The Ultimate Guide to Backup and Disaster Recovery Best Practices
AI Overview:
In 2025, data is the lifeblood of business—and the threats to it are more severe than ever. Ransomware, natural disasters, and human error can cripple operations in minutes. Statistics show 94% of companies with major data loss don’t survive, making backup and disaster recovery (BDR) best practices essential for survival, not optional. This comprehensive Backup and disaster recovery guide outlines the strategies necessary to protect your business.
Backup and disaster recovery best practices: Fortify in 2025
This Backup and disaster recovery guide offers a clear framework for businesses to implement effective strategies.
Why Backup and Disaster Recovery Best Practices Are Critical for Business Survival
A solid disaster recovery strategy isn’t optional—it’s essential for survival. With sophisticated cyber threats and exponential data growth, backup and disaster recovery best practices are the foundation that keeps businesses running when disaster strikes. Modern cloud technologies and automation make robust data protection more accessible than ever.
Here are the core best practices every business needs:
- Follow the 3-2-1-1-0 rule: 3 data copies, 2 media types, 1 copy off-site, 1 immutable backup, and 0 errors after testing.
- Define clear objectives: Set Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO).
- Implement security: Use immutable backups, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
- Choose the right strategy: Select from backup/restore, pilot light, warm standby, or multi-site active/active.
- Test regularly: Conduct annual full tests and quarterly tabletop exercises.
- Maintain documentation: Keep your disaster recovery plan updated.
The statistics are sobering: 94% of businesses that experience major data loss fail to survive, with 43% never reopening and 51% shutting down within two years. Even minimal downtime can result in significant losses for businesses dependent on constant data access.
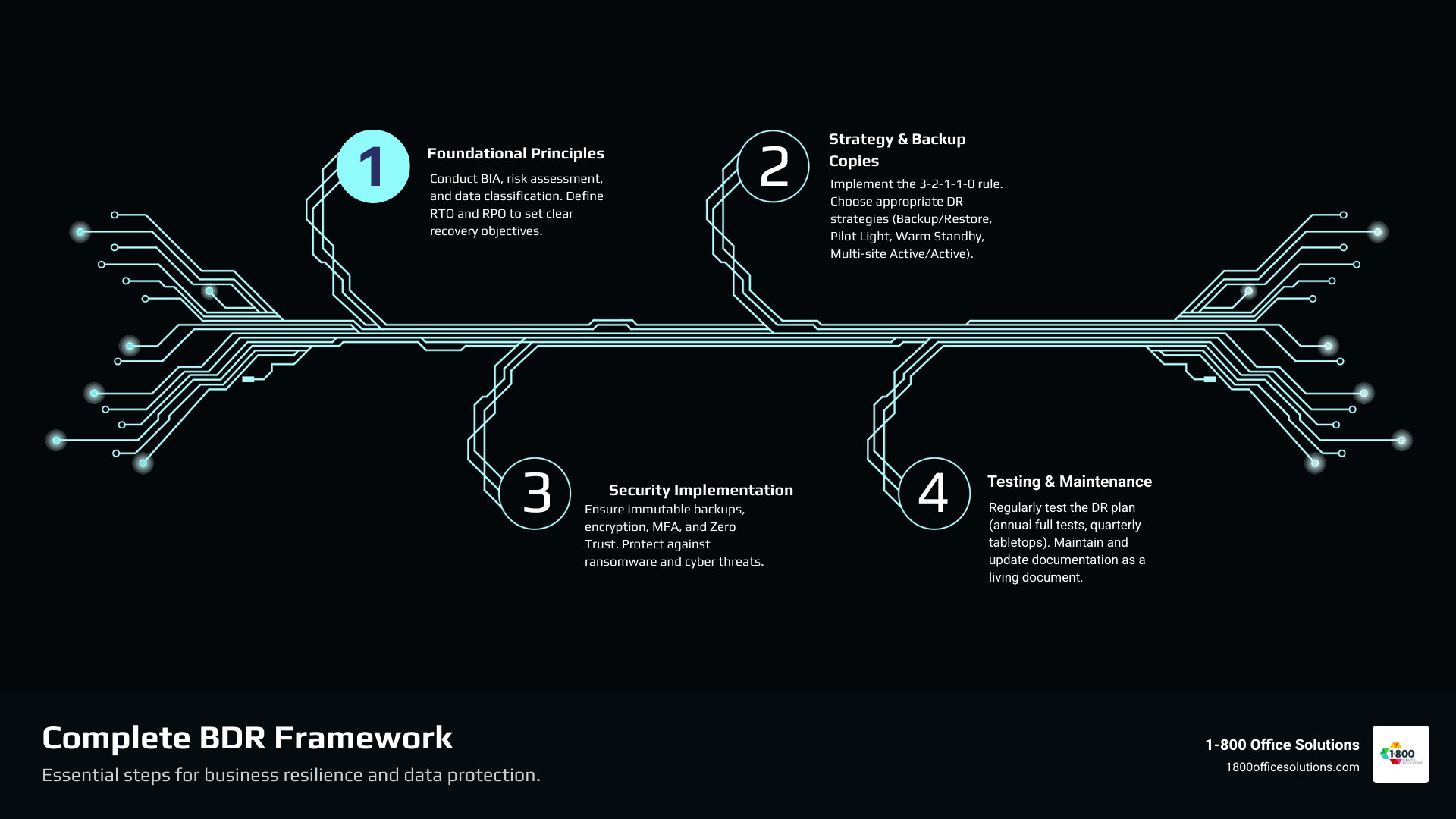
Foundational Principles: Building Your Backup and Recovery Framework
Building a solid foundation for your backup and disaster recovery best practices starts with understanding your unique risks and requirements. This begins with a comprehensive Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and a thorough risk assessment to inventory potential threats like ransomware, natural disasters, human error, and hardware failures.
Next, data classification helps prioritize information. Critical data, like a customer database, requires more stringent protection than less sensitive files. This classification informs your backup frequency—mission-critical data might need hourly backups, while archives could be weekly.
Retention policies define how long backups are kept, balancing regulatory needs with storage costs. Finally, physical backups (tape, drives) and off-site storage (cloud or a separate facility) provide essential protection against media-specific failures and localized disasters.
Defining Your Objectives: RTO and RPO
Before choosing technology, you must define clear recovery targets.
Your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable downtime your business can endure. For example, a dispatch system for a freight company might have an RTO of minutes, while a seasonal business in its off-season could tolerate hours.
Your Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the maximum data loss you can tolerate, measured from the last backup. An e-commerce site processing constant orders needs a very low RPO, while a firm with less dynamic data might accept a day’s worth of loss.
These objectives are determined by a critical systems analysis to understand business impact. Tools like AWS Resilience Hub can help validate and monitor how well your systems meet these targets.
Choosing the Right Disaster Recovery Strategy
With your RTO and RPO defined, you can select a strategy that balances cost vs. complexity. Your workload architecture also plays a key role.
- Backup and Restore: The most budget-friendly option. Data and applications are restored to new infrastructure after a disaster. Best for higher RTO/RPO tolerance.
- Pilot Light: A minimal version of your infrastructure is kept ready in a recovery location. Resources are scaled up when needed, offering faster recovery than backup/restore at a lower cost than a warm standby.
- Warm Standby: A scaled-down but fully functional copy of your production environment is always running, ready to handle traffic at reduced capacity. This significantly reduces recovery time.
- Multi-site Active/Active: The premium strategy for near-zero RTO and minimal data loss. Applications run concurrently across multiple sites, with traffic failing over seamlessly if one site goes down.
Microsoft’s documentation on Disaster recovery options in the cloud offers more technical guidance.
The 3-2-1-1-0 Rule: A Modern Approach to Backup Copies
The traditional 3-2-1 rule has evolved to combat modern threats like ransomware. The 3-2-1-1-0 Rule adds critical protections:
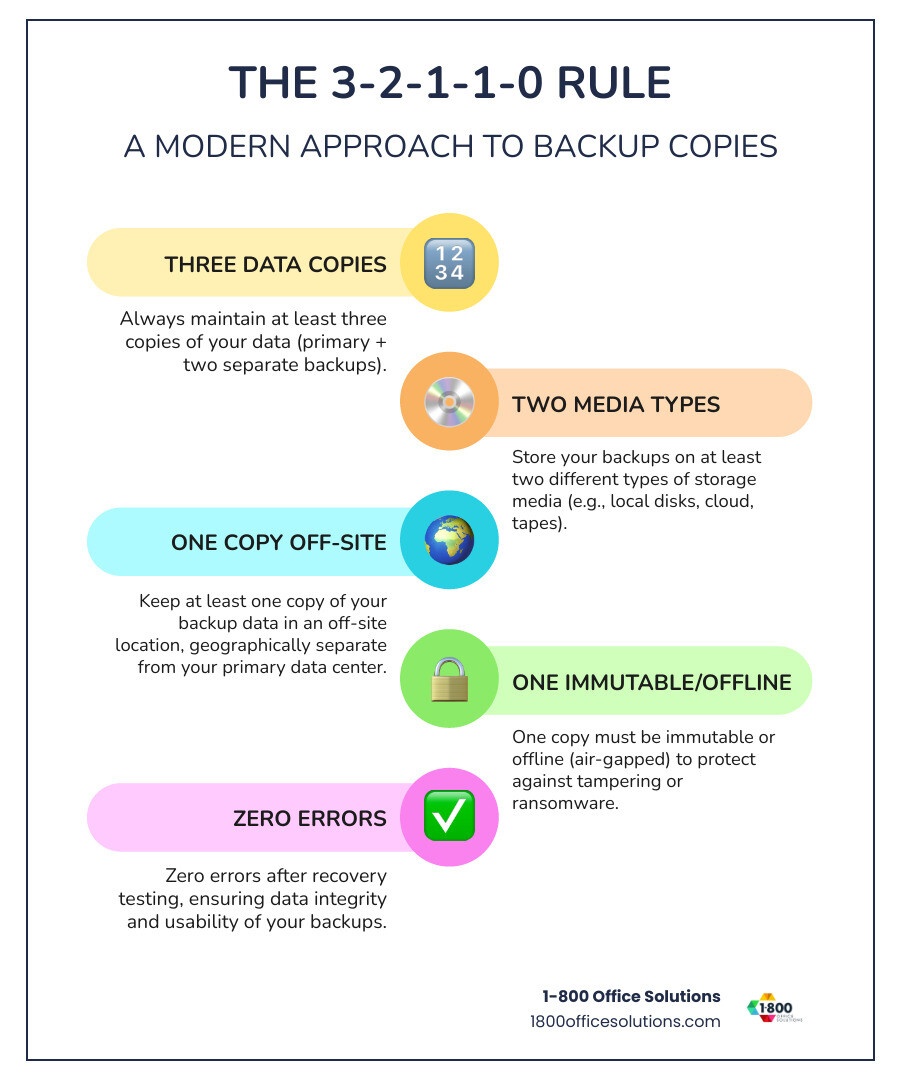
- 3 Data Copies: Your primary data plus two separate backups.
- 2 Different Media Types: Store backups on different technologies (e.g., disk and cloud) to protect against media-specific failures.
- 1 Copy Off-Site: Keep one backup in a separate geographic location to protect against site-wide disasters.
- 1 Copy Immutable or Offline: This is the key defense against ransomware. Immutable backups cannot be altered or deleted. Air-gapped backups are physically or logically isolated from the network. As Backblaze notes in their disaster recovery best practices, this is crucial as attackers now target backups.
- 0 Errors After Recovery Testing: Your backups are useless if they don’t work. Regular testing and validation are mandatory.
Modern Backup and Disaster Recovery Best Practices for Security

Modern backup and disaster recovery best practices must be security-first. Sophisticated attackers now specifically target backup systems to neutralize your recovery options. With the number of ransomware attacks almost doubling recently, your backup strategy must be designed to survive targeted cyber warfare, not just hardware failures.
Building a Cyber-Resilient Backup Architecture
A cyber-resilient architecture assumes attackers will breach your network. Key defenses include:
- Immutable Storage: This is a primary defense against ransomware. Once written, backup data cannot be changed, deleted, or encrypted, even by administrators.
- Air Gapping: Creates total isolation between backups and the production network, either physically (offline tapes) or logically (in the cloud), making them unreachable by malware.
- Zero Trust Principles: Assumes every access request is potentially malicious, requiring continuous verification. Resources like Secure Backup Best Practice from UPenn highlight this approach.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Limits user and system permissions to the absolute minimum required, containing damage if an account is compromised.
- Data Corruption Prevention: Ensures backup integrity through robust error checking and validation.
Our cybersecurity services integrate these measures into your DR strategy.
Proactive Defense: Encryption, MFA, and Threat Detection
Proactive defense requires multiple layers of protection:
- End-to-End Encryption: Protects data both in transit (as it travels to storage) and at rest (while stored), making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): A critical step that blocks most credential-based attacks by requiring a second verification factor to access backup systems.
- Anomaly Detection: Uses AI to spot unusual activity, such as mass deletions or encryption, providing AI-powered threat hunting to catch attacks early.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scans backup infrastructure for security weaknesses that need patching.
- Insider Threat Protection: Implements strict access controls and auditing to mitigate risks from internal personnel, whether malicious or accidental.
These layers create a comprehensive shield around your ability to recover.
Implementing Your Strategy: From Cloud to Automation
With a secure strategy in place, it’s time to implement your backup and disaster recovery best practices. This phase transforms your plan into a live system that protects your business 24/7. At 1-800 Office Solutions, we focus on three critical elements: leveraging cloud scalability, protecting modern workloads like SaaS and containers, and streamlining operations with automation. Our managed IT services are designed to guide you through these complexities.
Leveraging the Cloud for Scalable Backup and Recovery
The cloud offers significant advantages for backup and recovery, eliminating concerns about storage capacity and obsolete hardware.
- Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness: The cloud scales automatically with your business needs, and you only pay for what you use. This shifts costs from large upfront investments to predictable operational expenses.
- Hybrid vs. Cloud-Only: A hybrid cloud strategy combines on-premises speed for recent data with cloud cost-savings for archives. A cloud-only strategy offloads all backup infrastructure management.
- Geographic Redundancy: Cloud providers like Oracle have data centers in multiple regions (see Oracle Cloud Regions), providing built-in protection against regional disasters. For more, see Learn about architecting a highly available cloud topology.
Protecting Modern Workloads: SaaS and Containers
Traditional backup methods often fail to protect modern workloads like SaaS applications and containers.
It’s crucial to understand the shared responsibility model. SaaS providers like Microsoft are responsible for their platform’s uptime, but you are responsible for protecting your data within it. Accidental deletion, corruption, or malicious attacks on your data are your problem to solve.
This makes third-party Microsoft 365 backup and Salesforce data protection essential. These tools provide granular recovery and longer retention than native options.
Container backup is another challenge, as platforms like Kubernetes are highly dynamic. Traditional methods can’t protect these ephemeral environments effectively. Specialized Kubernetes backup solutions are needed to protect not just data, but entire application configurations, integrating recovery into your DevSecOps pipeline.
Streamlining Operations with Automation, AI, and Managed Services
Automation, AI, and managed services are key to making your DR plan efficient and reliable.
- Automating Backup Schedules: Eliminates human error and ensures backups run consistently.
- AI for Anomaly Detection: Provides proactive threat detection by identifying unusual patterns (like mass deletions) that could signal a ransomware attack in its early stages.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Simplifies recovery into manageable, often single-click, operations. This dramatically reduces RTOs and pressure on your staff during a crisis.
- Managed Services: Reduces the IT burden, allowing your team to focus on strategic work instead of backup monitoring. This includes stakeholder identification and crisis communication planning to ensure a coordinated response.
Our backup and disaster recovery solutions integrate these services for enterprise-level protection without the complexity.
Testing and Maintenance: Ensuring Your Plan Actually Works
A backup and disaster recovery best practices plan is useless without regular testing and maintenance. An untested plan is likely to fail when you need it most. Think of it like a fire drill: testing reveals problems before a real disaster strikes, which is critical since 70% of outages require significant recovery efforts.
The Critical Importance of Regular Testing and Validation
Regular testing is a continuous process that builds confidence and validates your strategy. Key benefits include:
- Validating RTO/RPO: Confirming you can actually meet your recovery time and data loss objectives. This includes verifying data integrity post-recovery.
- Identifying Gaps: Testing uncovers weaknesses, bottlenecks, or outdated procedures in your plan, allowing you to fix them proactively.
- Refining Procedures: Each test provides feedback to streamline and optimize recovery steps.
- Building Operator Familiarity: Drills ensure your team knows their roles and can execute the plan under pressure.
Simulating outages can range from tabletop exercises to full failover tests. Resources like the AWS Well-Architected Lab: Testing Backup and Restore of Data and Microsoft’s Recommendations for designing a disaster recovery strategy provide practical guidance.
Follow this simplified DR plan testing checklist:
- [ ] Define Test Scope & Objectives: What systems/data are we testing? What RTO/RPO are we validating?
- [ ] Schedule Test: Plan a date and time, notify stakeholders, and identify a test environment.
- [ ] Execute Test Scenario: Follow documented DR procedures step-by-step.
- [ ] Monitor & Document: Record timings, issues, and deviations from the plan.
- [ ] Verify Recovery: Confirm data integrity and system functionality.
- [ ] Review & Analyze: Conduct a post-test review with all involved parties.
- [ ] Update Plan: Implement necessary changes to the DR plan and documentation.
- [ ] Report Findings: Communicate results and action items to management.
Maintaining Your DR Plan as a Living Document
Your DR plan must be a living document that evolves with your business. Maintenance is not optional.
- Scheduled Reviews: Conduct comprehensive plan reviews at least annually, with more frequent checks after significant IT changes.
- Update for New Technology: As your IT environment evolves (e.g., new cloud services, migrated servers), your DR plan must be updated to match.
- Align with Business Changes: Ensure the plan reflects changes in business priorities, regulatory requirements, or market expansion.
- Update Roles and Responsibilities: Keep contact lists and role assignments current as personnel changes.
- Use Document Version Control: Ensure everyone is working from the latest version of the plan to avoid confusion during an emergency.
Continuous improvement should be the goal. Every test and review is an opportunity to make your DR capabilities more robust and reliable.
Frequently Asked Questions about Backup and Disaster Recovery Best Practices
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we receive about backup and disaster recovery best practices.
How often should I test my disaster recovery plan?
A full test of your entire recovery process should be conducted at least annually. This simulation validates that you can meet your RTOs and RPOs under pressure and ensures your team can execute their roles. In addition to the annual full test, tabletop exercises and component-level tests should be performed quarterly. These smaller-scale drills keep the team sharp and help identify gaps in specific procedures without the disruption of a full test.
What is the difference between a backup and a disaster recovery plan?
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they are very different.
A backup is a copy of data. Its purpose is to restore information that is lost, corrupted, or accidentally deleted.
A disaster recovery (DR) plan is a comprehensive strategy for restoring your entire IT infrastructure and business operations after a major disruption. A DR plan is a complete playbook that includes communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and recovery sequencing. Backups are a critical component of a DR plan, but they are not the plan itself.
Is cloud backup more secure than on-premises?
Often, cloud backup can be more secure than on-premises solutions. Major cloud providers invest heavily in physical and cybersecurity, employing dedicated security teams and offering advanced features like immutable storage and enterprise-grade encryption that are too costly for most businesses to replicate.
However, security is not automatic. Overall security depends on proper configuration and adherence to the shared responsibility model. You are still responsible for managing access controls and configuring the service securely. An improperly configured cloud backup can be just as vulnerable as any on-premises system. Best practices like using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are essential.
Conclusion: Fortify Your Business with a Modern Recovery Strategy
Solid backup and disaster recovery best practices are non-negotiable. They are the difference between a manageable inconvenience and a business-ending catastrophe.
We’ve covered the core principles, from defining RTOs/RPOs and following the 3-2-1-1-0 rule to implementing modern security defenses and leveraging the cloud. But remember, a plan is only effective if it is regularly tested and maintained.
Building this cyber resilience protects your operations, improves customer trust, and provides a true competitive advantage. A robust BDR strategy is not an IT expense but a core business investment in your company’s future.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we specialize in providing enterprise-level protection without the enterprise-level complexity or cost. We partner with small and mid-sized businesses to design, implement, and manage BDR solutions that fit their unique risks and budget.
Learn how our managed IT services can implement these backup and disaster recovery solutions for your business. Because when it comes to protecting what you’ve built, there’s no such thing as being too prepared.











