Anti-Spam Protection Explained: How It Works and Why It Matters
Understanding Anti-Spam Protection
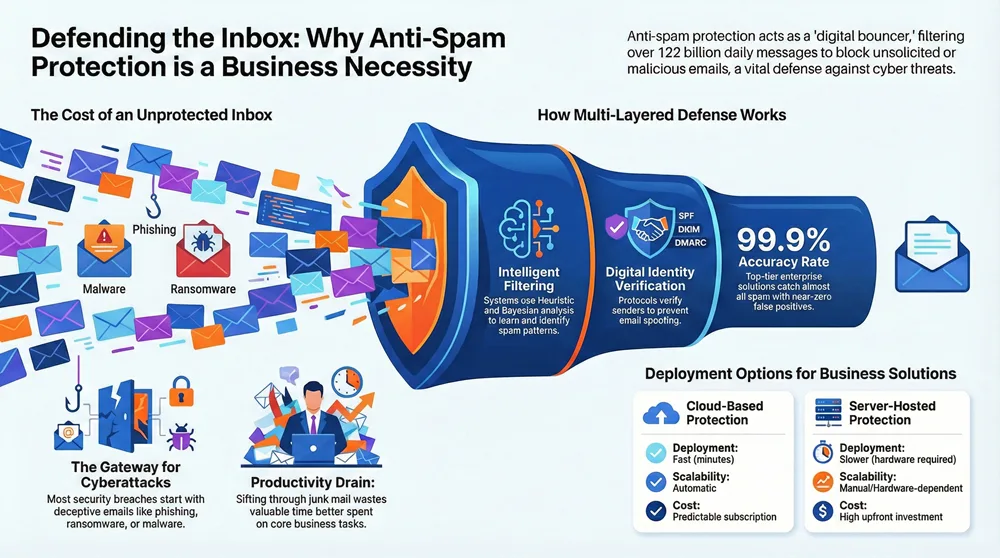
Every day, your inbox faces a barrage of unwanted emails. That’s why anti spam protection is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for any business.
In short, anti-spam protection is any software or system designed to detect, filter, and block unsolicited or malicious emails (spam) before they reach your inbox. Think of it as a digital bouncer for your email.
Spam is more than a nuisance; it’s a massive problem, with over 122 billion spam emails sent daily. These messages can carry serious threats like phishing scams, viruses, and ransomware that can cripple your business.
This guide will break down how anti-spam protection works and why it’s vital for keeping your business safe, productive, and clutter-free.

Why Spam Is More Than Just an Annoyance for Businesses
For businesses, spam is more than inbox clutter. It’s a drain on your team’s time, a killer of productivity, and a wide-open door for serious security risks. Sifting through unwanted emails wastes valuable time that could be spent on core tasks.
More critically, spam is a primary delivery method for damaging cyber threats. The vast majority of security breaches start with a deceptive email. These aren’t just junk mail; they are often sophisticated attacks designed to trick even cautious employees.
Key threats delivered via spam include:
- Phishing: Deceptive emails that trick users into revealing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. They often impersonate trusted entities and may use clever tricks like homographs to make fake websites look real.
- Malware: Malicious software, including viruses, spyware, and ransomware, often delivered through email attachments. A single click can lock down your network or steal sensitive data.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts your files and demands a ransom for their release. Email is a common entry point.
- Data Leaks: The theft of sensitive company information, often initiated through a compromised email account.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Attackers impersonate executives or vendors to trick employees into making fraudulent payments or sharing confidential data.
Understanding these threats is the first step to preventing security breaches. The financial and reputational damage from these attacks can be massive, which is why strong anti spam protection is a critical business defense.
The Role of Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL)
Fighting spam is also a legal battle. Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL), launched in 2014, is one of the world’s toughest laws of its kind. It requires businesses to get consent before sending commercial electronic messages (CEMs).
This consent-based approach has been highly effective. Within a year of CASL’s introduction, spam from Canada dropped by 37%, and Canadians saw 29% fewer emails overall. By 2019, Canada, which once hosted 7 of the world’s top 100 spamming organizations, had none. CASL demonstrates how smart legislation, combined with international cooperation through groups like the Unsolicited Communications Enforcement Network (UCENet), can create a safer digital marketplace. For any business operating in Canada, complying with Canada’s anti-spam legislation (CASL) is essential for building customer trust.
Core Techniques for Effective Anti-Spam Protection
How does anti spam protection work its magic? It uses a combination of sophisticated techniques to identify and neutralize unwanted messages.
Anti-spam software uses filters that analyze incoming messages against a set of criteria. Here are some common techniques:
- Content Filtering: Scans the email’s subject, body, and attachments for suspicious keywords or patterns typical of spam.
- Heuristic Analysis: Looks for spam-like characteristics or behaviors, such as an unusual sender and suspicious links, to understand the message’s intent.
- Rule-Based Filtering: Uses specific “if-then” rules to automatically block or quarantine emails, such as those with dangerous file types or from known spamming IP addresses.
- Bayesian Filtering: A statistical method that learns over time. As you mark emails as spam or not spam, it gets better at calculating the probability that new messages are junk.
- Blacklists and Whitelists: Blacklists are lists of known spammers that are automatically blocked. Whitelists are lists of approved senders that bypass most filters, ensuring important emails are delivered.
- Reputation Checks: Uses global databases to check the sender’s reputation. A poor reputation score can cause an email to be blocked or scrutinized more heavily.
By combining these techniques, anti spam protection builds a multi-layered defense to keep your inbox clean and safe.
The Power of Email Authentication: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Email authentication protocols act as digital IDs to verify who sent an email. The three main protocols are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): An SPF record lists all the mail servers authorized to send email for a domain. If a message comes from an unlisted server, it can be flagged as suspicious.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): Adds a unique digital signature to an email. This signature is verified by the receiving server to ensure the message hasn’t been altered in transit.
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC): Unifies SPF and DKIM. It tells receiving servers what to do if an email fails authentication checks (reject, quarantine, or allow) and sends reports back to the domain owner. This feedback is crucial for spotting spoofing attempts, helping to create a world of less phishing.
Together, these protocols are a powerful defense against email spoofing and a cornerstone of modern anti spam protection.
Understanding Technical Filtering Metrics
Anti-spam systems use several technical metrics to classify emails:
- Message Headers: The hidden “passport” of an email, containing sender information and the path it took. Filters scrutinize headers for forged information or other signs of spam.
- Spam Confidence Level (SCL): A score assigned to an email indicating the likelihood it is spam. A higher score means a higher probability, leading to actions like sending it to junk or quarantine.
- Bulk Complaint Level (BCL): A metric for bulk mail (like newsletters) that measures how likely a sender is to generate complaints. High BCL mail may be treated as spam.
- Zero-hour Auto Purge (ZAP): A feature that can remove malicious messages after they’ve been delivered to an inbox if a new threat is identified. It’s an automatic recall system for phishing and spam.
- High Confidence Phishing: A verdict for messages that are almost certainly phishing attempts. These are handled with maximum security, typically being quarantined without user access.
- Quarantine Policies: Rules that define how flagged emails are managed in a secure holding area. Policies determine who can review messages and how long they are held.
Choosing the Right Anti-Spam Solution
Choosing the right anti spam protection is crucial for safeguarding your operation. You need a solution that is reliable, smart, and always on guard. Here’s what to look for:
- High Accuracy Rate: Look for a solution that catches over 99% of spam. Top solutions boast over 99.9% accuracy.
- Low False Positives: A great solution won’t block legitimate emails. The best have a false positive rate near 0.0001%.
- Granular Policy Control: You need the ability to fine-tune settings and create custom rules for different users or departments.
- User-Friendly Management: The system should be easy for administrators to set up and for users to manage their own settings.
- Comprehensive Threat Protection: It must protect against malware, ransomware, phishing, and Business Email Compromise (BEC).
- Reporting and Analytics: Good reporting provides insight into blocked threats and helps you refine your security policies.
- Business Continuity: Features like email caching ensure you receive emails even if your primary server is down.
Personal vs. Enterprise-Level Solutions
Anti spam protection needs differ for individuals and businesses. Personal solutions are great for decluttering a home inbox, offering simple rules and safe sender lists.
Enterprise-Level Solutions are built to protect entire organizations. They offer:
- Scalability: Handle massive email volume and grow with your business.
- Advanced Threat Protection: Fight sophisticated attacks like targeted phishing, BEC, and zero-day threats using sandboxing and link rewriting.
- Compliance Features: Include tools like Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and email archiving to meet legal and industry regulations.
- Centralized Management: A single dashboard to control security for all mailboxes and generate detailed reports.
For small and mid-sized businesses, an enterprise-level solution is essential for protecting critical data and ensuring smooth operations.
Cloud-Based vs. Server-Hosted Filters
Another key decision is whether to host your filter in the cloud or on your own server.
| Feature | Cloud-Based Anti-Spam Protection | Server-Hosted Anti-Spam Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Fast setup, often in minutes. | Slower; requires hardware and software installation. |
| Maintenance | Handled by the provider. | Your IT team is responsible for all updates and fixes. |
| Scalability | Scales automatically with your needs. | Requires purchasing more hardware and licenses to scale. |
| Accessibility | Access from anywhere with an internet connection. | Typically accessed only from the company network. |
| Cost | Predictable subscription fees; lower upfront cost. | High upfront cost for hardware/software, plus ongoing maintenance. |
| Updates | Automatic and continuous security updates. | Manual updates that may require downtime. |
| Control | High-level policy control via a web portal. | Full control over hardware, software, and data. |
| Traffic Flow | Email is filtered in the cloud before reaching your network. | Email is filtered on your own equipment. |
For most businesses, cloud-based anti spam protection is easier to manage, more scalable, and reduces the burden on IT teams.
Free vs. Paid Software: Benefits and Drawbacks
Should you use a free or paid solution? While free is tempting, it often comes with limitations for businesses.
- Free Solutions: The main benefit is the cost. They provide basic filtering but often have limited features, no dedicated support, and lack the granular control a business needs. They may not catch sophisticated threats like targeted phishing.
- Paid Solutions: These offer advanced, multi-layered defense against a wide range of threats. They provide high accuracy, low false positives, dedicated support, and comprehensive reporting. Many include crucial business features like data loss prevention (DLP) and email archiving. The investment in a paid solution is often justified by the improved security and peace of mind it provides.
Best Practices for Users and Administrators
Effective anti spam protection requires both the right software and a culture of security awareness. It’s a team effort where users and administrators work together.
Your employees are your first line of defense. Empowering them with knowledge is key.
- Recognize phishing attempts: Teach teams to spot suspicious sender addresses, poor grammar, urgent language, and unexpected requests for personal information.
- Avoid suspicious links and attachments: Encourage a “think before you click” mindset. Verify unexpected links or attachments, even from known senders, with a quick call or message.
- Use strong password practices: Password managers can help enforce strong, unique passwords. Explain the risks of auto-complete passwords to highlight the importance of careful management.
- Be aware of Business Email Compromise (BEC): Educate employees on how attackers impersonate executives or vendors. Understanding the tactics of different types of hackers helps them stay vigilant.
- Report suspicious emails: Using the “report spam” or “report phishing” button helps train the filter for everyone, improving collective security.
How to Report Spam and Contribute to a Safer Internet
Reporting spam helps protect everyone. Most email clients like Outlook and Gmail have built-in “Report Spam” buttons that feed data back to improve global filters.
For more serious threats like phishing or financial scams, report them to the proper authorities. In Canada, for example, users can file a complaint with the Spam Reporting Centre. Every report helps authorities identify spammers and build cases against them.
Configuring Your Anti-Spam Protection Policies
For IT administrators, effective anti spam protection is an ongoing process of optimization.
- Set appropriate filtering levels: Balance security with usability, applying stricter policies for high-risk users and more lenient ones where needed.
- Manage allow and block lists: Use whitelists and blacklists to gain precise control over email flow, but use whitelists judiciously as they can bypass security checks.
- Customize quarantine management: Define how long quarantined messages are held and who can release them. High-confidence phishing should generally remain administrator-only.
- Provide ongoing user education: Regularly update staff on new threats and security best practices.
- Review and adjust policies regularly: The threat landscape is always changing. Review filter logs and adjust policies monthly to keep your defenses optimized.
Frequently Asked Questions about Anti-Spam Protection
Here are answers to some common questions about anti spam protection.
What is the most effective anti-spam technique?
There is no single most effective technique. The best strategy is a multi-layered approach that combines technical filters (like content analysis and email authentication with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC), robust software, and continuous user education. When these elements work together, they provide the strongest defense.
Can I completely turn off anti-spam filtering?
Generally, no. Most professional email systems like Microsoft 365 use a "secure by default" approach and do not allow you to completely disable anti spam protection. This is a critical safety measure, especially for blocking high-confidence phishing attempts that pose a significant risk to your business.
How does anti-spam protection work on mobile devices?
Your mobile devices are protected primarily through server-side filtering. Your email provider filters out most spam and threats before the messages are ever downloaded to your phone. Additionally, some dedicated mobile apps offer on-device filtering and management, giving you more control over your inbox on the go.
Conclusion
In an age where inboxes are constantly under siege, robust anti spam protection is a fundamental pillar of modern cybersecurity. As we’ve seen, spam poses significant risks to your productivity, data integrity, and overall business security.
The fight against spam is powered by evolving technology—from smart filters like heuristic analysis to authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. When combined with strong legislation and user vigilance, these tools create a formidable defense.
Choosing the right solution means prioritizing a high accuracy rate, low false positives, and comprehensive threat protection. The goal is to implement a system that keeps your digital communications clean, secure, and efficient. Don’t let spam be the weakest link in your security chain.
Ready to take a proactive step toward a more secure and less cluttered inbox? We invite you to learn more about how we can support your business’s digital security needs. Explore our complete email security solutions today and find out how easy it can be to protect your organization.