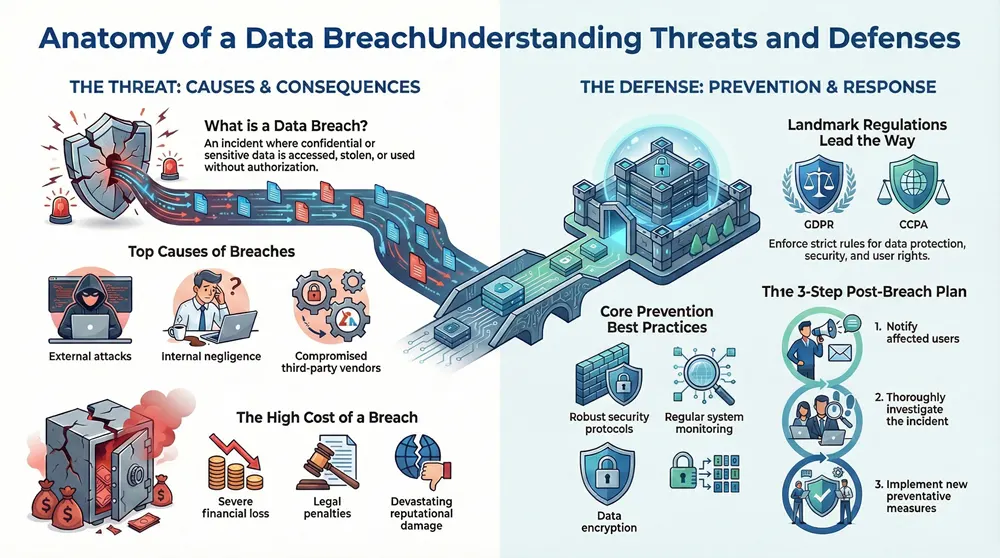
Data Breaches: Data Protection Remains a Primary Concern, with Regulations Like GDPR and CCPA in Place to Safeguard User Data
AI Overview:
This blog provides a comprehensive look at data breaches—what they are, how they occur, and why they pose serious financial, legal, and reputational risks to organizations. It explains key causes, impacts, and prevention strategies, highlights major data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and emphasizes the roles of technology, education, businesses, and governments in safeguarding data. Overall, it underscores the importance of proactive security measures, regulatory compliance, and continuous awareness to protect sensitive information in an increasingly connected world.
Data Breaches
Data security is an issue of utmost importance in the modern-age, where malicious actors are continuously attempting to access sensitive data. In response, governments and organizations around the world have enacted regulations to ensure user data is adequately protected. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are two prominent regulations that have been put in place to protect citizens’ data from data breaches.
Data breaches remain an ever-present danger, as malicious actors continually attempt to gain access to user data for illicit purposes. It’s essential that organizations take the necessary steps to protect their user data and adhere to the regulations outlined by GDPR and CCPA. Cybersecurity experts should be consulted to ensure that the latest best practices are implemented and that data remains secure.
Overview of Data Breaches
A data breach is an incident in which private, confidential or sensitive data is accessed, stolen or lost without authorization. Breaches can be caused by an external hacker, an insider, or a malicious or negligent third party. Cyberattacks, malware, phishing and social engineering are some of the most common mechanisms used to gain unauthorized access to personal data. Data breaches can seriously impact an organization’s reputation, lead to financial losses, and cause identity theft for the individuals whose data has been compromised.
Data breach prevention measures should include robust security protocols, regular system updates, employee training and the implementation of identity and access management solutions.
What Is a Data Breach?
Transitioning from the previous section, it is important to understand what a data breach is and how it can cause significant harm to both individuals and organizations. A data breach is an incident in which confidential, sensitive, or protected data is accessed, viewed, stolen, or used without authorization. It can be carried out by external attackers, often referred to as hackers, or by internal actors such as careless employees, malicious insiders, or disgruntled former staff members. Hackers may gain access to data through a variety of methods including phishing, malicious malware, social engineering, or exploiting vulnerabilities in a company’s infrastructure.
Once a data breach occurs, it can be used to steal personal data such as passwords, social security numbers, credit card numbers, bank account numbers, or other confidential information. Furthermore, it can also be used to gain access to sensitive corporate data or customer records. In some cases, a data breach can even lead to identity theft or financial losses. The Equifax data breach of 2017, for example, exposed the personal data of 147 million people and resulted in a settlement of up to $700 million.
Data breaches can have a substantial impact on organizations, including significant reputational damage, increased regulatory scrutiny, and hefty fines.
Causes of Data Breaches
Following an overview of data breaches, it is important to understand the causes of data breaches. Cybersecurity is a complex issue that involves many different factors. There is no single cause of data breaches, but there are several common sources of vulnerability and attack vectors that hackers use to gain access to confidential data. Understanding these causes can help organizations take steps to prevent a data breach from occurring.
The causes of data breaches can be divided into three main categories:
- External sources: These include vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure, often exploited by external attackers. Common examples include phishing scams, external malware, credential stuffing, and social engineering.
- Internal sources: These include employee negligence or malicious behavior, such as unauthorized access to data or the installation of malware.
- Third-party sources: These include data breaches related to third-party vendors or other organizations. Common examples include data breaches involving Equifax, the Federal Trade Commission, the U.S. government, and large healthcare data breaches.
Data breaches can have serious consequences. They can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liability. It is important for organizations to understand the sources of data breaches and take steps to prevent them.
Potential Impact of Data Breaches
Transitioning from the causes of data breaches to the potential impacts, it is clear that data breaches can have a significant financial, legal, and reputational toll on organizations. In fact, the cost of a data breach is soaring and is estimated to reach $6 trillion globally by the year 2023. Depending on the magnitude and scope of the data breach, the cost can range from hundreds of thousands of dollars to hundreds of millions of dollars.
From a legal perspective, the impact of a data breach can be even more damaging. Depending on the particular type of data, there could be a significant risk of lawsuits and other legal action. Organizations that handle personal data are also subject to different regulations and laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and a data breach could result in hefty fines and other sanctions.
Finally, a data breach can have a devastating effect on an organization’s reputation. Once a data breach occurs, customers may lose trust in the organization and the organization may have to spend significant amounts of money to repair its reputation.
Overall, data breaches can cause serious financial, legal, and reputational damage to organizations. The potential impacts of data breaches can be divided into three main categories:
Regulations to Help Protect Data
As cyber security experts, we must be aware of the regulations to help protect data from being compromised. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are two of the most prominent. GDPR, which came into effect in 2018, requires companies to protect personal data and adhere to strict accountability protocols.
For example, companies must inform individuals of any data breach within 72 hours of its occurrence. The CCPA, which will come into effect in 2023, will give California residents more control over their personal data by allowing them to opt-out of their data being shared or sold.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
With the rising threats of data breaches, it is becoming increasingly important to protect personal and confidential information. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are being implemented around the world in order to safeguard data integrity and security.
The GDPR is an EU-wide law that was introduced in order to protect EU citizens from data breach risks. It requires companies to put in place appropriate measures to protect any personal data they process and to keep it secure. It also requires companies to report any data breaches that occur, within 72 hours of becoming aware of them.
The GDPR also ensures that organizations are held accountable for any breach of the regulations, with fines of up to 4% of the company’s annual global turnover or 20 million euros, whichever is higher.
The GDPR covers the following areas:
- Data Access: Organizations must provide individuals with access to their data, as well as information on how it is being used and shared.
- Data Security: Organizations must protect personal data from unauthorized access, destruction, alteration, and theft.
- Technical Security Measures: Organizations must use appropriate technical security measures to protect data. This includes encryption, firewalls, and other measures.
- Physical Security Measures:
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
As we have seen, data breaches are an ever-growing concern for businesses and individuals. While there are many steps organizations can take to protect sensitive information, it is also important to be aware of the various laws and regulations that are in place to ensure data security. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is one of the most important pieces of legislation governing data protection.
The CCPA was passed in 2018 and is set to take effect in January 2022. It is the first of its kind in the United States and is designed to give consumers the right to know what data companies are collecting, the right to delete their data, and the right to opt out of the sale of their data. Additionally, the CCPA requires companies to notify consumers when a data breach occurs and provides consumers with the right to file a lawsuit if their information is obtained by an unauthorized person.
Under the CCPA, businesses are required to take the following steps to protect data:
- Secure personal information and other confidential data:
- Use encryption to protect confidential information
- Establish access control to restrict access to sensitive data
- Implement strong authentication measures
- Limit the collection and use of sensitive data:
Other Data Protection Regulations
With the increasing number of data breaches, businesses are looking for more regulations to help protect data. Alongside the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), other data protection regulations have been enacted that seek to reduce the risk of data breaches.
These regulations include:
- International Regulations:
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework
- Council of Europe Convention on Cybercrime
- Regional Regulations:
- Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD)
- Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
- Mexico’s Federal Law on the Protection of Personal Data Held by Private Parties
- The European Union’s ePrivacy Directive
By complying with these regulations, companies can mitigate the potential risks of data breaches and secure the safety and privacy of their customer’s personal information. The regulations provide a framework for companies to follow in order to protect data, such as the requirement to delete and dispose of personal data securely, update security measures, and provide customers with the right to access, delete, and transfer their personal data.
Understanding the Risk of Data Breaches
Identifying vulnerable areas, assessing potential damage, and creating an incident response plan are essential components in understanding the risk of data breaches. Cybersecurity experts must conduct regular scans to detect any weaknesses in computer systems that hackers could exploit.
In addition to identifying any possible vulnerabilities, they must assess the potential damage of a successful attack. From stolen personal data and confidential information to compromised financial information and social security numbers, the cost of a data breach can be immense. Creating an incident response plan ahead of time can help reduce the cost of a data breach.
Identifying Vulnerable Areas
The thought of a data breach can be daunting, and with the risk seemingly growing every day, understanding the vulnerable areas of a business is paramount to avoiding disaster. Identifying and protecting these areas can be the difference between a secure business and one that falls victim to a malicious attack.
When it comes to pinpointing areas of vulnerability, here is a list of areas to consider:
- Data Sources:
- External
- Cloud Services
- 3rd Party Services
- Mobile Devices
- Internal
- File Systems
- Databases
- Mobile Devices
- External
- Access Controls:
- Password Policies
- Physical Access Restrictions
- Network Access Controls
- Multi-Factor Authentication
Understanding these vulnerable areas can help businesses create policies and procedures to protect themselves from malicious cyber attacks. Adopting a security strategy that includes data breach prevention, security monitoring, and incident response plans can help businesses protect their data and minimize the chances of a costly data breach.
Businesses should also train their employees on cybersecurity and data protection best practices.
Assessing Potential Damage
As the world of cyber security continues to evolve, it is becoming increasingly important to understand the potential risks associated with data breaches. Assessing damage can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to the financial costs, but it is a necessary part of any data breach prevention plan.
When assessing potential damage from a data breach, it is important to consider both the short-term and long-term financial consequences. In the short-term, companies may be faced with the cost of implementing a data breach response plan, including hiring a third-party firm to investigate the incident, notifying customers of the breach, and providing credit monitoring services. In the long-term, companies may face future liabilities for compromised data, such as lawsuits and penalties for not complying with data privacy regulations.
Additionally, it is important to consider the cost of lost customer trust. A data breach can severely damage a company’s reputation, causing customers to lose confidence and take their business elsewhere. This can result in lost sales, reduced brand loyalty, and higher customer acquisition costs.
The following are some of the topics to consider when assessing potential damage from a data breach:
- Financial Costs:
Creating an Incident Response Plan
It is clear that protecting data is an important priority, and understanding the risk of data breaches is essential for taking the necessary precautions. One of the most important steps to preventing and responding to a data breach is creating an incident response plan. This plan should detail the steps to take if a data breach occurs, how to identify and respond to a breach, and how to protect data from future attacks.
Creating an incident response plan can be broken down into the following steps:
- Identifying vulnerable areas:
- Evaluate existing security systems and protocols
- Identify potential weak spots
- Assessing potential damage:
- Understand the possible consequences of a breach
- Analyze the potential impact on revenue and reputation
Best Practices for Data Protection
Strengthening security protocols, regularly monitoring user data, and implementing data encryption are essential best practices for effective data protection.
Robust security protocols like multi-factor authentication, password policies, and strong encryption help safeguard confidential information from potential cyber attackers. Consistent monitoring of user data further provides insight into any suspicious activities. Data encryption is essential to protect sensitive personal data, such as social security numbers and passwords, from malicious hackers.
Data breach prevention also involves the use of security measures such as firewalls, anti-malware programs, and intrusion detection systems.
Strengthening Security Protocols
The risk of a data breach is clear, but there are ways to mitigate the chances of it happening. Specifically, strengthening security protocols is a top priority for any organization looking to protect its data. To do this, there are several steps that should be taken:
- Establishing secure user authentication: This includes setting up complex passwords that are regularly updated and implementing two-factor authentication or multi-factor authentication.
- Implementing firewalls and other protective measures: Firewalls are one of the most important tools for preventing unauthorized access to data. Other measures include monitoring network activity, using antivirus software, and deploying intrusion detection systems.
- Educating employees on security best practices: Employees should be trained on safe internet and email usage, how to recognize potential threats, and how to properly handle confidential information.
- Updating software and systems: Software and systems should be updated regularly to ensure they are secure and up-to-date. This includes patching any vulnerabilities and keeping track of all software licenses.
- Investigating suspicious activity: All suspicious activity should be investigated thoroughly to ensure there are no breaches or malicious actors. This includes monitoring system logs and identifying any unusual patterns or trends.
Regularly Monitoring User Data
With the ever-growing threat of data breaches, it is imperative that businesses stay vigilant and regularly monitor their user data. By proactively implementing data protection best practices, businesses can be better prepared to quickly detect and respond to any potential risks. Here are the top two ways to monitor user data:
- Strengthening Security Protocols:
- Implementing two-factor authentication: This method requires two forms of identification from the user to gain access to the system. It provides an extra layer of security by making it more difficult for hackers to access confidential data.
- Installing malware protection systems: These systems help detect and remove malicious software from the system, as well as alert the users to potential security threats.
- Regularly Monitoring User Data:
- Monitoring user access: It is important to keep track of who has access to what data, and ensure that only authorized personnel have access to confidential information.
Performing regular security audits: Regularly auditing the system helps ensure that any security vulnerabilities are identified and addressed in a timely manner.
Implementing Data Encryption
After understanding the risk of data breaches, it is time to turn to best practices for data protection. Implementing data encryption is one of the most important steps in data protection, as it renders data unreadable by unauthorized users. To ensure maximum security, it is important to understand the following types of data encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: This type of encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption. It is suitable for encrypting large amounts of data in a short time, however, it does not offer the same level of security as more complex encryption methods.
- Asymmetric Encryption: This type of encryption uses two keys, a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is used to decrypt data. Asymmetric encryption is more secure than symmetric encryption, as the keys are not shared between parties.
- Hashing: Hashing is a form of encryption that uses a mathematical algorithm to convert data into a fixed-length string of characters. It is used to verify the integrity of data, as it is not possible to reverse the process and retrieve the original data from the hash.
Steps to Take After a Data Breach
When a data breach occurs, the first step is to notify affected users. Informing clients of the breach helps them protect their information, such as passwords and personal data. After notifying the affected users, investigate the breach to figure out how the hacker gained access to the system.
This includes looking for vulnerabilities and scanning for malware. Taking preventative measures is the last step: implementing policies and procedures to reduce the risk of future attacks. Investing in cybersecurity, such as encrypting confidential information and creating strong passwords, can improve data security. Companies must also ensure they are compliant with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation and the Federal Trade Commission.
Notifying Affected Users
As organizations face mounting pressure to protect their data, it is essential to have a plan in place if a breach occurs. If an organization fails to protect customer data, one of the first steps is to notify the affected users. Notifying users in a timely manner is essential in order to avoid any damages that could arise from a data breach.
To ensure that users are properly informed of the breach, the following procedures need to be taken:
Notifying Affected Users:
- Investigating the Breach: It is important to investigate the breach thoroughly in order to determine the cause and magnitude of the attack. This process should include steps such as identifying the type of attack, the amount of data that was exposed, and the attackers involved.
- Notifying the Right People: After the investigation is complete, it is important to notify the right individuals. This includes informing the victims of the breach, as well as any regulatory bodies that may need to be notified.
- Creating Effective Messages: It is important to create a message that is clear and concise. The message should provide an explanation of the breach, the details of the attack, and the steps that are taken to prevent future attacks.
Investigating the Breach
After establishing the best practices for data protection, the next logical step is to investigate a data breach thoroughly. Taking a methodical approach to investigating a data breach is paramount, as it can provide much-needed information to assist in preventing future breaches. It should start by carefully logging and assessing the breach to determine what happened, how it happened, and why it happened. The process of investigating a data breach can be broken down into the following steps:
Investigating the Breach:
- Gathering Evidence: The first step is to collect evidence, including any and all details of the breach. This includes examining the systems that were breached, examining user accounts, logging activities, and evaluating what data was affected.
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: To determine the cause of the breach, it is important to identify any potential vulnerabilities that were exploited by the hacker. This may involve looking for weaknesses in the system, such as poorly configured firewalls or outdated software.
- Analyzing the Breach: Once the evidence has been collected, it must be analyzed to determine where the breach originated and how the hacker gained access to the system. This can involve reviewing user logs, system logs, and any other available data to piece together the timeline of events.
Taking Preventative Measures
With the increase in frequency and cost of data breaches, taking preventative measures to protect data is of utmost importance. Organizations must take steps to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in their systems, to protect their data and that of their customers. To ensure a strong data breach prevention strategy, organizations should consider the following:
- Identifying Vulnerabilities:
- Identify potential vulnerabilities in the systems and networks
- Evaluate the effectiveness of existing policies and procedures around data security
- Identify any gaps in the security strategy and address them
- Implementing Security Measures:
- Implement multi-factor authentication for user accounts
- Enforce secure password policies across the organization
- Regularly patch systems to ensure that all security vulnerabilities are patched
The Role of Technology in Data Protection
The role of technology in data protection is becoming increasingly important. Automated solutions, artificial intelligence and blockchain technology are all being leveraged to protect data from malicious attacks. Automated solutions can detect and alert organizations of suspicious activity, reducing the risk of a data breach. Artificial intelligence is used to analyze data for anomalies and to develop systems that can detect and prevent breaches. Blockchain technology offers a secure way to store and protect sensitive data from hackers and attackers.
In addition to these technological solutions, organizations must also pay attention to the human factor. Malware, phishing scams, social engineering, and insider threats are all serious concerns in data protection.
Implementing Automated Solutions
The role of technology in data protection is becoming increasingly important in the wake of the rising number of data breaches. Automated solutions provide an effective way to identify and respond to potential security incidents, mitigate risks, and ensure data integrity. Here is an overview of implementing automated solutions to protect data:
- Monitoring Software: Automated monitoring software can be used to detect any suspicious activity on a system that could lead to a data breach. This software can be used to detect unauthorized access attempts, detect unusual user activities, identify potential vulnerabilities, and alert administrators to any malicious activity.
- Identity Verification: Automated identity verification solutions can help protect against insider threats and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This solution can identify suspicious activity based on user behavior analysis, detect malicious insiders, and help ensure that only authorized personnel gain access to confidential information.
- Data Encryption: Automated data encryption solutions can be used to protect data and ensure that sensitive information is kept secure. This solution can prevent data from being accessed by unauthorized people, help protect against data leaks, and protect data from being stolen.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence
The role of technology in data protection is paramount. Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) can help strengthen data security protocols and detect any possible data breaches faster. AI-driven solutions enable organizations to analyze data behaviors, identify anomalies, and detect threats before they become data breaches.
AI-driven security systems provide proactive protection against the growing number of malicious cyberattacks and prevent data breaches from occurring in the first place.
To properly leverage AI for data security, organizations should consider the following:
- Implementing Automated Solutions:
- Automated solutions can help detect suspicious activities and malicious actors attempting to gain access to data.
- AI-driven security systems can monitor and analyze data behaviors to detect any potential threats.
- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence:
- AI-powered security solutions can learn from past data breaches and detect threats more quickly.
AI can also be used to detect any potential vulnerabilities in a system before they are exploited by hackers.
Utilizing Blockchain Technology
The utilization of blockchain technology is proving to be a game-changer in data protection. As a cybersecurity expert, there are many ways to leverage the technology to help prevent data breaches and protect personal data.
The key points to consider when utilizing blockchain technology for data protection include:
- Implementing Automated Solutions:
- Automating the process of protecting data by utilizing smart contracts, so that breaches can be detected and prevented in real-time.
- Setting up automated alerts to immediately notify businesses in the event of a breach, allowing them to take the necessary steps to minimize the impact.
- Implementing automated processes for data access control, enabling a secure way to share data with trusted third-parties and customers.
- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence:
- Utilizing AI-driven solutions to monitor the system for any suspicious activity, allowing businesses to detect and counter potential breaches in a timely manner.
- Applying AI algorithms to detect threats before they happen, by identifying patterns of malicious behavior and potential vulnerabilities.
- Integrating AI-driven tools to identify and classify confidential data, to ensure it is properly encrypted and stored securely.
The Role of Education in Data Protection
Raising awareness of data protection is essential in educating the public about the risks of data breaches, the potential implications of mishandling sensitive information, and the importance of cybersecurity. Implementing training programs that teach good cybersecurity practices can help prevent potential data breaches and ensure that users are aware of the necessary steps to protect their data.
Furthermore, teaching users good cybersecurity practices can help reduce the risk of data being stolen by malicious attackers. Finally, educating users about data protection can help them understand the risks associated with data loss, such as financial loss and identity theft, and the necessary steps to protect their data.
Raising Awareness of Data Protection
As the previous section discussed, technology plays a key role in data protection. However, it is not the only factor that needs to be considered. Education is also essential in helping to raise awareness of data protection and implement training programs so that individuals and organizations can learn how to better protect their data.
Raising awareness of data protection starts with understanding the risks associated with data breaches, such as identity theft, financial losses, and reputational damage. People should be aware of the ways that hackers can gain access to confidential information through methods like phishing scams, malware, or social engineering.
Organizations should also implement training programs to teach their employees how to better protect their data. They should provide employees with information about:
- Types of data:
- Data that should be kept confidential, such as social security numbers, passwords, and financial information
- Sensitive information that needs to be protected, such as health data, customer data, and corporate data
Implementing Training Programs
It is clear that technology plays an important role in data protection, but it is not the only solution. Education is also a powerful tool that can combat data breaches and protect personal data. Implementing training programs is one way to raise awareness of data protection and ensure that individuals are equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to protect themselves and their data.
Training programs should cover a range of topics, including:
- Raising Awareness of Data Protection
- Common cyberattacks
- Understanding the value of personal data
- Potential consequences of a data breach
- Teaching Good Cybersecurity Practices
- Identifying and avoiding phishing scams
- Creating strong passwords
- Best practices for protecting sensitive data
- Preventing Data Breaches
- Recognizing insider threats
- Understanding the risk of a data breach
- Spotting potential vulnerabilities
Educating individuals is essential to protecting data and preventing data breaches. By raising awareness, teaching good cybersecurity practices, and preventing data breaches, training programs can help protect personal data and keep it out of the hands of hackers.
Teaching Good Cybersecurity Practices
In order to protect data, it is essential to teach good cybersecurity practices. Cybersecurity education should be comprehensive, including everything from raising awareness of data protection to implementing training programs. By understanding the fundamentals of cybersecurity, individuals can recognize and prevent potential attacks, as well as limit the damage if a breach should occur.
When it comes to teaching good cybersecurity practices, it is important to:
- Raise Awareness:
- Educate individuals about the dangers of data breaches and the importance of data security.
- Make sure everyone is aware of the risks associated with their personal data and the potential consequences of a data breach.
- Alert them about the latest data protection trends and threats.
- Implement Training Programs:
- Provide courses and training sessions that cover topics such as cyber threats, online security, and data protection.
- Give tips on how to create strong passwords and keep them secure.
- Teach individuals the best practices for protecting their data, including data encryption, two-factor authentication, and anti-virus software.
- Teach Good Cybersecurity Practices:
- Explain the basics of cybersecurity and how to protect yourself online.
The Role of Businesses in Data Protection
Businesses have a responsibility to protect their customers’ data. Creating a comprehensive data protection plan, establishing comprehensive privacy policies, and hiring a data protection officer are all critical steps in this process.

Data breaches are one of the most common threats to customer data. Measures must be taken to enhance data security, such as regular password changes and strong security protocols. Additionally, businesses should be vigilant when it comes to protecting customer data, such as social security numbers, passwords, and other sensitive information.
Hackers, attackers, and malware are all potential sources of data breaches.
Creating a Data Protection Plan
It is clear that businesses have an important role to play in protecting data. One of the most important steps businesses can take to protect data is to create a data protection plan. A data protection plan is a set of steps a business takes to protect its data from unauthorized access or damage. It includes measures such as regular security audits, backup and recovery plans, and data encryption.
When creating a data protection plan, businesses should consider the following:
- Risk Assessment: Businesses should identify potential risks to their data, including the risk of a data breach or cyber attack. They should also consider the potential cost of a data breach, including the cost of lost data, damages, and legal fees.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data is one of the most important steps businesses can take to protect their data. Encryption makes it more difficult for hackers to gain access to data.
- Data Backups: Regularly backing up data can help businesses recover from a data breach or other security incident. Businesses should create multiple copies of their data and store them in secure locations.
- Security Audits: Security audits help businesses identify weaknesses in their security systems and take steps to address them.
Establishing Privacy Policies
The importance of setting up privacy policies in order to protect data cannot be overstated. Businesses must take the necessary steps to ensure that their data is safeguarded and that the proper policies and procedures are in place to protect it. Establishing privacy policies is a key part of any data protection plan. When drafting these policies, companies should consider the following:
- Data Collection: Companies must be clear and transparent about what data they are collecting, how it is being used, and who will have access to it. They should also provide an opportunity for customers to opt-out of data collection if they choose.
- Data Storage and Sharing: Companies should ensure that data is securely stored and only shared with external parties on an as-needed basis. If the data is shared, safeguards should be in place to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Data Security: Companies should also ensure that their data security measures are up to date and in line with industry standards. This includes ensuring that there are adequate levels of encryption, authentication, and authorization in place. Additionally, companies should have processes in place to quickly detect and respond to any potential threats.
By establishing clear, comprehensive privacy policies, companies can take a proactive approach to data protection.
Hiring a Data Protection Officer
With the role of education in data protection now understood, businesses are further responsible for creating a data protection plan, establishing privacy policies, and hiring a data protection officer (DPO). In particular, hiring a DPO is essential for organizations to keep up with the rapidly-evolving landscape of data protection. A DPO will act as the central point of contact for all data protection-related matters, such as responding to data breaches, investigating data security incidents, and developing strategies for data protection.
Moreover, the DPO is expected to offer guidance on the following areas:
- Assessing the organization’s data processing activities:
- Identifying areas of risk
- Identifying potential vulnerabilities
- Developing policies and procedures for data security
- Monitoring compliance with data protection principles
- Developing a data breach response plan:
- Identifying key personnel
- Establishing a timeline for response
- Establishing communication protocols
- Developing a data breach notification procedure
The Role of Governments in Data Protection
As a cybersecurity expert, I understand the importance of governments in enforcing data protection regulations and investigating data breaches. It is crucial that they protect consumer privacy rights, as well as secure sensitive information such as social security numbers, passwords, and credentials. Cyber criminals use various methods like malware, phishing scams, social engineering, and unauthorized access to steal confidential data, and governments must be vigilant in preventing these attacks.
The Equifax data breach exposed the financial information of 143 million people, demonstrating the cost of a data breach and the risks of identity theft. According to a study, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.
Enforcing Data Protection Regulations
Given the increasingly prevalent reality of cybercrime, governments have a central role to play in enforcing data protection regulations. Governments bear responsibility in ensuring that companies are held accountable for their data security practices, and must investigate breaches and protect consumer privacy rights. In particular, governments must focus on the enforcement of data protection regulations in order to effectively protect citizens from data breaches.
This includes:
- Establishing protocols for data collection, storage, and protection
- Implementing technical measures to secure data
- Establishing rules for identifying and responding to data breaches
- Developing specific procedures for data breach incidents
- Setting up independent regulatory bodies to oversee the enforcement of data protection regulations
- Establishing robust penalties for data breaches
- Creating a system for reporting data breaches
- Developing an enforcement mechanism to ensure organizations comply with data protection regulations
The most effective way to ensure companies are protecting consumer data is for governments to implement and enforce regulations that protect consumer privacy rights. This could include implementing comprehensive data privacy laws, setting up independent regulatory bodies, and establishing robust penalties for data breaches. Additionally, governments must ensure that companies are properly identifying and responding to data breach incidents, and that organizations are adhering to the regulations put in place.
Investigating Data Breaches
With the rise in cyber-attacks, governments around the world have taken note of the importance of protecting consumer data and are doing their part to protect citizens’ data from malicious attackers. Investigating data breaches has become a priority for governments, and they are taking a variety of steps to ensure that all data is safeguarded.
From assigning dedicated teams to investigate data breaches and creating special laws to protect consumer data, governments are taking a proactive approach to data security. Here are some of the ways governments are involved in investigating data breaches:
- Dedicated Teams: Governments are assigning dedicated teams to investigate data breaches and report their findings. These teams are usually composed of computer security experts and investigative officers, and they work together to track the source of the breach and identify any potential vulnerabilities.
- Creating Laws: Governments are creating special laws to protect consumer data, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU. These laws create strict guidelines for how data is handled and require businesses to take certain measures to protect personal data.
- Offering Guidance: Governments are offering guidance to businesses on how to prevent data breaches and protect consumer data.
Protecting Consumer Privacy Rights
Having established the importance of businesses in protecting data, governments must also play a role in protecting consumer privacy and data. Governments are tasked with the responsibility of enforcing data protection regulations, investigating data breaches, and protecting consumer privacy rights. Specifically, when it comes to protecting consumer privacy rights, governments must take a proactive stance in preventing data loss and unauthorized access.
This includes:
- Establishing a Regulatory Framework: Governments must create a framework for businesses to follow when collecting and processing personal data. This framework must adhere to laws and regulations that protect a user’s personal information and ensure its privacy.
- Implementing Security Measures: Government must also implement measures to protect consumer data from cyber criminals. These measures include identifying potential vulnerabilities, detecting cyber attacks, and creating a response plan to minimize damage.
- Educating Consumers: Governments must educate consumers on the importance of data security and the risks associated with data breaches. This includes teaching users how to create strong passwords, store confidential data, and spot potential phishing scams.
The Future of Data Protection
The Future of Data Protection is dependent on the development of new technologies, strengthening data protection regulations, and creating international data standards. By 2023, organizations must face the growing complexity of data security, as well as the consequences of data breaches.
Cybersecurity experts must be aware of the vulnerabilities that hackers and attackers exploit to steal data. Malware, social engineering, and phishing scams are just a few of the methods used in data breaches. Companies must create secure passwords and protect their customers’ confidential information, or risk the cost of a data breach.
Developing New Technologies
With the increasing sophistication of hackers and the risks of data breaches across the globe, the development of new technologies for data protection is essential in the future of data protection. From leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to create smarter and safer systems, to utilizing blockchain technology to secure data, there are a number of ways to protect digital data and information.
Developing new technologies for data protection includes:
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning can be used to create smarter systems with the ability to detect anomalies and suspicious behavior, and alert operators to potential risks. These technologies can also be used to identify patterns in large datasets, detect early signs of a breach, and even protect the system from malicious actors.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that records and stores data securely and transparently. It can help protect data from unauthorized access, malicious actors, and provide proof of authenticity.
- Encryption: Encryption is a key component of data protection, as it helps protect data from being accessed by unauthorized individuals. Encryption can be used to protect data in transit, as well as data that is stored in the cloud or on physical devices.
Strengthening Data Protection Regulations
The future of data protection is very much dependent on the proactive steps taken to strengthen data protection regulations. Governments around the world are beginning to realize the importance of data protection and are taking the necessary steps to safeguard data. Here are some of the most significant steps currently being taken to strengthen data protection regulations:
Developing New Technologies:
- Creating new tools and technologies to help detect and prevent data breaches.
- Developing more secure networks and infrastructure to protect data.
Strengthening Data Protection Regulations:
- Imposing stricter laws and regulations to protect personal data.
- Enforcing more stringent security protocols for storing and handling data.
Creating International Data Standards
As the global connectivity of today’s world continues to grow, so does the need for creating international data standards to protect the personal data of individuals. To ensure data is protected and secure, organizations must work in unison to develop and implement data protection regulations across the globe. This means establishing a strong baseline of requirements and best practices, as well as creating a culture of data security awareness and data protection enforcement.
Creating international data standards begins with understanding the risks associated with data breaches. Common risks include: hackers, malware, phishing scams, social engineering, and insider threats. These threats can lead to data loss, financial loss, and identity theft. By understanding the possible vulnerabilities and identifying the weaknesses in organizations’ security systems, organizations can develop effective strategies to prevent data breaches and ensure data is kept secure.
Organizations should also be aware of the cost of a data breach. According to the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million, which is a 6.4% increase from the previous year. The cost of a data breach can include damages for legal fees, customer notification, and credit monitoring. By understanding the financial consequences, organizations can create better data protection policies, procedures, and technologies to help prevent and minimize the cost of a data breach.
Conclusion
Data protection is paramount in our increasingly connected world, and the need for robust and effective regulations to protect user data is paramount. With the implementation of regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, as well as best practices for data protection, businesses, governments, and individuals can take steps to ensure their data is secure and protected.
Technology, education, and businesses must continue to work together to ensure that data remains secure and protected, and that data breaches are prevented. This will help to ensure that the future of data protection is secure and that user data remains safe.