutions, security awareness training, and threat management.
Limiting Data Storage and Sharing
As we have discussed, minimizing data loss is critical to an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. One key strategy for doing this is to limit data storage and sharing. By limiting access to data, organizations can better protect against malicious insider threats, external threats, and user behavior that could lead to a data breach.
Security teams should focus on limiting the storage and sharing of sensitive data, intellectual property, proprietary information, and confidential customer information—all of which are potential targets of malicious insiders, competitors, and other threat actors. Best practices for limiting data storage and sharing include implementing security policies and procedures that define the types of data that can be stored, who can access it, and how it can be shared.
Organizations should also implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions. These solutions can help detect and prevent large quantities of data from being sent outside of the organization’s network. Additionally, DLP solutions can detect malicious insider behavior, such as a user attempting to upload a large amount of data to a cloud storage service.
The security team should also monitor insider behavior and user activities for insider threat indicators. These indicators can include sudden changes in user behavior, downloading large amounts of data from the organization’s network, or accessing confidential information that is beyond the scope of the user’s role.
Encrypting Data and Communications
Having secured data access, the next step in minimizing data loss is to implement data encryption to protect data and communications from malicious insiders and external threats. Encryption is a process by which data is converted into an encoded form that is only accessible to authorized personnel. This ensures that any data that is stolen or leaked is unreadable without the encryption key.
Organizations must apply encryption to all areas of their data infrastructure, including data stored on physical or virtual servers, in the cloud, and in transit. It is also essential to encrypt communications, such as email, telephone calls, and text messages, to protect them from eavesdropping.
In addition to encryption, organizations can use firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent malicious actors from accessing sensitive data. These systems work by monitoring user behavior and identifying any suspicious or malicious activities. Furthermore, organizations should focus on user education and threat management to ensure employees are familiar with security measures and can identify potential insider threats.
Organizations should also consider implementing data loss prevention solutions to monitor data sources and identify any unauthorized access or potential breaches. Additionally, organizations can use security policies and procedures to mitigate insider behavior and ensure employees are aware of the potential risk of insider threats.
Enhancing Security Awareness
Enhancing security awareness is essential in today’s world, especially with the increasing variety of cyber threats. Educating employees on security protocols and creating a security culture within the organization are key to making this happen.
Malicious insider threats, external threats, and cyber threats are all potential risks to an organization’s network and confidential information. By training current and former employees on security measures and mitigating insider behavior, organizations can protect their intellectual property and trade secrets from competitors.
Organizations must focus on both external and internal threats to detect and prevent malicious behavior.
Educating Employees
In order to maximize security awareness, it is essential to educate employees on the potential risks of insider threats. Insider threats are internal threats that originate from malicious or negligent behavior of a current or former employee, contractor, or partner that has access to the organization’s network and confidential information.
An insider threat can be malicious or unintentional, and examples include, but are not limited to, insider access to intellectual property, disruptive or competitive behavior, and theft of trade secrets. Insider threats are more difficult to detect than external threats and can have a high cost, which is why it is important to focus on mitigating insider threats with security measures, such as monitoring user behavior and recognizing insider threat indicators.
Security professionals must be familiar with the security risk that originates from potential insider threats. They should be aware of the types of insider threats, indicators of malicious insider threats, and best practices for protecting critical assets, such as proprietary information, from insider attack. It is important to consider the potential for an insider to use their authorized access, whether intentionally or unintentionally, to steal information or cause disruption to the organization’s network.
Organizations must also consider the data sources they use and the large quantities of data that contain sensitive information.
Training Employees on Security Protocols
It is essential to train employees on security protocols to mitigate the risk of insider threats and protect confidential information. Organizations can create an effective security culture by training their employees on the types of insider threats, the potential for an insider to use their authorized access to gain an advantage, and the potential for an insider to unintentionally or maliciously expose the organization’s network to external threats.
Organizations can focus on training employees on the best practices to protect against malicious insiders, as well as external cyber security threats such as phishing attacks and malware. They can also educate their employees on the cost of insider threats, the value of intellectual property and trade secrets, the risk of insider threats to an organization’s competitive advantage, and the security measures they can take to mitigate insider behavior.
Organizations need to provide their employees with the tools and resources necessary to protect the organization’s confidential information, such as data loss prevention solutions, security policies and procedures, user behavior monitoring, and access controls. They can also train their employees on the threat indicators of malicious insider activity, such as credential theft, privileged access, and the theft of large quantities of data.
Organizations should also train their employees on the potential risks of social engineering techniques and how to recognize potential insider threats.
Creating a Security Culture
Having discussed the importance of minimizing data loss, it is just as critical to understand the security risks associated with malicious insider threats. Creating a culture of security within an organization is one of the best ways to mitigate these risks.
To create a security culture, it is essential to educate and train employees on the latest security protocols and provide a secure work environment. The following are some of the measures that can be taken:
- Educating Employees: Create security awareness among the employees by providing them with regular security training and timely security alerts. Encourage them to report suspicious activities and share any security concerns they have.
- Training Employees on Security Protocols: Make sure that all employees receive regular training on the latest security protocols and are aware of the security policies and procedures. Educate them on the types of insider threats, such as malicious insiders, negligent insiders, and external threats, and how to detect and prevent them.
- Creating a Security Culture: Establish a culture of security by implementing security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to protect the organization’s network and data sources. Encourage employees to focus on security instead of just external threats and incentivize them to detect and report suspicious behavior.
Utilizing Security Technologies
Utilizing security technologies such as data loss prevention tools, implementing intrusion detection systems, and utilizing automated monitoring systems to protect against malicious insider and external threats is essential to protecting an organization’s network and critical assets.
Cybersecurity professionals should focus on mitigating insider threats, as well as threats from external actors. Potential insider threats include negligent or malicious insiders, former employees, and competitors. Insider threat indicators include user behavior, privileged access, and social engineering. To mitigate these risks, organizations should conduct security risk assessments, implement security policies and procedures, and focus on security awareness.
Using Data Loss Prevention Tools
From the potential of malicious insider threats to the focus on external threats, it is clear that enhancing security awareness should go hand-in-hand with utilizing security technologies. Utilizing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools is one such approach to strengthening an organization’s cybersecurity posture. DLP helps to protect the organization by detecting, preventing, and responding to security incidents involving the loss of sensitive or proprietary data.
DLP solutions monitor and control data flows across the entire organization, such as data stored on desktops and servers, sent via email, and transferred via the web. They also scan for and detect sensitive information like personally identifiable information (PII), credit card numbers, and intellectual property. With DLP tools, organizations can:
- Monitor and control data at rest:
- Keep a centralized inventory of data sources containing sensitive information
- Track the movement of data across the organization
- Identify suspicious user behavior
- Monitor and control data in transit:
- Monitor and control file transfers over the internet
- Monitor and control emails containing sensitive data
- Scan for and detect phishing attacks
When used in combination with other security solutions, DLP tools can help organizations prevent data breaches, protect their critical assets, and mitigate the risk of insider threats.
Implementing Intrusion Detection Systems
After enhancing security awareness to protect against external threats, it is equally important to use security technologies to protect against insider attacks. Implementing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is an effective way to monitor and detect unauthorized access to an organization’s network, and can be used to detect malicious activity, data breaches, and breaches of confidential information.
IDS systems employ a range of technologies to detect malicious or suspicious activity, which include firewalls, deep packet inspection, and anomaly detection. Firewalls are used to restrict access to the network, while deep packet inspection is used to monitor data packets sent and received by the network to identify malicious activity. Anomaly detection works by identifying any unusual or suspicious behavior, such as a user logging in from a foreign country or making an unusually high number of requests within a short period of time.
IDS systems are also capable of detecting potential insider threats, as they can be used to monitor user behavior and detect any suspicious activity. For example, an IDS system can be used to detect when a user is accessing large quantities of data or downloading confidential information. With the right security measures in place, intrusion detection systems can be used to alert the security team to any potential insider threats, allowing them to take appropriate action and mitigate the risk.
Utilizing Automated Monitoring Systems
The security of an organization is only as strong as its weakest link, and when it comes to cyber security, the greatest risk often comes from within. Insider threats, such as malicious insiders, can be incredibly difficult to detect due to their authorized access to sensitive information, intellectual property, and critical assets.
For businesses, the potential for an insider to use their privileges for malicious intent can be incredibly costly, leading to data breaches, loss of confidential information, and even the theft of trade secrets. Security teams must take steps to mitigate the risk of insider threats and focus on both external and internal threats to protect their organization.
One of the best practices for mitigating insider threats is utilizing automated monitoring systems. These systems allow for the detection, analysis, and response to suspicious user behavior. Security professionals can leverage these systems to detect potential insider threats by monitoring data sources and analyzing user behavior.
Security teams can also set up data loss prevention tools and intrusion detection systems to detect malicious activity and prevent the exfiltration of sensitive data. Additionally, security professionals can focus on insider threat prevention and implement security solutions to protect against potential insider threats. By focusing on these cyber security measures and incorporating threat management into their overall security strategy, businesses can better protect themselves from both intentional and unintentional insider threats.
Developing a Response Plan
Developing a response plan for data breaches starts with establishing an incident response team. Cybersecurity professionals on this team can help identify and prevent malicious insider threats, external threats, and potential threats that originate from within the organization’s network. Best practices such as user behavior monitoring, firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and security awareness training can help mitigate insider threats.
Potential insider threats include malicious insiders, negligent insiders, and former employees who have access to the organization’s sensitive data or intellectual property. Data breach reporting to the appropriate authorities should also be part of the breach response plan.
Developing a Breach Response Plan
In addition to utilizing security technologies to protect against external threats, organizations must also develop a response plan in case of a breach. Developing a breach response plan helps to mitigate any damage and ensure a swift response to a potential insider threat or malicious attack.
The first step in creating a breach response plan is to establish an incident response team. This team should include a variety of stakeholders and professionals, such as cybersecurity engineers, data security and privacy officers, and legal and HR experts. This team should be equipped with the knowledge necessary to identify and respond to any suspicious activity or malicious behavior.
Once the team is in place, it should focus on developing and documenting the plan for identifying, responding to, and mitigating any potential threats. This plan should include procedures for identifying threats, determining the source of the breach, and determining the extent of the damage. It should also include steps for notifying the appropriate authorities, such as law enforcement or customer service. In addition, the plan should include protocols for restoring the organization’s network, protecting sensitive information, and preventing further damage.
Finally, the plan should include measures for preventing future breaches. This may include implementing proactive security measures such as malware and intrusion detection systems, as well as establishing policies and procedures to mitigate risk of insider threats.
Establishing an Incident Response Team
To further fortify an organization’s cyber security, establishing an incident response team is key. This team should include members from various areas of the organization, such as legal, human resources, IT, and finance. The team should be familiar with the security policies and procedures in place and be on the lookout for insider threat indicators. They must also be able to identify and respond quickly to advanced threats and data breaches from both external and internal sources.
Common insider threat indicators include unauthorized access to confidential information, large quantities of data being moved or accessed, and suspicious user behavior. Additionally, if a former employee is still able to access the organization’s network with their credentials, or privileged access is given to a competitor, these are all signs of a potential insider threat.
To mitigate the risk of insider threats, it’s important to focus on user behavior. Organizations should monitor and analyze user behavior and activities to detect any malicious insider behavior. Security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention can help identify and prevent malicious attacks. Security engineers should also ensure that insider access is limited to only the resources they need.
Reporting Data Breaches to Appropriate Authorities
Transitioning from security technologies to response plans, organizations must also be prepared to report data breaches to the appropriate authorities. Cybersecurity teams must be able to detect and mitigate any malicious insider threats or external threats that may have caused the breach. The team should also be aware of potential insider threats, such as phishing attacks, malware, credential theft, and user behavior that may have caused the breach.
It is important to understand the types of insider threats and the risks of insider threats that can occur within an organization’s network. Examples include negligent insiders, malicious insiders, and former employees who have access to the organization’s confidential information, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Organizations should focus on preventing insider threats as they can be more difficult to detect than external threats.
Organizations should put security measures in place to mitigate the potential for an insider to use their privileged access to do harm intentionally or unintentionally. Security teams should monitor insider behavior, implement intrusion detection systems, and use best practices when mitigating insider threats. Security professionals should also be aware of the cost of insider threats, as they can cause a large amount of data loss if they are not detected or prevented on time.
Conclusion
Insider threats are a serious security challenge that organizations must address. Human error continues to be the leading cause of data breaches, and organizations must take steps to ensure access is secure. This includes identifying potential risks, enhancing security awareness, utilizing security technologies, and developing a response plan.
By taking these steps, organizations can minimize the potential for data loss and protect their sensitive information. As data breaches become more common, organizations must take the necessary steps to protect their data and information from malicious actors.