Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act: What You Need to Know
AI Overview:
This blog explains the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA), outlining its purpose, key provisions, and impact on businesses. It shows how CISA enables secure, timely sharing of cyber threat information between the private sector and government to strengthen national security, improve incident response, and reduce risk. Readers learn about mandatory reporting, liability and privacy protections, collaboration opportunities, and practical steps to stay compliant while protecting critical digital assets.
What You Need to Know About the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA)
Are you struggling to understand the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) and how it impacts your business? This blog post explains what CISA is and breaks down its key provisions. It also shows how businesses can address common cybersecurity challenges while ensuring compliance. Readers will gain clear insights to protect their organizations from cyber threats and navigate regulations with confidence.
What Is the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA)?
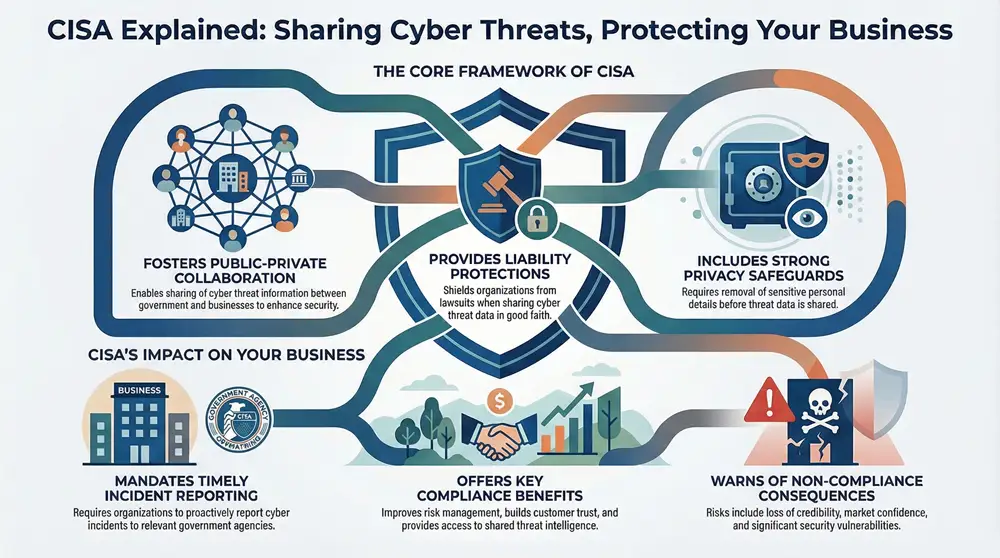
The Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) promotes national security by strengthening information systems and safeguarding protected health information. It sets the framework for efficient data breach notifications and facilitates seamless collaboration across entities. This segment outlines CISA’s purpose, key principles, and the role of organizations like the center for democracy and technology in enhancing cybersecurity.

Understanding the Purpose of CISA
The purpose of CISA centers on promoting secure data practices and ensuring that critical information flows efficiently between government and private organizations. The act guides a clear policy for sharing cybersecurity information and involves coordination with entities like the central intelligence agency and the cybersecurity and infrastructure security agency to address evolving digital threats.
CISA also facilitates collaboration with leading entities such as the federal bureau of investigation, helping address and mitigate cyber risks in real time. Its framework supports practical measures that empower organizations to respond effectively when security breaches occur and safeguard vital digital assets.
Overview of Key Principles Behind the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act
The act establishes a practical framework that emphasizes principles such as ethics, security, and risk management while ensuring that sharing information remains transparent and accountable. It promotes a clear contract between public and private stakeholders, enabling each agency involved to prioritize strong risk management practices and maintain sound operational security.
The framework underlines the significance of a structured approach to risk management and ethical data handling, ensuring agencies work together effectively. It supports the establishment of clear contracts, which serve as the foundation for secure information sharing and create a manageable environment for addressing potential risks.
The Role of CISA in Enhancing National Security
The legislation supports a coordinated effort to secure sensitive information and mitigate risk across various sectors, ensuring that the law serves as a reliable framework for enhancing national security on the internet. By establishing clear guidelines for data sharing, the act provides businesses with concrete measures to protect critical assets and reduce potential vulnerabilities.
The law aligns the interests of both government and private organizations by promoting timely information exchange that addresses emerging cyber risk. This approach bolsters defenses against threats that could jeopardize infrastructure and reinforces accountability in the management of digital assets on the internet.
How CISA Facilitates Information Sharing Among Entities
The framework establishes clear channels for sharing personal information between entities, enabling a chief information officer and their team to quickly relay data that highlights potential cyberattack patterns and malware incidents. The mechanism supports trusted information exchange, offering guidance that aligns with insights observed by the united states chamber of commerce.
Organizations benefit from the act’s structure by receiving actionable insights during cyberattack events, thus improving their response strategies and security posture. The system ensures that critical information about personal information vulnerabilities and malware trends is communicated effectively, fostering a coordinated approach to threat mitigation.
Key Provisions Within CISA
Mandatory reporting for cyber incidents, liability protections, and privacy safeguards form the backbone of CISA. The act requires timely reporting of cyber threats, including ransomware, and establishes guidelines recognized by intelligence and the center. The homeland security department and freedom of information laws by country support this framework, ensuring clear, accountable practices throughout the process.
Mandatory Reporting Requirements for Cyber Incidents
The act mandates timely cyber incident reports to ensure that organizations remain proactive in managing a cyber threat. The guidelines require a robust system of information security and physical security measures, while balancing freedom of information provisions with the necessary safeguards enforced by the federal emergency management agency.
Organizations adopt stringent protocols to report incidents, providing detailed insights that aid in the prompt resolution of cyber threat challenges. This requirement supports a comprehensive approach to information security, ensuring that relevant entities share data responsibly and align with both privacy expectations and mandated federal oversight.
Liability Protections for Information Sharing
The provisions grant liability protections that offer reassurance to organizations managing sensitive data. This framework provides clear guidelines concerning intellectual property and encourages collaboration with a dedicated committee and the united states department of defense to mitigate risks related to cybercrime.
By establishing these protections, the act fosters an environment where entities can share data without undue fear of legal repercussions while reinforcing robust management practices. This structure benefits businesses by enabling them to focus on strengthening their cybersecurity measures in the face of rising cybercrime threats.
Privacy Protections Established by CISA
The privacy safeguards outlined in CISA establish strict criteria to ensure that data sharing occurs under a secure framework, reducing potential exposure to cybersecurity threats. The framework enables oversight by the national security agency and an appointed inspector general to review procedures and preserve privacy, assisting every engineer engaged in cyber operations to trust the system’s integrity.
CISA mandates that sensitive personal details receive robust protection and careful handling under clearly defined standards. This measure provides a secure pathway that supports regular audits by an inspector general, ensuring engineers involved in cyber endeavors can operate confidently while the national security agency remains vigilant against emerging cyber threats.
The Importance of Timely Reporting
Timely reporting provides the foundation for a swift and informed response to cyber threats, which benefits both the private sector and governmental entities such as the senate. This focus on early detection supports robust information technology practices and assists in aligning with freedom of information act mandates, ensuring that all relevant data, even that involving regions like Korea, is shared securely and promptly.
Quick reporting enables organizations to implement protective measures and adjust strategies based on accurate, real-time information. Such proactive steps empower businesses and public agencies to mitigate risks effectively, fostering trust and streamlined operations across various sectors impacted by the evolving landscape of information technology.
How CISA Affects Businesses and Organizations
Businesses gain key benefits by following the act, which promotes innovation, supports secure infrastructure, and aligns software practices with homeland security standards. Private sector entities assume clear responsibilities while fostering collaboration with government agencies, including counterparts in Italy. Non-compliance may lead to significant repercussions that affect overall security and operational integrity.

Benefits of Compliance With the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act
Compliance with the act offers businesses an improved framework for managing cybersecurity risks, ensuring that regulation remains clear and actionable for organizations. It helps create a safe environment for technology implementation while aligning operational practices with standards enacted by the united states congress, making cyberincident response more effective and building customer trust.
By adhering to the act, organizations benefit from streamlined surveillance protocols that support efficient data handling and real-time threat analysis. This commitment to cybersecurity translates into competitive operational efficiency, where practical measures protect critical assets and improve the overall integrity of business technology systems.
Responsibilities of Private Sector Entities Under CISA
Private sector entities bear several responsibilities under CISA that include actively gathering and sharing cyber threat intelligence to safeguard their business operations. They must maintain robust computer security measures and integrate artificial intelligence tools to monitor and counter disinformation, ensuring the protection of their critical infrastructure from emerging threats.
These organizations are expected to implement structured protocols for rapid data reporting and risk assessment to effectively manage cyber incidents. By adhering to CISA, the private sector promotes a secure network environment while reinforcing overall stability through continual updates to computer security practices and proactive incident response systems.
Collaboration Opportunities With Government Agencies Under CISA
Government agencies, including the united states department of homeland security, offer actionable data that supports organizations in addressing cybersecurity threats effectively. Businesses benefit from direct collaboration with a trusted security agency where clear language guidelines minimize misinformation and improve overall data sharing practices.
This coordinated effort enables organizations to access timely data updates and implement proactive security measures. By engaging with government bodies, companies gain access to expert insights and reliable security agency support that help manage cyber risks and reduce the spread of misinformation.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Businesses that disregard the cybersecurity information sharing act risk severe setbacks in internet security, with penalties that extend to loss of credibility and market confidence. The general services administration may impose stringent measures on organizations failing to meet sharing protocols, reducing opportunities for collaborative threat mitigation.
Non-compliance creates vulnerabilities that limit access to actionable cybersecurity information sharing trends and best practices. Enterprise leaders are urged to align their systems with the guidelines of the cybersecurity information sharing act to maintain robust protection and effective response strategies.
Recent Developments in CISA and Cybersecurity
Recent updates to CISA include legislative changes that streamline how agencies share cybersecurity information. Practical case studies demonstrate the act’s impact on incident response. Future trends in cyber information sharing highlight evolving strategies for risk management, offering organizations an informed view of new practices and regulatory adjustments.
Updates to CISA and Legislative Changes
The recent modifications to the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act have refined guidelines for data reporting and liability. These legislative changes improve the coordination between businesses and government, ensuring a streamlined approach to handling cyber threats.
The updates emphasize clearer definitions and stronger privacy safeguards to support secure information exchange. This progress allows organizations to adopt more effective risk assessment practices and maintain an efficient cybersecurity posture.
Case Studies of CISA in Action
The act’s practical impact is evident in real-life examples where organizations successfully managed cybersecurity incidents with the guidance of CISA. These examples highlight how accurate data sharing enabled a rapid response to threats, improving system integrity and reducing downtime.
Noteworthy instances show businesses attaining effective risk management by following CISA protocols during cyberattacks. These experiences provide actionable insights for organizations seeking to bolster their digital defenses and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Future Trends in Cyber Information Sharing
The future trends in cyber information sharing indicate a shift toward greater automation and real-time data exchange. Technological advancements support faster response times and simpler integration with current cybersecurity practices, which directly benefit businesses by reducing downtime during cyber incidents.
Industry experts observe that emerging tools will improve the accuracy in threat detection and risk assessment. Enhanced cooperation between technology providers and cybersecurity professionals is expected to result in clearer reporting and more efficient response strategies, ensuring that companies remain well-prepared against cyber risks.
How to Stay Compliant With CISA
Organizations can implement CISA provisions by following clear steps, accessing essential resources, and adopting reliable reporting procedures. This section presents practical insights into effective CISA compliance, including structured steps for organizations, available resources for adherence, and best practices for cyber incident reporting.
Steps for Organizations to Implement CISA Provisions
Organizations develop internal guidelines that align with established cybersecurity practices while meeting federal reporting standards. They assign dedicated teams to monitor and report cyber incidents, ensuring that the steps taken improve rapid response and safeguard sensitive data.
Companies streamline their processes by integrating regular training sessions on cyber threat detection and incident management. They adopt practical measures that support proactive risk management, ensuring that their practices are consistent with clear regulatory standards while reducing potential vulnerabilities.
Resources Available for CISA Compliance
Resources for meeting CISA standards include official guidelines from federal agencies and dedicated support centers specializing in cybersecurity and IT services. Business owners benefit from accessing practical compliance toolkits that offer clear instructions and best practices for regular data reporting and risk analysis.
Well-established industry resources provide detailed documentation and expert advice useful for aligning with regulatory standards. These materials help organizations strengthen cybersecurity measures while ensuring that risk management practices remain current and effective.
Best Practices for Cyber Incident Reporting
Organizations ensure effective cyber incident reporting by establishing clear internal procedures that support CISA compliance. They rely on consistent, timely documentation to provide accurate, actionable data on cybersecurity events, enabling rapid resolution and protecting vital IT systems.
Experts advise incorporating regular evaluations of reporting protocols to enhance overall security and streamline incident management. This approach builds a reliable framework for handling breaches while meeting federal guidelines and fostering a secure operational environment.
Resources and References for Further Learning on CISA
Official CISA documentation and guidelines provide a solid foundation for understanding cybersecurity information sharing. Relevant organizations and support networks offer expert assistance and practical tools, while additional reading materials enhance knowledge on managing cyber risks. These resources deliver key insights and support tailored solutions for businesses seeking robust cybersecurity measures.
Official CISA Documentation and Guidelines
The official CISA documentation serves as a reliable source for accurate details regarding cybersecurity information sharing processes. It offers clear guidelines that assist organizations in aligning their practices with established standards, ensuring a secure and compliant environment for handling data.
Expert materials within these guidelines provide actionable insights and practical examples, which aid professionals in developing robust data protection measures. The documentation is designed to support businesses in enhancing their cybersecurity posture and ensures that organizations have access to up-to-date information on regulatory changes.
Relevant Organizations and Support Networks
Organizations such as federal cybersecurity centers and industry support networks provide clear guidelines and trusted assistance in understanding CISA protocols. These groups offer valuable insights and practical training, helping businesses build a secure framework for effective data sharing and cyber incident response.
Support networks that specialize in IT services and cybersecurity share expertise to simplify CISA compliance for business owners. They deliver actionable advice and tailored solutions based on real-world applications, ensuring organizations remain proactive in managing cyber threats.
Additional Reading Materials on Cybersecurity Information Sharing
Industry publications provide essential insights into cybersecurity information sharing, offering guidance that business owners and IT professionals can rely on. These materials feature practical examples from experienced practitioners and present actionable techniques for improving data sharing strategies across organizations.
Specialized journals and digital repositories serve as valuable references for organizations seeking to expand their understanding of cybersecurity protocols. They deliver clear analysis and real-world case studies, enabling stakeholders to identify best practices and refine their incident response measures effectively.
Conclusion
CISA provides a structured framework that supports secure data sharing and effective cybersecurity practices. Business entities and government agencies benefit from clear guidelines that promote rapid incident reporting and robust risk management. The act reinforces the importance of transparent collaboration to safeguard critical digital assets. Organizations gain measurable advantages by aligning their practices with CISA requirements, ensuring a safer digital environment for all parties involved.