The Ins and Outs of Data Backup Options
Data backup is crucial in today’s digitally-driven world, ensuring that your important files and information are safely preserved. For businesses and office managers, understanding data backup options is key to safeguarding against data loss from failures or cyber threats. Here’s what you should know about data backup:
- Importance: Protects critical data from loss and downtime, which can be costly.
- Challenges: Involves complexity, potential inaccessibility, and security risks.
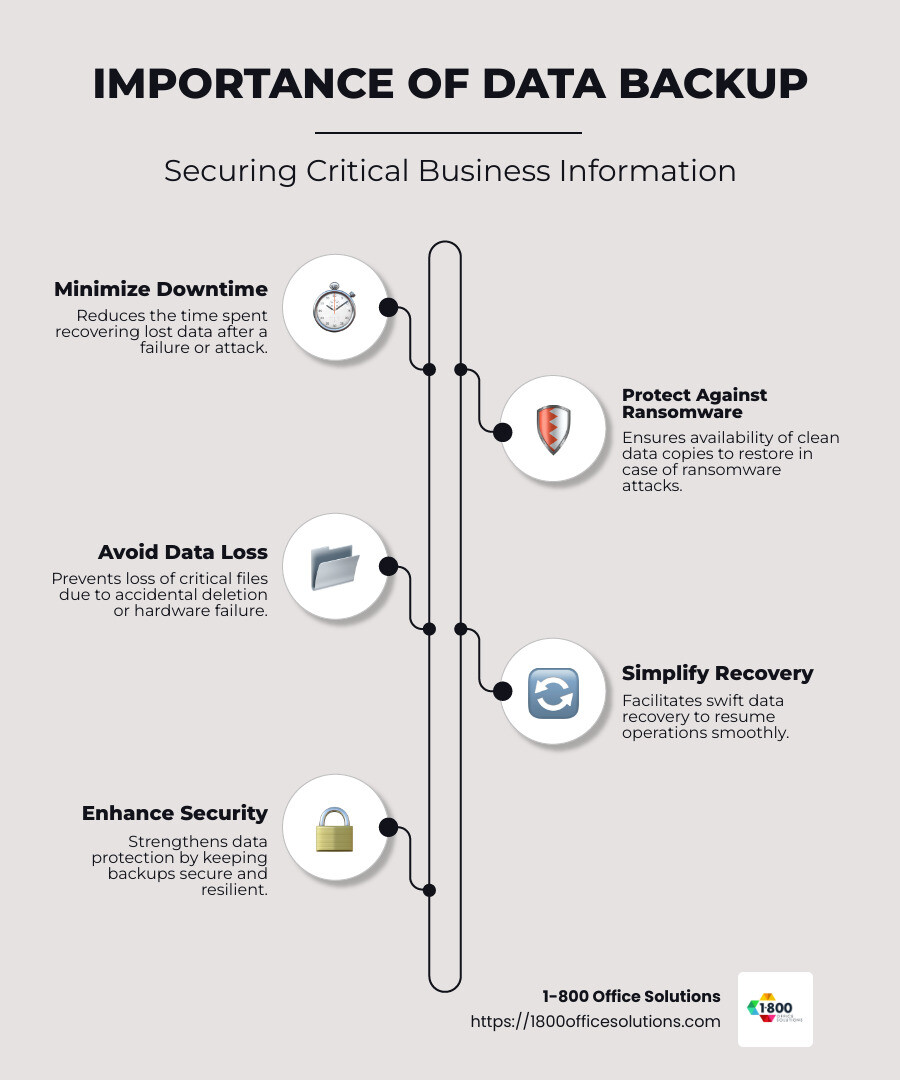
Simple guide to data backup terms:
Understanding Data Backup
Data backup is the process of creating a copy of your data to protect it from loss, corruption, or accidental deletion. Think of it as a safety net for your digital information. If something goes wrong with the primary data, you can restore it from your backup.
Purpose of Data Backup
The main goal of data backup is to ensure business continuity. Imagine a scenario where critical business data is lost due to a system failure or a cyberattack. Without a backup, recovering that data might be impossible. With a reliable backup, you can restore your data and get back to business quickly.
Data backup also helps in recovering older versions of files. If an important document was mistakenly altered or deleted, you can retrieve its previous version from your backup.
Data Protection
Data protection is a key aspect of data backup. This involves safeguarding data from threats like cyberattacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters.
- Encryption: Encrypting your backup data is crucial. It ensures that even if unauthorized individuals access your backups, they can’t read the data without the encryption key.
- Redundancy: Having multiple copies of your data in different locations (like on-site and in the cloud) adds an extra layer of protection. This way, if one backup is compromised, others are still available.
- Regular Testing: It’s important to regularly test your backups. This ensures they are functional and can be restored when needed. Regular tests help identify issues like corrupted files or incomplete backups before they become a problem.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of data backup, you can make informed decisions to protect your critical data and ensure your business operations continue smoothly, even in the face of unexpected events.

Types of Data Backup
When it comes to data backup, there are several strategies you can use. Each has its own strengths and best use cases. Let’s explore the main types: full backup, incremental backup, differential backup, and mirror backup.
Full Backup
A full backup is like taking a complete snapshot of your entire data set. It copies every piece of data you want to protect. This method is straightforward and easy to understand. You get a single restore point with everything included.
However, full backups can be time-consuming and require a lot of storage space. Because of this, they’re often done less frequently, such as weekly or monthly.
The advantage? When it’s time to restore, full backups are the fastest because all your data is in one place.
Incremental Backup
An incremental backup only saves the data that has changed since the last backup, whether that was a full or another incremental backup. This makes incremental backups much quicker and less storage-intensive.
For example, if you do a full backup on Sunday and incremental backups on Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday, the backup on Wednesday will only include changes made since Tuesday.
The downside? Restoring from incremental backups can take longer because you need to piece together data from the last full backup and all subsequent incremental backups.
Differential Backup
A differential backup is a middle ground between full and incremental backups. It saves data changes since the last full backup.
Imagine you did a full backup on Sunday. A differential backup on Wednesday will include all changes from Sunday to Wednesday. This means that differential backups grow larger with each day until the next full backup.
Restoring from differential backups is faster than incremental because you only need the last full backup and the latest differential backup.
Mirror Backup
A mirror backup creates an exact replica of your data at a specific point in time. It mirrors every change, including deletions. This means if a file is deleted from the main system, it will also be deleted from the mirror backup.
Mirror backups are excellent for quick access to the most current data. However, they don’t protect against accidental deletions or corruption, as changes are mirrored instantly.
Each backup type serves different needs and situations. By understanding these options, you can choose the right strategy to keep your data safe and your operations running smoothly.

Next, we’ll explore the various data backup options available, including hardware and software solutions.
Data Backup Options
When it comes to data backup, choosing the right method is crucial. Let’s explore some common options: removable media, redundancy, external hard drives, hardware appliances, backup software, and cloud backup services.
Removable Media
Removable media like CDs, DVDs, and flash drives have been reliable backup options for years. They’re affordable and portable, making them ideal for simple and small-scale backups. You can store them in a safe place away from your main system.
However, removable media have limitations. They offer less storage capacity compared to other options and are prone to physical damage. Imagine scratching a CD or losing a USB drive. Plus, they can be slow to transfer large amounts of data.
Redundancy
Redundancy means having multiple copies of your data. It’s a safety net against data loss. You can achieve redundancy through various means, such as RAID setups or using multiple hard drives.
For example, RAID 1 mirrors data across two drives, providing a backup if one fails. Redundancy is essential for critical data, but remember, more redundancy means more cost and complexity.
External Hard Drive
An external hard drive connects to your computer via USB or other interfaces. It’s a popular choice because it offers ample storage and is easy to use. You can quickly back up data and store the drive off-site for added security.
But, like all hardware, external drives can fail or get damaged. They can also be stolen. So, it’s wise to use them as part of a broader backup strategy, not the sole solution.
Hardware Appliances
Hardware appliances are dedicated devices for data backup. They often come with built-in software and support various storage types. These appliances are comprehensive solutions, offering features like encryption and automated backups.
The downside? They can be expensive, especially for small businesses. Plus, technology evolves, and these devices can become outdated, requiring upgrades.
Backup Software
Backup software automates and manages your backup process. It can be simple or complex, depending on your needs. Key features to look for include automation, encryption, and the ability to back up to multiple destinations.
While free software exists, paid versions often offer more features and support, making them a better choice for businesses.
Cloud Backup Services
Cloud backup services store your data on remote servers, accessible via the internet. They’re convenient and scalable, allowing you to access data from anywhere. Many services offer encryption and redundancy, enhancing security.
However, cloud services can be costly, especially for large data volumes. There’s also a risk of data breaches, though many providers implement robust security measures.
Each data backup option has its pros and cons. The best choice depends on your specific needs, budget, and the importance of your data. Next, we’ll look at key metrics to consider when evaluating data backup solutions.
Key Metrics in Data Backup
When planning your data backup strategy, two critical metrics come into play: Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Understanding these can help you minimize data loss and downtime.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
RPO is all about how much data you can afford to lose. It’s measured in time. For example, if your RPO is one hour, you’re prepared to lose up to an hour of data in case of a failure.
Think of it like this: if your business backs up data every night, your RPO is 24 hours. In the worst-case scenario, you could lose a whole day’s worth of data. To reduce data loss, you need more frequent backups, but this requires more storage and resources.
Many small businesses might aim for a 24-hour RPO, but with modern technology, it’s possible to aim for just a few minutes for critical systems.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
RTO is about speed. It defines how quickly you need your systems back online after a failure. If your RTO is 30 minutes, your recovery process must restore operations within that time frame.
Imagine your business relies heavily on online sales. If your website goes down, every minute counts. A shorter RTO means less downtime and less impact on your bottom line, but achieving this can be costly. It requires faster storage, networks, and technologies.
For many companies, an RTO of a few hours is common, but critical systems might need to be back up in minutes.
Both RPO and RTO are essential for ensuring minimal disruption to your business. Involve your business stakeholders in setting these objectives to align them with your operational needs. Once defined, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right backup solutions and storage methods.
Next, we’ll explore the different storage technologies available for data backup.
Data Backup Storage Technologies
When considering data backup, choosing the right storage technology is crucial. Each option has its own strengths and weaknesses, so let’s break down the most common choices: local disks, NAS/SAN, tape storage, and cloud storage.
Local Disks
Local disks are the simplest form of backup storage. They involve using external hard drives or internal disks to store backup data. This method is easy to set up and cost-effective. However, local disks are vulnerable to physical damage and theft. They also require manual management and are not ideal for large-scale backups.
Pros:
- Cost-effective
- Easy setup
Cons:
- Prone to physical damage
- Limited scalability
NAS/SAN
Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Network (SAN) systems offer centralized storage solutions. NAS is like having a personal cloud at your office, allowing multiple devices to access shared storage over a network. SAN is more complex, providing high-speed data access for larger enterprises. Both offer redundancy, meaning your data is safer from hardware failures.
Pros:
- Centralized storage
- Supports redundancy
Cons:
- More expensive than local disks
- Requires network infrastructure
Tape Storage
Tape storage is a tried-and-true method, great for long-term data archiving. It involves storing data on magnetic tapes, which are then kept offsite for safety. While it’s reliable and cost-effective for large volumes of data, tape storage has a high Recovery Time Objective (RTO) due to the need to physically retrieve and load the tapes.
Pros:
- Cost-effective for large data volumes
- Reliable for long-term storage
Cons:
- Slow data retrieval
- Requires physical handling
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a modern solution offering flexibility and scalability. It allows businesses to store data offsite, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud storage provides features like automatic backups, geo-redundancy, and rapid data restoration. However, costs can add up with frequent data access, and you need a reliable internet connection.
Pros:
- Highly scalable
- Accessible from anywhere
Cons:
- Costs can increase with usage
- Dependent on internet connectivity
Each of these data backup storage technologies has its place, depending on your business needs and budget. By understanding these options, you can better protect your data and ensure business continuity. In the next section, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about data backup.
Frequently Asked Questions about Data Backup
What is a data backup?
Data backup is the process of copying your important data to a separate location. This ensures you can recover it if something goes wrong, like a computer crash, accidental deletion, or a cyberattack. Think of it as a safety net for your digital life. The purpose is simple: to protect your valuable information from being lost forever.
How do I backup data from my phone?
Backing up data from your phone is essential to keep your photos, contacts, and settings safe. For Android users, Google One offers a straightforward solution. Here’s how to use it:
- Open Settings on your Android device.
- Tap Google > Backup.
- Turn on Backup your device with Google One.
- Choose the data you wish to back up, like photos, videos, and device settings.
- Tap Back up now to start the process.
For Samsung users, the Samsung Account provides a similar service. You can back up your data using Samsung Cloud by following these steps:
- Go to Settings > Accounts and backup.
- Tap Samsung Cloud.
- Select Back up data and choose what to back up.
- Tap Back up now.
These services ensure that your data is safely stored in the cloud, ready to be restored whenever needed.
What are the three types of data backup?
Understanding the different types of data backup can help you choose the best strategy for protecting your information. Here are the three main types:
- Full Backup: This is the most comprehensive type, where all your data is copied. It’s the best option for a complete snapshot of your system, but it can be time-consuming and require a lot of storage space.
- Incremental Backup: This method only backs up the data that has changed since the last backup (whether full or incremental). It’s fast and saves space, but restoring data can take longer because you need the last full backup and all subsequent incremental backups.
- Differential Backup: This type backs up all the changes made since the last full backup. It strikes a balance between full and incremental backups. While it requires more storage than incremental backups, it’s quicker to restore because you only need the last full backup and the last differential backup.
Each type has its advantages and drawbacks, so choose the one that best fits your needs and resources.
Conclusion
The importance of data backup cannot be overstated. Imagine losing years of work, cherished photos, or critical business data in a blink. A robust backup strategy acts as a lifeline, ensuring your data is safe from disasters, cyberattacks, or accidental deletions. With the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.88 million in 2024, having a reliable backup plan is not just a safety measure—it’s a necessity for survival.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we understand the critical role that data backup plays in safeguarding your business. Our comprehensive Document Management System is designed to protect your valuable information, streamline your processes, and improve your operational efficiency. We offer custom solutions that fit your unique needs, whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise.
By choosing us, you’re not just investing in a service—you’re investing in peace of mind. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the tools and support you need to keep your data secure, accessible, and compliant with industry standards. Don’t leave your data to chance; let us help you build a resilient backup strategy that ensures your business can thrive, no matter what challenges come your way.