In-Depth Guide to Understanding the Security Audit Process
Security audits are an essential shield against the rising tide of cybercrime, especially as remote work continues to expand digital vulnerabilities. Cybercrime is projected to cost businesses and individuals $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making cybersecurity a top priority. With strict regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) shaping compliance requirements, understanding security audits is critical for businesses of all sizes.
What You’ll Learn in This Guide:
- The purpose and components of security audits
- Different types of security audits and their functions
- A step-by-step breakdown of the security audit process
- The importance of security audits in strengthening cybersecurity defenses
- How security audits compare to other security measures
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of security audits and how they can help protect your organization from cyber threats.
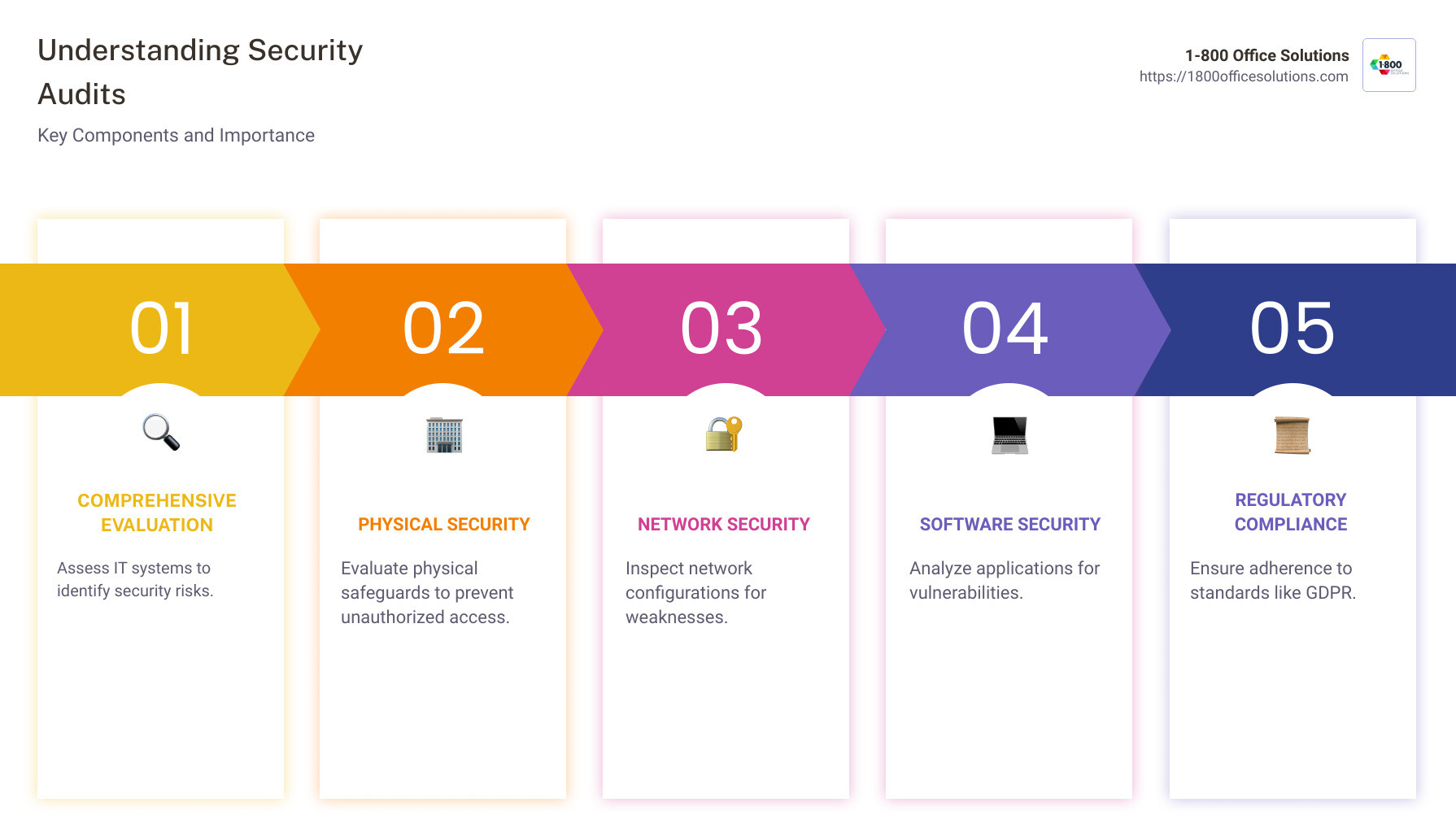
What is a Security Audit?
A security audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s information systems, assessing security policies, protocols, and vulnerabilities. Think of it as a health check for your IT infrastructure, ensuring that security measures are in place and functioning effectively.
Objectives of a Security Audit:
- Identify vulnerabilities – Uncover weaknesses in software, hardware, and user practices.
- Evaluate compliance – Ensure alignment with legal and industry security standards.
- Assess risk management – Analyze how well an organization detects, prevents, and responds to security threats.
- Improve security protocols – Recommend enhancements to policies and controls to strengthen defenses.
- Protect sensitive data – Prevent unauthorized access, breaches, and data loss.
A security audit not only reveals potential risks but also provides a roadmap for organizations to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Types of Security Audits
Different types of security audits serve distinct purposes, each playing a vital role in an organization’s overall security strategy. Here are the most common types:
1. Compliance Audits
- Ensure adherence to industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and ISO 27001.
- Ideal for businesses handling sensitive customer data such as financial institutions and healthcare providers.
2. Risk Assessment Audits
- Identify and analyze security threats and their potential impact.
- Helps organizations prioritize security measures and allocate resources efficiently.
3. Vulnerability Assessment Audits
- Scan systems for known security weaknesses and misconfigurations.
- A proactive approach to closing security gaps before cybercriminals exploit them.
4. Penetration Testing (Pen Test)
- Simulates a cyberattack to assess system defenses.
- Often performed by ethical hackers to test real-world resilience.
5. Internal Security Audits
- Conducted by an organization’s internal IT or security team.
- Reviews internal policies, employee access controls, and overall security readiness.
6. External Security Audits
- Performed by third-party cybersecurity firms.
- Provides unbiased insights and often required for regulatory compliance.
Understanding the right type of audit for your business ensures you get the most value out of the process.
The Security Audit Process
A security audit may seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into clear steps simplifies the process. Below is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Define the Scope
- Identify which systems, networks, and data need to be audited.
- Set goals aligned with compliance, risk assessment, or security improvements.
Step 2: Gather Data
- Collect logs, system configurations, and network maps.
- Interview employees and IT staff about current security policies and procedures.
Step 3: Conduct Risk and Vulnerability Assessments
- Perform penetration testing and scan for vulnerabilities.
- Identify weak passwords, outdated software, and unsecured data storage.
Step 4: Review Security Policies and Controls
- Evaluate access control mechanisms (who can access what data?).
- Assess physical security measures like surveillance cameras and restricted areas.
Step 5: Analyze Findings and Generate a Report
- Document vulnerabilities, risks, and compliance gaps.
- Provide recommendations for improvement with priority levels.
Step 6: Implement Security Improvements
- Apply necessary patches, updates, and security upgrades.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices.
Step 7: Monitor and Repeat
- Security is an ongoing process; regular audits help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
Importance of Security Audits
Security audits are not optional—they are crucial for organizations looking to protect sensitive data and maintain trust. Here’s why they matter:
1. Prevent Data Breaches
- Identifies weak points before hackers exploit them.
- Reduces financial and reputational damage caused by cyber incidents.
2. Ensure Compliance with Regulations
- Helps businesses avoid hefty fines for failing to meet GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS compliance.
- Builds customer trust by demonstrating a commitment to security.
3. Enhance Incident Response Readiness
- Strengthens response plans for phishing attacks, ransomware, and data leaks.
- Improves ability to detect, respond, and recover from cyber threats.
4. Increase Employee Awareness
- Educates staff on cybersecurity best practices.
- Reduces human errors that often lead to security breaches.
Security Audits vs. Other Security Measures
Security audits are just one part of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Here’s how they compare to other security measures:
| Security Measure | Purpose | How It Differs from Security Audits |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration Testing | Simulates cyberattacks | Focuses on testing defenses, not full security assessment |
| Vulnerability Assessment | Identifies system weaknesses | More technical, doesn’t include policy reviews |
| Governance & Compliance | Ensures adherence to security regulations | Audits assess compliance, but governance maintains it |
| Risk Management | Identifies & mitigates potential risks | Security audits provide data to inform risk management |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should security audits be conducted?
- At least once a year, but more frequently for high-risk industries like finance and healthcare.
2. Who should perform a security audit?
- Internal IT teams can conduct audits, but third-party auditors provide unbiased insights.
3. How long does a security audit take?
- Depends on scope and organization size; typically between a few days to several weeks.
Conclusion
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we recognize that cybersecurity is a business necessity, not a luxury. Security audits provide critical insights into vulnerabilities, helping businesses proactively defend against cyber threats. By investing in regular audits, organizations can ensure data protection, regulatory compliance, and long-term security success.
Partner with us to implement a robust cybersecurity strategy that keeps your business safe from evolving threats.











