A Business Leader’s Guide to IT Security Solutions
Protecting your business from digital threats is no longer optional—it’s a fundamental requirement for survival and growth. Robust IT security solutions for business are not just defensive measures; they are strategic assets that build customer trust, ensure operational continuity, and secure your competitive advantage. This guide provides a clear, practical roadmap for business leaders, cutting through technical jargon to focus on what truly matters for protecting your organization.
Building Your Digital Fortress Against Modern Threats

Whether you are a startup or a global enterprise, your business possesses a digital footprint vulnerable to a wide array of threats. From sophisticated ransomware that can halt your operations to clever phishing scams designed to steal sensitive credentials, the risks are significant and persistent. Ignoring these threats is a direct invitation to operational and financial disruption.
A recent report highlighted a critical internal vulnerability: a staggering 69% of employees admitted to bypassing their company’s cybersecurity protocols. This statistic alone underscores why a robust security framework is your most essential line of defense.
Transforming security from a simple cost center into a core business advantage begins with understanding what you’re up against. The primary goal is to build a layered defense—a digital fortress—that protects your most valuable assets. This involves safeguarding:
- Your Data: Preventing unauthorized access to customer lists, intellectual property, and financial records.
- Your Operations: Ensuring business continuity by fending off disruptions like ransomware and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Your Reputation: Maintaining the trust of your clients and partners by demonstrating a serious commitment to data protection.
Creating a Proactive Defense Strategy
An effective security strategy does not wait for an attack to occur; it anticipates threats and neutralizes them before they can cause harm. This is especially true for businesses leveraging cloud infrastructure. For instance, implementing robust AWS security best practices is a non-negotiable first step in building a resilient digital fortress.
The fundamental objective is to make your organization a difficult and unappealing target. This is achieved by blending the right technology with smart, well-defined processes and, crucially, an educated team.
By understanding the key components of a complete security plan, you can begin making informed decisions that will secure your company’s future. It starts with identifying common threats and recognizing how the right security framework can serve as the foundation for long-term success. This guide will provide the insights you need, covering everything from foundational tools to advanced strategies for cybersecurity in the modern office.
Understanding Your Core Security Defenses
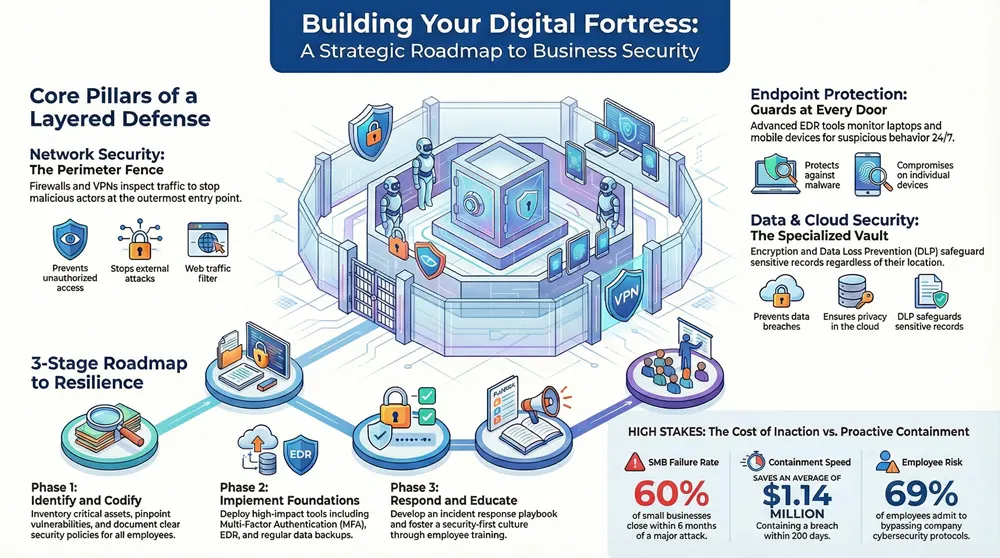
Effective it security solutions for business are not about a single magic bullet. It’s about constructing a layered defense.
Consider how you would secure a physical building. You would not simply lock the front door. You would likely install a perimeter fence, security cameras, and access controls at every entrance. Each layer serves a specific purpose, and together, they create a formidable barrier.
The same principle applies in the digital world. Each of your core security defenses is designed to protect a different part of your business, from the network that connects everything to the laptops and mobile devices your team uses daily. Understanding how these components fit together is the first step toward building a security posture that can withstand an attack.
The Perimeter Fence: Network Security
Network security is your outermost layer of defense, acting as a digital perimeter for your entire operation. Its primary purpose is to inspect all incoming and outgoing traffic, stopping malicious actors before they can access your valuable data. This is your first line of defense.
The foundation of any good network security setup is the firewall. Modern firewalls do much more than just block unauthorized connections. They analyze the content of traffic to identify and neutralize threats that may be hidden within seemingly normal data. They are the vigilant gatekeepers ensuring only safe, approved traffic gets through.
Another key component is the Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your remote employees to access company resources. This means that even if your team is working from a public Wi-Fi network, their connection remains private and shielded from eavesdroppers.
The Guards at Every Door: Endpoint Protection
While network security protects the perimeter, endpoint protection secures every individual entry point. Endpoints include all the “doors and windows” to your organization—laptops, desktops, servers, and smartphones. Each one is a potential weak point that an attacker could exploit.
Traditional antivirus software is no longer sufficient. Today’s threats require advanced solutions like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). EDR tools don’t just block known viruses; they continuously monitor device activity, looking for suspicious behavior that could indicate a sophisticated attack. These systems are a core part of https://1800officesolutions.com/real-time-threat-detection/, providing 24/7 visibility into your devices.
Endpoint protection is critical because it addresses the human element of security. It is your last line of defense when an employee accidentally clicks a malicious link or downloads an infected file.
A key part of securing endpoints is controlling who gains access. This requires strong identity and access management (IAM) policies to ensure only authorized individuals can log in and access sensitive information. A crucial step often involves implementing solutions like Okta for robust identity and access management, which helps secure credentials and enforce user permissions.
Specialized Vaults: Data and Cloud Security
Your most valuable assets—customer data, financial records, and intellectual property—require specialized protection, much like a bank vault. This is where data and cloud security solutions are essential. These tools are focused on protecting the information itself, regardless of where it is stored or who is trying to access it.
Key technologies in this area include:
- Data Encryption: This process scrambles your data, making it unreadable to anyone without the specific decryption key. It protects information whether it is stored on a server (“at rest”) or being transmitted across the network (“in transit”).
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools act as a watchdog, monitoring for sensitive data attempting to leave your network. They can detect and block unauthorized data transfers, preventing both accidental leaks and deliberate theft.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): With many businesses relying on cloud applications like Office 365 or Salesforce, CASBs have become indispensable. They sit between your users and cloud services, acting as a security checkpoint to enforce policies and maintain compliance.
This vault-like approach is particularly vital for smaller businesses, which have become a prime target for cybercriminals. In fact, SMB spending on IT security is projected to hit $109 billion by 2026. This is not just a trend; it is a survival tactic. A staggering 60% of small businesses that suffer a major cyberattack go out of business within six months, making these defenses non-negotiable.
To provide a clearer picture, here is how these security layers map to the business problems they solve.
Key IT Security Solutions and Their Business Purpose
This table offers a quick reference for the major categories of security solutions and their business functions.
| Solution Category | Primary Function | Business Problem Solved |
|---|---|---|
| Network Security | Controls and monitors traffic into and out of the network | Prevents unauthorized access and external attacks |
| Endpoint Protection | Secures individual devices like laptops and servers | Protects against malware and compromises on devices |
| Cloud Security | Secures data and applications in cloud environments | Manages risks associated with cloud service usage |
| Data Security | Protects data from unauthorized access and exfiltration | Prevents data breaches and ensures data privacy |
| Identity & Access | Manages user identities and access permissions | Ensures only authorized users can access resources |
By layering these core defenses, you are not just purchasing tools; you are building a comprehensive security framework that protects your business from multiple angles.
Choosing Your Security Management Model

Once you have identified the essential it security solutions for your business, you face a critical decision: who will manage them? This is the classic “build vs. buy” dilemma. Do you invest in building an in-house security team, or do you partner with a specialized firm to manage security for you?
There is no single correct answer. Each path significantly impacts your budget, your team’s focus, and your overall security posture. The best choice depends on your company’s size, complexity, and long-term goals. This decision is just as critical as selecting the security tools themselves.
The In-House Approach: Building Your Own Team
Building your own security operations center (SOC) provides the ultimate control. Your internal team will have deep knowledge of your network, workflows, and unique risks. This allows for tight integration of security into business operations and, in theory, rapid response to internal threats.
However, the “build” option is a massive financial and operational commitment. The costs extend far beyond salaries.
- Talent Acquisition: The cybersecurity skills shortage is a significant challenge. Finding, hiring, and retaining qualified security professionals is highly competitive and expensive.
- Continuous Training: The threat environment evolves daily. Your team requires ongoing training, certifications, and professional development to stay current, representing a permanent budget item.
- Technology Investment: An effective SOC requires sophisticated tools for threat intelligence, log management (SIEM), and incident response. These platforms have high licensing fees and require expertise to configure and maintain.
- 24/7/365 Coverage: Cyberattacks do not adhere to business hours. True round-the-clock protection requires staffing at least three shifts, which can triple personnel costs and add management complexity.
This approach is typically feasible only for large enterprises with the financial resources and operational scale to justify such a substantial, ongoing investment. For most small to mid-sized businesses, the cost and complexity are prohibitive.
The Outsourced Model: Partnering with an MSSP
The alternative is to “buy” expertise by partnering with a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP). An MSSP acts as your outsourced security department. For a predictable subscription fee, you gain access to a team of experts and their entire suite of advanced security tools. This allows you to achieve a level of security maturity that might otherwise take years and significant capital to build independently.
Partnering with an MSSP provides access to a world-class security team and enterprise-grade technology for a fraction of the cost of building it from scratch. It is a model that makes high-end security accessible to companies of all sizes.
The benefits of using an MSSP are compelling, particularly for businesses without in-house security experts or the resources to build a team.
- Instant Expertise: You immediately gain access to a team of seasoned professionals who manage threats daily across various industries and attack vectors.
- Predictable Costs: A fixed monthly or annual fee simplifies budgeting and typically results in a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to an in-house team.
- Enterprise-Grade Technology: MSSPs utilize best-in-class security platforms that are often too expensive for a single company to purchase and manage.
- Focus on Core Business: Outsourcing security frees your internal IT team to concentrate on strategic projects that drive business growth, rather than being consumed by security alerts.
Working with an MSSP leverages economies of scale. Because they serve numerous clients, they can invest in top-tier talent and technology, distributing the cost and passing the benefits to you. For most businesses, this model provides a practical path to implementing robust it security solutions for business without the overwhelming cost and operational burden of a DIY approach.
How To Build Your Business Security Roadmap
Effective security is not an off-the-shelf product; it is a strategic, continuous process. A strong defense is built upon a deliberate plan—a security roadmap. This roadmap guides your security approach from reactive to proactive, ensuring every dollar spent on IT security solutions for business is targeted and effective.
Developing this roadmap begins with a thorough and honest self-assessment. You cannot protect what you do not understand. The first and most critical stage is a comprehensive risk assessment to gain a clear picture of your current security posture.
Stage 1: Identify Your Assets and Vulnerabilities
Before building a fortress, you must map the terrain—identifying what you need to protect and where your defenses are weakest. This initial phase is about discovery. The goal is to create a detailed inventory of your critical assets and pinpoint the vulnerabilities that expose them to risk.
Start by cataloging key assets:
- Data: Customer lists, intellectual property, financial records, and employee information.
- Systems: Core applications, servers, cloud infrastructure, and databases.
- People: Key personnel, executives, and individuals with privileged system access.
Once you know what is valuable, you can identify weaknesses, such as unpatched software, inadequate access controls, or gaps in your network security. This process provides the foundational knowledge to prioritize your efforts for maximum impact.
Stage 2: Define Clear Security Policies
With a firm grasp of your risks, the next step is to establish clear rules. Security policies are the documented guidelines that define acceptable behavior and security practices for your entire organization. They serve as the constitution for your security program, ensuring everyone understands their role in protecting the company.
These policies must be clear, enforceable, and communicated to every employee. Essential policies include:
- Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Outlines the rules for using company technology and data.
- Access Control Policy: Defines who has access to what information and under what circumstances.
- Incident Response Policy: Provides a step-by-step plan for responding to a security incident.
These policies act as guardrails, creating consistency and eliminating guesswork, which is vital for building a strong security culture.
Stage 3: Implement Foundational Technologies
Now you can begin deploying the right tools for the job. Guided by your risk assessment, you can strategically implement IT security solutions for business that directly address your most significant vulnerabilities. The goal is to create layers of defense, making it more difficult for an attacker to succeed.
Focus on the fundamentals first:
- Endpoint Protection: Deploy modern Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) on all company devices.
- Access Control: Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across all critical applications without exception.
- Data Backup: Implement a robust backup and disaster recovery solution and test it regularly.
This infographic compares the two most common approaches to managing these technologies.
The choice between an in-house team and an expert provider is a major decision with significant trade-offs to consider during implementation.
Stage 4: Develop an Incident Response Plan
No defense is perfect. It is not a matter of if a security incident will occur, but when. An incident response (IR) plan is your playbook for that crisis. It is designed to minimize damage, reduce recovery time, and maintain business operations. A well-rehearsed plan is a powerful tool for resilience.
A strong incident response plan is the difference between a manageable event and a business-ending catastrophe. It ensures a calm, coordinated, and effective reaction when the pressure is highest.
The importance of a swift response cannot be overstated. In a recent year, there were over 3,100 data compromises in the U.S. alone. Organizations that identified and contained those breaches within 200 days spent an average of $3.87 million, a significant saving compared to the $5.01 million spent by companies with slower response times. You can discover more insights about the financial impact of data breaches on bluefire-redteam.com.
Stage 5: Foster a Security-First Culture
Ultimately, technology and policies are only as effective as the people who use them. The final and most crucial stage of your roadmap is to build a security-first culture through ongoing employee training and awareness. Your team is your first and last line of defense.
Regular training should cover real-world threats like identifying phishing emails, creating strong passwords, and understanding their responsibilities under your security policies. When every employee views themselves as part of the security team, your entire organization becomes exponentially safer. This continuous effort transforms your roadmap from a static document into a living part of your business culture.
Effective security is not just about defending against cyberattacks. Your IT security solutions for business are also essential for complying with legal and industry regulations. These rules exist to protect sensitive data and hold businesses accountable. Failure to comply can result in crippling fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
For example, a healthcare clinic handling patient records is bound by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). A retail business processing credit card payments must adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). These are not suggestions—they are mandatory requirements.
Connecting Security Solutions to Compliance
The good news is that the tools you implement to protect your business are the same ones that help you achieve compliance. Security and compliance should not be viewed as separate initiatives. Instead, see compliance as a natural outcome of a solid security strategy. Every regulation has specific requirements that map directly to security controls.
The connection is logical:
- Encryption and GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires strong protection for the personal data of EU citizens. Encryption for data at rest and in transit is a fundamental control that renders stolen data useless to thieves.
- Access Controls and HIPAA: HIPAA mandates strict control over who can access Protected Health Information (PHI). Solutions like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) are essential for ensuring only authorized personnel can view or modify patient records.
- Network Security and PCI DSS: To protect credit card data, PCI DSS requires a secure network. This includes robust firewalls, secure configurations, and continuous monitoring of network traffic for suspicious activity.
Compliance is not a one-time checkbox. It is a continuous commitment to protecting customer and partner data, turning a potential risk into a competitive advantage.
A Framework for Compliance Management
Navigating the web of regulations can be straightforward. Start by identifying which regulations apply to your business. A retail store will focus on PCI DSS, while a financial firm will be more concerned with rules like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX).
Once you know your requirements, integrate them into your security roadmap. As you roll out new IT security solutions for business, you will simultaneously address compliance obligations. This proactive approach transforms compliance from a burden into a strategic asset, demonstrating to clients and partners that you are a trustworthy custodian of their information.
How To Evaluate and Select a Security Provider
Choosing the right security partner is one of the most critical decisions you will make. This is not just about purchasing software; you are engaging a trusted advisor who will become an extension of your team. Moving beyond a simple price comparison is essential to find a partner that genuinely understands your business, challenges, and goals.
This partner will have deep access to your most sensitive systems and data. The selection process must be a meticulous evaluation of their expertise, reliability, and cultural fit. Thoroughly vetting potential partners is non-negotiable. Start by assessing their technical capabilities and industry reputation to build a solid shortlist.
Ask the Right Questions
Once you have a few potential providers, it is time to dig deep. Their answers to specific, probing questions will reveal their real-world capabilities and whether they can deliver on their promises.
Focus your questions on these key areas:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Ask for specific, guaranteed response and resolution times. What are the penalties if they miss those targets?
- Support Model: Who will you be speaking to during a critical incident? Understand their support structure, including access to senior engineers and their escalation process.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing: How will their it security solutions for business grow with your company? Inquire about their technology roadmap and how they adapt to new threats.
Verify Expertise and Reputation
A provider’s claims are only as good as their track record. Independent verification is crucial for building trust.
A great security provider does more than just sell technology; they invest in your success. They should function as a strategic partner, offering guidance and adapting their services to help you navigate an ever-changing threat environment.
Look for concrete proof of their expertise. Ask for recent, relevant case studies that demonstrate how they have solved problems similar to yours. Request client references you can speak with to get an unfiltered perspective.
Industry certifications like CISSP or CISM are valuable indicators of a team’s proficiency. If your business handles sensitive data, explore the benefits of a managed Security Operations Center (SOC) for dedicated, 24/7 monitoring.
The demand for proven expertise is reflected in global investment. Worldwide security spending is projected to grow by 12.2% year over year, reaching $377 billion by 2028. This growth is driven by the demand for advanced solutions in cloud security, identity management, and security analytics. (Read the full research about global security spending on my.idc.com).
By prioritizing a provider’s proven track record and strategic alignment over price, you ensure your investment delivers genuine, long-term security and peace of mind.
Got Questions About Business Security? We’ve Got Answers.
Here are straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often from business leaders about IT security. We will cover where to start, how to justify the budget, and the role of insurance.
What Is the First Security Solution My Small Business Should Implement?
For most small businesses, the greatest impact comes from focusing on three foundational controls that address the most common attack vectors.
Your starting point should be modern Endpoint Protection (next-generation antivirus and anti-malware) on every computer and server. Simultaneously, you must enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all critical accounts, especially email and financial systems. The third piece is a robust data backup and recovery system that you test regularly.
These three layers form a powerful baseline defense. They protect your devices, secure your team's identities, and provide a means of recovery from an incident like ransomware. It's about blocking common attacks, containing damage, and ensuring business continuity.
How Can I Justify the Cost of Security Solutions to My Leadership?
Frame security as a core business decision, not just an IT expense. Shift the conversation from "cost" to "risk management" and demonstrate how strong security enables business growth.
When building your case, use these points:
Quantify the Financial Risk: Use industry data on the average cost of a data breach for a business of your size. Presenting a real dollar amount for potential damages is a powerful motivator.
Highlight Intangible Damage: Emphasize the impact of a breach on your brand's reputation, customer loyalty, and operational downtime.
Frame It as a Competitive Advantage: Solid security is increasingly a prerequisite for winning new business. Larger clients will vet your security posture, and being prepared can be a deciding factor in landing a major contract.
Connect It to Compliance: In regulated industries, tie the investment directly to meeting mandatory requirements to avoid hefty fines and legal penalties.
Is Cybersecurity Insurance a Substitute for IT Security Solutions?
Absolutely not. This is a common and dangerous misconception. They are two complementary parts of a comprehensive risk management strategy; one cannot replace the other.
Cybersecurity insurance helps you recover financially after an incident has occurred. It covers costs like legal fees, customer notifications, and data recovery services. In contrast, IT security solutions for business are the tools and processes designed to prevent an incident from happening in the first place.
Most insurance carriers now require proof of specific security controls—such as MFA, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and a consistent patching program—before they will even issue a policy. Think of it like a car: your security solutions are the seatbelts and airbags, while insurance helps pay for repairs after a crash. You need both to be fully protected.
Protecting your business requires more than just software; it demands a strategic partner who understands your challenges. 1-800 Office Solutions offers comprehensive managed IT and cybersecurity services, from foundational endpoint protection to advanced compliance management, designed to help your business thrive securely. Learn how our expertise can become your peace of mind.











