A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Artificial Intelligence Basics
AI Overview:
This blog explains what Artificial Intelligence is, how it learns from data, and why it’s transforming modern businesses. It covers the basics of how AI works—using algorithms, pattern recognition, and neural networks—along with the difference between today’s Narrow AI and the future goal of AGI. The article highlights core subfields like machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI, and shows real-world applications in healthcare, finance, retail, and office technology.
It also outlines key benefits such as automation, accuracy, and smarter decision-making, while acknowledging challenges like bias, privacy, and job disruption. Overall, the guide provides a simple, practical introduction to AI and its growing impact on everyday operations.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
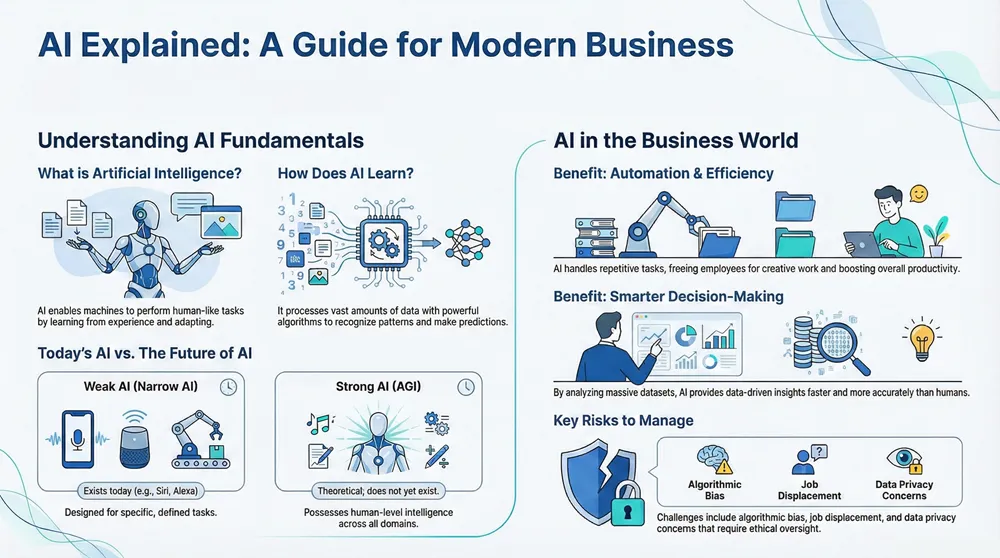
Artificial intelligence (AI) enables machines to learn from experience, adapt to new information, and perform human-like tasks. AI teaches computers to think and act in ways that traditionally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
AI systems are designed to analyze vast datasets to find patterns, automate high-volume tasks without fatigue, and reduce human error by guiding or taking over processes. From the virtual assistant on your phone to the software that seems to get smarter over time, AI is a rapidly growing field changing the world around us.
This guide will walk you through the core concepts of AI, including what it is, how it works, and its different forms. We’ll explore its history, key applications, and the benefits it offers modern businesses. Understanding AI is no longer just for tech experts; it’s crucial for any office looking to boost productivity, streamline workflows, and make smarter decisions.
Must-know Artificial Intelligence terms:
- GPT-4o explained: Everything you need to know
- Pros and cons of facial recognition
- SearchGPT explained: Details about OpenAI’s search engine
What is Artificial Intelligence and How Does It Work?

Artificial intelligence is a field of computer science focused on creating machines that perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as reasoning, decision-making, and creativity. We define Artificial Intelligence as a computer’s ability to perform complex tasks typically done by humans, including learning and problem-solving.
At its core, AI works by processing vast amounts of data to identify patterns, which it then uses to make predictions or decisions. This concept is widely adopted, with organizations like NASA defining AI as systems that can perform tasks without significant human oversight, learn from experience, and solve problems requiring human-like perception or cognition. Many of these systems use techniques like machine learning to achieve their goals.
Core Components
For Artificial Intelligence to function, it relies on several key components:
- Data: AI systems require massive datasets to learn and improve. This data fuels the AI, allowing it to identify patterns and relationships that humans might miss.
- Algorithms: These are the rules and processes AI systems follow to analyze data, learn, and make decisions. They are the “brains” of the operation.
- Computing Power: The volume of data and complexity of AI algorithms demand significant computing power. Advances in graphical processing units (GPUs) have been crucial for training complex AI models.
The Learning Process
Instead of being explicitly programmed for every scenario, AI systems are designed to learn and adapt.
- Pattern Recognition: AI systems analyze data to find recurring patterns. For example, a model might analyze thousands of images to learn to recognize a specific object.
- Neural Networks: Inspired by the human brain, these interconnected units process information in layers. They are fundamental to how AI learns, allowing it to adapt as it’s trained with new data. Deep neural networks enable high accuracy in tasks like image and speech recognition.
- Adjusting to New Inputs: As AI encounters new data, it refines its performance. This progressive learning makes it increasingly adept at specific tasks.
- Making Predictions: Based on learned patterns, AI can generate predictions or classifications, a vital capability for applications from financial forecasting to system diagnostics.
The Evolution and Types of AI

The journey of Artificial Intelligence has moved from a theoretical concept to a tangible technology that is rapidly changing our world. This acceleration, especially since 2012, is fueled by increased computing power, vast data availability, and refined algorithms.
A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence
The idea of thinking machines dates back centuries, but the modern story of Artificial Intelligence began in the mid-20th century. In 1950, Alan Turing’s paper posed the question, “Can machines think?” and introduced the “Turing Test.” The field was formally born in 1956 at the Dartmouth Summer Research Project, where John McCarthy coined the term “artificial intelligence.”
Key milestones demonstrated AI’s growing power. IBM’s Deep Blue defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997, and its Watson won on Jeopardy! in 2011. In 2016, Google’s AlphaGo mastered the complex game of Go. These breakthroughs paved the way for the modern era of AI, where big data and cloud computing in the 2000s enabled the training of sophisticated models, leading to the current “AI boom” and fields like generative AI.
Understanding the Different Types of AI
AI can be classified into four main types based on its capabilities:
- Reactive Machines: The most basic AI, these systems react to current stimuli without any memory of past events. IBM’s Deep Blue is a classic example, as it analyzed the board and made moves without learning from past games.
- Limited Memory: Most modern Artificial Intelligence systems fall here. They use past data temporarily to make decisions, like a self-driving car remembering recent road conditions. AI tools used at 1-800 Office Solutions and NASA fit this category, improving over time with new data.
- Theory of Mind: A theoretical future AI that could understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions, and adjust its interactions accordingly.
- Self-Awareness: The most advanced and purely hypothetical type, this AI would possess consciousness and self-awareness, a concept often explored in science fiction.
Weak AI (Narrow) vs. Strong AI (AGI)
It’s crucial to distinguish between the AI of today and the AI of the future.
| Feature | Weak AI (Narrow AI) | Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence – AGI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Designed for specific tasks or a set of tasks | Possesses human-level intelligence across domains |
| Capabilities | Excels at defined tasks; no general intelligence | Understands, learns, and applies knowledge broadly |
| Consciousness | Not conscious; does not simulate human thought | Potentially conscious; simulates human cognition |
| Current Status | Exists and is widely deployed | Theoretical; does not yet exist |
| Examples | Siri, Alexa, self-driving cars, recommendation systems | A machine that can perform any intellectual task a human can |
Weak AI, or Narrow AI, is the technology you interact with daily. It’s designed for specific tasks and excels at them, powering everything from voice assistants and facial recognition to search engines. These systems operate within defined limits.
Strong AI, or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), remains a future concept. It refers to an AI that could understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a vast range of tasks at a human level or beyond. Achieving AGI is a primary goal for some researchers but is still theoretical.
Exploring the Core Subfields of Modern AI
The world of Artificial Intelligence is a vast ecosystem of interconnected disciplines. Each subfield plays a vital role in building the intelligent solutions that streamline office operations and drive major industry breakthroughs.
Machine Learning (ML): The Engine of Modern AI
Machine Learning is the core method that allows computers to “learn” from data without being explicitly programmed for every task. Instead of rigid instructions, the machine identifies patterns in data to improve its performance over time.
Machines learn in several ways:
- Supervised Learning: The AI is trained on labeled data (e.g., images of cats labeled “cat”) to learn how to make accurate predictions on new, unlabeled data.
- Unsupervised Learning: The AI analyzes unlabeled data to find hidden patterns or structures on its own, which is useful for tasks like customer segmentation.
- Reinforcement Learning: An AI agent learns through trial and error, receiving “rewards” for good actions and “penalties” for bad ones. This is how AI masters complex games or control systems.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we see ML powering many business solutions, including predictive analytics and customer segmentation. For businesses looking to boost efficiency, understanding ML is a game-changer. For more info about IT support for businesses, we can help you explore how these technologies fit your operations.
Deep Learning and Generative Artificial Intelligence
Deep Learning and Generative AI are behind some of today’s most exciting AI applications.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML that uses multi-layered artificial neural networks to mimic the human brain. It processes massive amounts of data to learn complex patterns, leading to breakthroughs in image recognition and natural language processing (NLP).
- Generative AI: Refers to AI models that can create new, original content like text, images, and audio from human prompts. Tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney have brought this field into the mainstream. Learn more at Explained: Generative AI.
- How it works: Generative AI relies on sophisticated deep learning structures like Large Language Models (LLMs) and Transformers. LLMs are trained on vast text and code datasets, while the Transformer architecture (introduced around 2017) allows models to process long texts and understand context effectively.
AI Agents and Agentic AI
A new frontier in Artificial Intelligence is the concept of AI agents and “agentic AI,” which are more autonomous and proactive.
- Defining AI Agents: An AI agent is an autonomous program designed to achieve goals on your behalf with minimal human supervision. It follows a cycle of perceiving its environment, reasoning on a course of action, and then acting.
- Agentic AI: This concept involves a team of coordinated AI agents working together to tackle a complex problem. They communicate and collaborate to solve intricate challenges with little human input, acting like a specialized AI team.
- Examples: Early versions of AI agents are already in use, such as advanced customer service chatbots and smart virtual assistants. Integrating these agents via APIs is already improving decision-making and optimizing processes. To learn more, see AI Agent Integration.
AI in Action: Benefits, Applications, and Challenges

Artificial Intelligence is not just a buzzword; it’s a practical tool actively changing industries and creating new opportunities. At 1-800 Office Solutions, we see how AI is reshaping everything from daily office tasks to long-term business strategy.
Key Benefits of Using AI
Integrating Artificial Intelligence into business operations offers significant advantages:
- Automation: AI excels at handling repetitive, high-volume tasks, freeing employees to focus on more creative and strategic work. This leads to smoother workflows and a major boost in productivity.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI systems analyze massive datasets far more quickly and thoroughly than humans, providing faster insights for smarter, data-driven business decisions.
- Efficiency and Accuracy: AI delivers consistent, 24/7 results with incredible accuracy, drastically reducing human error by guiding or automating processes.
- Increased Safety: AI can perform dangerous tasks, such as handling hazardous materials or working in extreme environments, protecting human workers from risk.
Real-World Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is already integrated into many industries, changing how they operate and serve customers.
- Healthcare: AI is revolutionizing patient care by assisting with medical diagnosis, creating personalized treatment plans, and accelerating drug findy. For more, see The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare and our insights on AI in Healthcare and 3 ways AI is changing the healthcare sector.
- Finance: The sector uses AI for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and sophisticated risk assessment to predict market trends.
- Retail: AI provides personalized product recommendations and optimizes complex supply chains to ensure products are available when and where they are needed.
- Office Technology: AI is becoming a core part of the modern office, with smart printers that predict maintenance needs, automated IT support, and AI-improved software. Learn more about its impact on our printing-and-ai page. We offer solutions like copier and printer leasing that leverage this technology.
Understanding the Risks and Challenges
While AI offers incredible advantages, it’s crucial to address its risks and challenges for responsible development.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues include algorithmic bias, where AI perpetuates societal biases from training data; the “black box” problem, where AI decisions lack transparency; and privacy concerns related to the vast amounts of data AI requires.
- Economic Impact: Automation raises concerns about job displacement. While AI is expected to create new roles, a skills gap may emerge. However, we believe AI can’t replace jobs that require human creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking.
- Technical Problems: AI systems are not perfect. They can suffer from “hallucinations” (generating incorrect information), which poses risks like spreading misinformation. They also have security vulnerabilities that must be managed.
Frequently Asked Questions about Artificial Intelligence
Here are straightforward answers to some of the most common questions about Artificial Intelligence.
What is the main goal of artificial intelligence?
The main goal of AI is to create computer systems that can perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, learning, and decision-making. This goal spans a spectrum from Narrow AI, which excels at specific tasks, to the theoretical ambition of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which would possess human-like cognitive abilities across any intellectual task.
Can AI replace all human jobs?
While Artificial Intelligence will automate many tasks, it is unlikely to replace all human jobs. The future is more about collaboration than replacement. At 1-800 Office Solutions, we see AI as a tool that frees people to focus on what humans do best: creativity, critical thinking, strategic planning, and emotional intelligence. AI is expected to create new roles that require human oversight and partnership, shifting work towards a model where technology improves human capabilities.
Is artificial intelligence dangerous?
Artificial Intelligence is a powerful tool; its impact depends on how it is built and used. It is not inherently dangerous, but there are significant risks to manage. These include:
Algorithmic bias: AI can perpetuate unfair biases if trained on biased data.
Misuse: The technology can be used for malicious purposes, such as spreading misinformation or launching cyberattacks.
Autonomous errors: Ensuring autonomous systems don't make critical errors without human oversight is a major challenge.
Addressing these risks requires robust ethical guidelines, strong governance, and a collective commitment to responsible AI development.
Conclusion
From its theoretical origins to its modern applications, Artificial Intelligence has evolved into a transformative technology for businesses and daily life. We’ve seen how AI learns from data to recognize patterns and make smart decisions, and we’ve distinguished between the specialized Weak AI of today and the future vision of Artificial General Intelligence.
For your business, the message is clear: AI is a practical tool that offers tangible benefits. It can automate repetitive tasks, enable smarter decisions through data analysis, and boost overall efficiency and accuracy. While it’s important to steer the ethical and technical challenges, embracing AI thoughtfully is key to building a competitive edge.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, our passion is helping businesses grow by leveraging smart technology. By understanding and integrating Artificial Intelligence into your operations, you’re not just keeping up—you’re preparing for the future. Ready to explore how AI can improve your productivity? We’re here to help. Find out how our solutions, including managed IT services, can help your business thrive in the AI age.











