10 Essential Document Management System Best Practices for 2025
AI Overview:
This blog outlines 10 essential document management system (DMS) best practices to help organizations eliminate digital chaos, reduce security and compliance risks, and improve productivity. It covers critical areas such as access controls, metadata and classification, workflow automation, version control, backup and disaster recovery, advanced search, governance, system integrations, quality monitoring, and user adoption. Together, these practices transform document management from basic file storage into a secure, efficient, and compliant information lifecycle that supports operational excellence and long-term business growth.
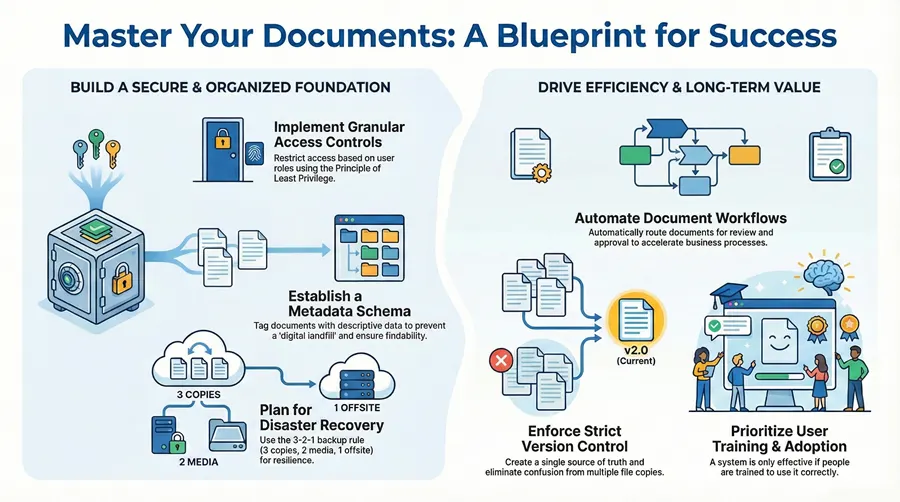
Disorganized digital files create significant business risks, from wasted productivity and security vulnerabilities to costly compliance violations. Without a structured approach, teams struggle to find critical information, slowing down decision-making and hindering growth. This guide provides a clear, actionable blueprint of 10 essential document management system best practices designed to transform your chaotic digital files into a secure, efficient, and valuable corporate asset.
Following these proven methods will help you establish a robust framework that ensures security, improves operational efficiency, and maintains unwavering compliance. From implementing granular access controls to automating critical workflows, these strategies will empower your team with immediate access to the right information at the right time. Let’s explore the concrete steps you can take to streamline operations, mitigate risk, and unlock the full potential of your digital assets.
1. Implement Robust Access Control and Permissions Management
Establishing granular user roles and permissions is the cornerstone of a secure document management system (DMS). This foundational practice ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized personnel, directly preventing data breaches and compliance failures. By defining who can view, edit, or delete specific documents, organizations create a secure framework that protects intellectual property and customer data.
For industries governed by regulations like HIPAA or GDPR, this control is non-negotiable. A healthcare provider, for example, can configure its DMS to grant doctors read/write access to patient records within their department, while billing staff have read-only access to specific financial sections. This role-based security is a critical component of data protection.

How to Implement Effective Access Controls
To successfully integrate this practice, adopt the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), which dictates that users should only be granted the minimum access necessary to perform their jobs. This simple rule dramatically reduces your organization’s security risk profile.
Follow these actionable steps for a robust implementation:
- Define User Roles: Group users based on job function (e.g., “HR Manager,” “Sales Associate”). Document the specific permissions associated with each role to ensure clarity and consistency.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule quarterly access reviews to remove permissions for former employees or users who have changed roles. This mitigates the risk of “privilege creep.”
- Test Permission Scenarios: Before going live, create test user accounts for different roles and attempt to access documents they shouldn’t be able to. This validates your security configuration.
- Monitor Access Logs: Regularly review DMS audit trails to track who accesses sensitive files. Unusual activity can be an early indicator of a potential security threat. Exploring robust access management solutions can provide automated monitoring.
2. Establish a Comprehensive Document Classification and Metadata Schema
Creating a standardized system for categorizing and tagging documents is essential for transforming a simple storage folder into a powerful, intelligent repository. A comprehensive metadata schema provides the descriptive data (e.g., author, date, project code) that makes each document instantly findable. This practice is foundational to enabling quick retrieval, supporting compliance, and facilitating automation.
This methodical approach unlocks tremendous efficiency. A legal firm can classify documents by case number and document type (“Pleading,” “Contract”), allowing attorneys to locate critical files in seconds. Similarly, a manufacturing company can tag engineering drawings with a product line and version number, ensuring teams always work from the most current specifications. Without this structure, a DMS quickly becomes a chaotic “digital landfill.”
How to Implement an Effective Metadata Schema
A successful metadata strategy should be detailed enough to be useful but simple enough for consistent user adoption. Ensuring all physical documents are properly digitized and tagged from the start is key; professional bulk scanning services can establish a clean, organized foundation.
Follow these actionable steps for a robust implementation:
- Start with a Core Schema: Begin by defining essential metadata fields like “Document Type,” “Creation Date,” and “Department.” Expand this schema with department-specific fields over time.
- Leverage Automation: Use your DMS’s capabilities for auto-tagging and AI-powered metadata extraction. This reduces manual entry and ensures consistency across the system.
- Create a Governance Plan: Designate an owner to manage the metadata dictionary. This ensures that new tags are added thoughtfully and that the schema remains clean and logical.
- Provide Clear Guidelines: Develop and share a simple guide with examples showing users how to classify and tag common document types to drive user adoption and maintain data quality.
3. Implement Automated Document Workflows and Approvals
Designing and deploying automated workflows turns a static document repository into a dynamic business asset. This practice involves creating predefined digital pathways that automatically route documents for review, approval, or action. It drastically reduces manual hand-offs, accelerates business cycles, and creates a transparent, auditable trail for every document-centric process.
This is essential for operations where speed and accuracy are paramount. For example, a corporate finance department can use automated workflows to manage expense report approvals, ensuring policy compliance and timely reimbursements without endless email chains. The process becomes faster, more transparent, and less prone to human error.
How to Implement Effective Document Workflows
To successfully integrate workflow automation, begin with high-impact, low-complexity processes. This approach allows you to demonstrate value quickly and build momentum for broader adoption across the organization.
Follow these actionable steps for a structured implementation:
- Map Current Processes: Before automating, visually map out your existing manual workflow. Identify every step, decision point, and stakeholder to pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Start with Repeatable Tasks: Target high-volume, rule-based processes for your initial automation efforts. Common examples include invoice processing or new-hire onboarding paperwork.
- Include Exception Handling: Build mechanisms into your workflow for handling exceptions, such as routing a document to a senior manager for an override if it requires special attention.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like average cycle time and approval rates. Use this data to identify areas for further optimization and refine your processes.
4. Ensure Version Control and Document Lifecycle Management
Implementing systematic version control is critical for maintaining document integrity and preventing costly errors that arise from using outdated information. This practice tracks every revision, creating a complete audit trail and ensuring that all stakeholders are working from the most current and approved version. It eliminates the confusion of multiple file copies and provides a single source of truth.
This process is indispensable for collaborative environments. For instance, a legal firm managing contract negotiations can track every redline and comment, with the ability to revert to any previous draft. Similarly, an engineering firm can manage complex design documents, ensuring that construction teams always build from the latest approved blueprints. This prevents rework and maintains compliance.
How to Implement Effective Version Control
To successfully integrate this practice, establish clear and consistent procedures that your team can easily follow. The goal is to make versioning an automatic, seamless part of the workflow rather than a manual chore.
Follow these actionable steps for a robust implementation:
- Define Versioning Policies: Create a clear convention for version numbering (e.g., v1.0 for major releases, v1.1 for minor revisions). Document when a new version should be created.
- Utilize Check-In/Check-Out: Train users on the check-in/check-out feature. This “locks” a document when someone is editing it, preventing conflicting changes from being made simultaneously.
- Enforce Descriptive Comments: Require users to add a brief comment when checking in a new version (e.g., “Updated Section 3 with new financial data”). This provides crucial context for the document’s history.
- Automate Archival: Configure your DMS to automatically archive older versions when a new one is approved. This keeps the active workspace clean while retaining historical versions for compliance.
5. Establish Data Backup, Disaster Recovery, and Business Continuity Plans
Developing a comprehensive strategy for data backup and disaster recovery is critical for safeguarding your organization’s digital assets. This practice ensures that in the event of a system failure, cyberattack, or natural disaster, your critical documents remain accessible and secure. A robust plan minimizes downtime, prevents data loss, and provides a clear roadmap for restoring operations.
This proactive approach is essential for maintaining business continuity. A financial services firm can leverage a 3-2-1 backup strategy (three copies of data on two different media types, with one copy offsite) to protect sensitive client information against ransomware attacks. Similarly, a healthcare provider can use compliant cloud backup solutions to ensure patient data is recoverable in a HIPAA-compliant manner.
How to Implement Effective Backup and Recovery Plans
To build a resilient document management environment, you must define your tolerance for data loss and downtime. Establish clear Recovery Point Objectives (RPO), which define the maximum acceptable data loss, and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO), which specify the maximum time allowed to restore business functions.
Follow these actionable steps for a solid implementation:
- Implement the 3-2-1 Backup Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different media types (e.g., local disk and cloud), and keep one copy offsite.
- Test Recovery Procedures Annually: Regularly conduct drills to simulate a disaster scenario. This practice validates your recovery plan and ensures your team can execute the procedures under pressure.
- Define and Document Everything: Clearly document the entire recovery process, including contact information for key personnel and step-by-step restoration guides. Make this accessible offline.
- Encrypt All Backups: Protect your backed-up data both in transit and at rest. Encryption is a non-negotiable step to prevent unauthorized access to your backup files. Building a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy plan is the first step toward true organizational resilience.
6. Implement Full-Text Search and Advanced Retrieval Capabilities
Deploying sophisticated search functionality is critical for transforming a static document repository into a dynamic knowledge base. This practice enables users to instantly locate information by searching not just metadata, but the entire content of every document. By leveraging full-text search and optical character recognition (OCR) for scanned files, organizations dramatically reduce time wasted searching for information.
This capability is indispensable in data-intensive environments. A legal firm can use it for e-discovery, sifting through millions of case files for specific keywords in seconds. Similarly, a compliance department can quickly locate all documents pertaining to a specific regulation. Without advanced retrieval, documents are effectively lost, rendering the DMS little more than a disorganized digital filing cabinet.
How to Implement Effective Search Capabilities
To make advanced retrieval one of your core document management system best practices, focus on building a comprehensive and user-friendly search experience. The goal is to make finding information as intuitive as a web search engine.
Follow these actionable steps for a powerful implementation:
- Create a Comprehensive Indexing Strategy: Ensure your DMS indexes the full text of all documents upon ingestion, including running OCR on all scanned images and PDFs.
- Utilize Filters and Facets: Implement search filters based on metadata (e.g., date, author) to allow users to narrow down thousands of results to a handful of relevant files quickly.
- Test OCR Quality: Before full deployment, process a diverse sample of your typical scanned documents to verify the accuracy of the OCR engine. Poor quality OCR leads to unreliable search results.
- Provide User Training: Teach users how to use advanced search syntax, such as Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and phrase searching with quotation marks, to execute more precise queries.
7. Establish Document Governance and Compliance Frameworks
Implementing a formal governance and compliance framework moves your document management from a simple storage tool to a strategic business asset. This practice involves creating clear policies and procedures to ensure all document handling aligns with legal, regulatory, and internal business requirements. It systematically reduces legal and financial risks and demonstrates due diligence to auditors.
This framework is critical for organizations operating under strict regulatory scrutiny. A financial institution can use its DMS to enforce SEC document retention rules, ensuring client communications are archived for the required period. Similarly, a public company can adhere to SOX requirements for financial record integrity and accessibility.
How to Implement a Governance and Compliance Framework
To build this into your document management system best practices, take a systematic approach. Start by conducting a comprehensive audit of all current document handling processes to identify gaps between your practices and your obligations.
Follow these actionable steps for a robust implementation:
- Map Regulatory Requirements: Identify all applicable regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA) and map them to specific document types and internal policies.
- Create Clear Retention Schedules: Define and automate retention and disposition schedules for every document category. This prevents the premature deletion of critical records.
- Implement Legal Hold Procedures: Configure a mechanism to place an immediate “legal hold” on relevant documents in the event of litigation, preserving evidence.
- Train and Enforce: Conduct mandatory training for all users on the governance policies and their responsibilities. Clearly communicate the consequences of non-compliance.
8. Integrate with Enterprise Systems and Workflow Applications
Connecting your document management system with other core business platforms like CRM, ERP, and HR systems transforms it from a static repository into a dynamic component of your operational ecosystem. This integration creates a single source of truth, eliminates data silos, and automates manual data entry. By ensuring a seamless information flow, organizations can significantly boost efficiency and reduce errors.
This practice is essential for creating a cohesive technology stack. For instance, a sales team can automatically save and retrieve client contracts directly from their CRM record, eliminating the need to switch between applications. An accounting department using an ERP can link vendor invoices stored in the DMS directly to purchase orders, accelerating approval cycles.
How to Implement Effective System Integrations
To make this one of your most impactful document management system best practices, approach integration strategically. Start by identifying the most critical points of data exchange that will deliver the highest immediate value in terms of time savings.
Follow these actionable steps for a successful integration strategy:
- Prioritize High-Value Integrations: Begin by connecting systems where data bottlenecks are most common, such as linking your CRM to contract storage or your ERP to invoice management.
- Use APIs and Standard Connectors: Leverage the native Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provided by your DMS and other enterprise software. Pre-built connectors can simplify the process.
- Document All Data Flows: Create a clear map of how information moves between systems. Document which system is the master record and the triggers for data synchronization.
- Conduct Thorough End-to-End Testing: Before deployment, rigorously test the entire workflow. For example, create a new client in the CRM and ensure the associated contract automatically appears correctly filed in the DMS.
9. Monitor, Audit, and Maintain Document Quality Standards
Implementing a document management system is an ongoing commitment to information integrity. Establishing procedures for continuous monitoring, auditing, and maintenance ensures that documents remain accurate, current, and compliant. This proactive practice prevents “information decay” and solidifies the reliability of your organization’s most critical information assets.
This approach is vital for organizations where document accuracy is directly tied to operational success. A manufacturing firm must regularly audit its technical schematics to ensure production lines are using the most current versions, preventing costly errors. Similarly, a bank must conduct quarterly audits of its customer loan files to verify completeness and accuracy, meeting strict financial regulations.
How to Implement Effective Quality Monitoring
To integrate this as one of your core document management system best practices, focus on creating a sustainable cycle of review and improvement. This moves your DMS from a simple storage tool to a dynamic, trustworthy information hub.
Follow these actionable steps for a robust implementation:
- Define Quality Metrics: Establish clear, measurable standards for your documents. This could include metadata completeness, version control adherence, or naming convention accuracy.
- Schedule Regular Audits: Implement a calendar for both automated and manual audits. Automated checks can flag missing metadata, while manual spot-checks can assess content relevance.
- Utilize Quality Dashboards: Create and monitor dashboards that display key quality trends over time. This visual representation helps identify systemic issues.
- Analyze and Address Root Causes: When audits reveal quality issues, investigate the underlying cause. Is it a lack of training or a confusing workflow? Use these findings to refine your processes.
10. Implement User Training, Change Management, and Adoption Programs
Even the most advanced document management system will fail if users don’t know how to use it. A structured training and change management program is crucial for bridging the gap between technology and people. This practice focuses on the human element, ensuring employees feel competent and confident with the new system, which directly drives user adoption and maximizes your return on investment.
This approach is vital for any organization undergoing a digital transformation. For instance, a healthcare system transitioning to electronic records must train clinical staff not just on the software, but on how the new workflows support patient care and compliance. Without this focus on people, even the best technology will underperform.
How to Implement Effective Training and Adoption
A proactive and well-planned change management strategy is non-negotiable for a successful DMS rollout. This requires a sustained effort to build proficiency and enthusiasm among your team.
Follow these actionable steps for a smooth transition:
- Tailor Training to Roles: Develop unique training modules for different user groups. An executive assistant needs different skills than a project engineer. Create content that addresses their daily tasks.
- Identify and Empower Champions: Select enthusiastic employees from various departments to act as “superusers.” Train them first and empower them to provide peer-to-peer support.
- Use Multiple Training Formats: Cater to different learning styles by offering a mix of instructor-led sessions, video tutorials, and quick-reference guides.
- Gather Feedback and Iterate: After the initial training, actively solicit feedback through surveys. Use this input to refine your training materials and address common pain points.
Build Your Foundation for Document Management Excellence
Moving from scattered files to a structured document management system (DMS) is a transformational journey. We’ve explored ten essential document management system best practices that serve as building blocks for a more resilient, efficient, and secure operational framework for your entire organization. Adopting these practices is a strategic imperative to change how your organization interacts with its most vital asset: information.
By shifting from a reactive “find the file” mentality to a proactive “manage the information lifecycle” approach, you unlock significant competitive advantages. Your teams spend less time searching and more time executing, operational friction decreases, and institutional knowledge becomes a reliable, accessible resource.
From Knowledge to Action
The journey to optimizing your document management begins with a single step. Use this guide as a roadmap to assess your current state and identify your most pressing priorities. Where are your biggest pain points? Is it security risk, inefficient manual processes, or simply the daily frustration of teams being unable to locate critical information?
Key Insight: The most successful DMS implementations are iterative. Focus on solving one or two high-impact problems first, such as securing HR documents or automating your accounts payable workflow. Early wins build momentum and demonstrate the value of these best practices.
Mastering these principles is about building an organization that is agile, informed, and secure. It’s about empowering your employees with the right information at the right time and creating a scalable foundation that will support your business as it grows. By committing to these practices, you are investing directly in your company’s operational excellence and long-term success.
Ready to transform your document management strategy from a challenge into a competitive advantage? For over 40 years, 1-800 Office Solutions has been the trusted partner for businesses across all 50 states, implementing secure, compliant, and efficient document solutions. Our experts specialize in designing and deploying tailored DMS and managed IT services that modernize operations and protect your critical data.











