Is Your Fax Machine a Security Blind Spot? Here’s How to Fix It
AI Overview:
Modern fax machines—now embedded in networked multifunction printers (MFPs)—are serious but often overlooked security risks. The blog explains how real-world exploits like Faxploit proved attackers can compromise an entire network through a single malicious fax. It outlines the business impact, including data theft, ransomware, and compliance violations, and provides a practical framework to reduce risk: harden MFPs, change default credentials, patch firmware, disable unused services, segment printers on isolated networks, encrypt fax transmissions, and adopt secure workflows.
The key takeaway: fax security is no longer legacy IT—it’s a critical part of modern cybersecurity and compliance strategy.
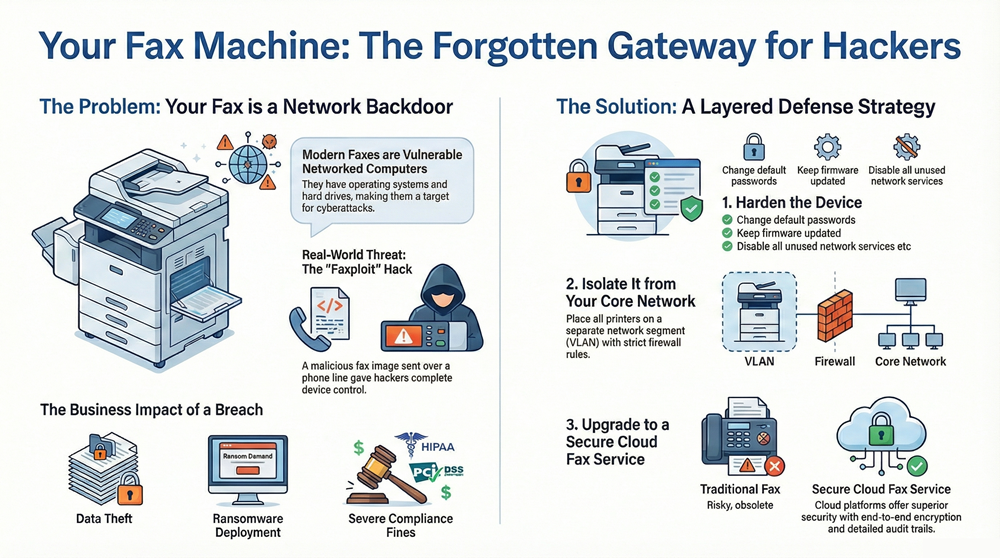
Thinking of fax machine security as an outdated problem is a common but dangerous mistake. The multifunction printers (MFPs) in your office aren’t just for printing; they are powerful, network-connected computers that handle sensitive data. This guide provides a clear, actionable framework for identifying the hidden risks associated with modern faxing and implementing robust safeguards to protect your network from a devastating breach.
The proof is undeniable: a critical vulnerability dubbed ‘Faxploit’ showed that a single, malicious fax sent over a plain phone line could give an attacker complete control of a printer. From there, they could pivot into your network, paving the way for data breaches or ransomware.
The Hidden Security Risks in Your Office Fax

A dangerous assumption persists that faxing is inherently secure, a belief rooted in the era of analog phone lines separate from digital threats. This creates a massive security blind spot because virtually no one uses a standalone analog fax machine anymore.
Instead, faxing is now a standard feature on networked MFPs. These are complex devices with their own operating systems, hard drives, and internet access. The moment you connect an MFP to your network for printing and scanning, its fax function becomes exposed to the same threats as any other endpoint.
From Isolated Tool to Network Gateway
The first step to better security is viewing your fax machine as a potential entry point for an attack. Hackers actively search for the path of least resistance, and an MFP with outdated firmware or default admin passwords is an inviting target.
Once a hacker compromises the printer, it becomes a launchpad for attacks across your entire infrastructure.
This isn’t theoretical. The “Faxploit” vulnerability was a real-world wake-up call. In 2018, security researchers proved they could completely take over an all-in-one printer just by sending a booby-trapped image file via fax. This exploit gave them remote code execution, effectively handing them the keys to the device. From there, spreading malware to other computers on the network was trivial.
That incident fundamentally changed how we should think about fax machine security. It proved that even a connection as simple as a phone line could be weaponized to kick off a full-scale network breach, with attackers moving laterally from the printer to your most sensitive corporate servers.
Understanding the Potential Business Impact
To grasp the full scope of these threats, here’s a breakdown of the common vulnerabilities targeting these devices.
Fax Security Vulnerabilities at a Glance
| Vulnerability | Threat Vector | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Faxploit & Firmware Flaws | Malicious fax image file sent over a phone line or network. | Remote code execution, full device takeover, malware deployment. |
| Default Credentials | Leaving factory admin username/passwords unchanged. | Unauthorized access to settings, stored documents, and network. |
| Unencrypted Data Storage | Documents stored on the MFP’s internal hard drive in plain text. | Theft of sensitive data (PII, PHI, financial records) if device is compromised or stolen. |
| Open Network Ports | Unnecessary services (FTP, Telnet) left active and exposed. | Provides additional avenues for attackers to exploit the device. |
| Lack of Network Segmentation | Placing MFPs on the same network segment as critical servers. | A compromised printer becomes a direct gateway to high-value assets. |
A compromised fax device can lead to devastating consequences far beyond a broken printer. It underscores why a dedicated security strategy isn’t just a good idea—it’s essential.
You might also want to review our guide on the purpose of a fax header for another layer of document security.
Here are just a few of the risks you’re facing:
- Data Theft: Attackers can intercept sensitive documents being faxed, scanned, or pulled from the device’s hard drive. Think financial records, patient data, or trade secrets.
- Ransomware Deployment: A compromised MFP is the perfect beachhead to launch ransomware across your network, grinding your operations to a halt.
- Network Espionage: Once inside, an adversary can sit quietly, monitoring network traffic, stealing credentials, and siphoning off data for months without anyone noticing.
- Compliance Violations: For businesses in regulated industries like healthcare (HIPAA) or finance (PCI DSS), a breach traced back to a fax machine can trigger massive fines and destroy your reputation.
Practical Steps to Harden Your Fax Devices
Securing your fax hardware is the first and most critical layer of defense. Plugging a new multifunction printer (MFP) into the network and walking away is an open invitation for trouble. That device, fresh out of the box, is an immediate, exploitable risk.
Turning that potential liability into a hardened asset requires deliberate, specific configuration changes that go far beyond factory defaults. Let’s walk through a practical checklist for locking down the device itself, significantly shrinking its attack surface.
Enforce Strong Administrative Controls
The most common—and most easily fixed—vulnerability is default administrator credentials. Every networked MFP ships with a default username and password like “admin” and “password.” These are public knowledge, and attackers have automated tools that scan for them constantly.
Leaving those defaults in place is like leaving the front door of your office unlocked. Your first move, before anything else, should be to change these credentials to a complex, unique password that aligns with your company’s security policy. This one action stops the most common brute-force attacks in their tracks.
An unprotected administrative account gives an attacker the keys to the kingdom. They can reroute faxes, rifle through stored documents, tweak network settings to bypass your firewalls, or even flash the device with malicious firmware.
Beyond that, be strict about who has these admin powers. Not every employee needs the ability to change network configurations. Use role-based access control (RBAC) on the device itself to ensure regular users can only perform basic functions, while administrative privileges are reserved for authorized IT staff.
Disable Unused Services and Protocols
Modern MFPs are packed with network services meant for convenience, but many are security risks your organization will never use. Services like FTP, Telnet, and older versions of SNMP are often enabled by default and can be significant security holes if not configured perfectly.
Every active service is another potential door for an attacker. A solid hardening process means you must systematically audit every service and protocol running on the device.
- Audit Network Ports: Access the device’s web admin panel and review the network settings. Make a list of all active ports and their associated services.
- Disable Non-Essentials: If you aren’t using FTP for scanning or Telnet for remote management (and you probably shouldn’t be), turn them off immediately. Unused protocols are nothing but unnecessary risk.
- Secure Necessary Services: For services you absolutely need, ensure they are locked down. If you use SNMP for network monitoring, for example, you should be using SNMPv3, which adds critical encryption and authentication that older versions lack.
By methodically disabling what you don’t need, you minimize the number of targets an attacker can aim for.
Implement a Strict Firmware Update Schedule
Think of firmware as the operating system for your MFP. Just like Windows or Linux, it has vulnerabilities that manufacturers discover and patch over time. Running outdated firmware is no different than running an unpatched server on your network—it’s a known, avoidable risk.
Establish a proactive schedule to check for and apply firmware updates for your entire fleet of fax-capable devices. MFPs are another form of network-connected IoT device and face similar security challenges. Understanding the broader principles for Securing IoT Devices provides a great framework for managing these endpoints.
Set a recurring calendar reminder—quarterly is a good starting point—to check manufacturer websites for updates. Better yet, use a managed print service that handles this patching for you. Staying current with firmware is one of the most effective things you can do to protect against new exploits.
If you want a complete picture of every potential weakness in your print environment, a professional print security assessment can uncover risks you never knew you had.
Isolate Fax Machines with Network Segmentation
A compromised fax machine should never be the domino that topples your entire network. After hardening the device, the next critical security layer is containment. The best way to achieve this is with network segmentation, a strategy that isolates your multifunction printer (MFP) from core business systems.
Think of your corporate network as a large, open-plan office. If a fire starts, it can spread everywhere in minutes. Network segmentation is like building firewalls between departments; a problem in one area gets contained. For your fax-capable MFPs, this means carving out a dedicated containment zone.
Create a Secure VLAN for Your Print Devices
The standard method for segmenting your network is creating a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). A VLAN is a subnetwork that groups devices together, even if they’re plugged into different switches. By placing all your MFPs on their own dedicated VLAN, you draw a digital boundary around them.
Once they’re isolated, the VLAN becomes a controlled environment. The real power comes from setting up strict firewall rules that govern all traffic flowing in and out of this segment.
The goal is to enforce a “default deny” policy. This means the firewall blocks all traffic to and from the fax VLAN unless a specific rule explicitly permits it. This shift in mindset—from allowing everything except known threats to blocking everything except known essentials—dramatically reduces the risk of an attacker moving laterally from a compromised device.
For instance, a printer on this segmented network should only be allowed to communicate with a specific print server or receive jobs from designated user workstations. It should have absolutely no ability to initiate connections to your domain controllers, file servers, or sensitive databases. This simple setup stops a “Faxploit” style attack from ever escalating into a full-blown data breach. Remember, isolating fax machines is just one piece of the puzzle; it works best as part of broader effective network protection strategies.
Secure Digital Transmissions with FoIP and Encryption
The fax security conversation must include the shift away from old-school analog phone lines. Many organizations now use Fax over IP (FoIP), which sends fax data over your existing network. While this modernizes the process, it also introduces new digital risks if not secured properly.
Sending a fax over an unencrypted IP network is like sending a postcard through the mail—anyone who intercepts it can read it. For industries handling sensitive data, that’s a massive compliance nightmare. The security of these transmissions is a real concern as more companies move to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) systems, which can be vulnerable to call interception.
To combat this, you must enforce encryption for all FoIP traffic.
- Implement Transport Layer Security (TLS): TLS is the gold standard for encrypting communications over a network. When setting up your FoIP system, enabling TLS is non-negotiable. It wraps the entire transmission in a secure, encrypted tunnel, protecting the fax data from being read or modified in transit.
- Verify Your Provider’s Capabilities: If you’re using a VoIP or FoIP service provider, get confirmation that they support and enforce TLS encryption for all fax transmissions. Don’t assume security is enabled by default.
The Superior Security of Cloud Fax Services
For businesses that want the strongest security posture without the management headache, secure cloud fax services are an excellent alternative. These platforms are built from the ground up with security and compliance baked in, offloading technical heavy lifting from your IT team.
Reputable cloud fax providers offer end-to-end encryption, meaning your document is encrypted from the moment you hit “send” until the recipient accesses it through their own secure portal. The faxes are stored in highly secure, audited data centers, not on a vulnerable machine in your office. This approach protects data in transit and at rest and provides a clear, unchangeable audit trail for every transmission—essential for meeting compliance standards like HIPAA.
Building Secure Workflows and User Access Controls
Even the best technology can’t stop a careless employee. A perfectly hardened and segmented fax machine is still vulnerable if someone leaves a sensitive document sitting on the output tray. This is where we must look beyond hardware and focus on the human side of security—the people and processes interacting with your fax system.
An unlocked fax machine in a busy hallway is an open invitation for a data breach. Anyone walking by could potentially scoop up confidential faxes. We can turn this weakness around by building smart workflows that transform your employees from a potential risk into your first line of defense.
Implement Secure Print and Fax Release
One of the most effective changes you can make is implementing a secure print release feature. Instead of faxes printing out immediately, jobs are held in a secure queue. To release the document, the authorized user must physically walk up to the multifunction printer (MFP) and authenticate themselves.
This is usually done with a PIN, an employee ID card, or a mobile app. The result? No more sensitive documents sitting out in the open. A fax containing patient records or financial data won’t print until the right person is standing right there to retrieve it. This simple step ensures confidentiality and creates an automatic, traceable handoff.
Real-World Example: The Misdialed Fax and the HIPAA Breach
A busy medical clinic staff member, rushing to get patient records to a specialist, misdials a single digit. That fax, containing the Protected Health Information (PHI) of multiple patients, ends up at a local car dealership. This isn’t a complex hack; it’s a simple process failure that spirals into a massive HIPAA breach, complete with costly fines and a damaged reputation.
This type of incident happens more often than you’d think and is a perfect example of why employee training and solid workflows are non-negotiable.
Apply Role-Based Access Controls
Does everyone in your organization really need the ability to send or view faxes? Probably not. Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is how you enforce the “principle of least privilege,” giving people access only to what they need for their job. RBAC lets you set up granular permissions for fax functions based on job responsibilities.
For example, you could set up roles like this:
- Finance Department: Can send and receive faxes from approved financial institutions, but they cannot access HR documents.
- Human Resources: Has access to send and receive faxes related to employee records but is blocked from viewing financial documents.
- General Staff: May only be able to receive general faxes sent to their personal extension, with no permission to send faxes externally.
By restricting access, you drastically reduce the odds of both accidental mix-ups and malicious misuse. It creates clear accountability and ensures sensitive information stays in the right hands.
Train Employees on Secure Faxing Protocols
Your security policies are only as good as the people using them. If your team doesn’t understand why these rules exist, they won’t follow them. Consistent, practical training is crucial for building a security-first culture.
Your training needs to cover the basics and address real risks. Ensure you emphasize these key points:
- Always Use Cover Sheets: Mandate the use of a standard fax cover sheet that includes a confidentiality disclaimer on every fax.
- Double-Check Every Number: Before hitting “send,” employees must verify the recipient’s fax number against a trusted source.
- Report Mistakes Immediately: Have a clear, no-blame protocol for what to do if a fax is sent to the wrong number or if a strange fax is received.
When you combine these technical controls with smart, human-centric workflows and diligent employee training, you build a multi-layered fax machine security strategy that truly protects your organization’s most critical information.
Staying on the Right Side of Industry Compliance
For anyone in healthcare, finance, or law, securing your fax machines and MFPs isn’t just a good practice—it’s a legal requirement. Failure to secure sensitive information can lead to crippling fines, a tarnished reputation, and a total loss of client trust. The rules are non-negotiable, and regulators demand proof that you’re protecting the data you handle.
Your security setup cannot be generic; it must be tailored to specific regulations. Standards like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) have clear rules about data protection. Your faxing solution, whether it’s a physical machine or a cloud service, must be configured to meet their demanding standards.
Meeting HIPAA Technical Safeguards
In healthcare, HIPAA is a major reason why secure faxing remains critical. The regulation’s technical safeguards focus on protecting electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) from unauthorized access, both in transit and at rest. Getting your fax security right is a huge part of this.
One of the most critical requirements is having detailed audit trails. A compliant system must log every fax that comes in or goes out, capturing key details like:
- Timestamp: The precise date and time of the transmission.
- Sender/Recipient Info: The phone numbers and identifiers for both parties.
- Transmission Status: A clear success or fail confirmation.
- User ID: The specific account that initiated the fax.
These logs are your compliance lifeline. In the event of an audit or a suspected breach, these records are your proof that you have the right controls in place to monitor and protect ePHI. For a closer look, check our guide on the key elements of HIPAA compliance.
Protecting Financial Data Under PCI DSS
In the financial sector, PCI DSS dictates exactly how companies must handle cardholder data. While organizations try to avoid faxing credit card information, it still happens. When it does, that transmission must be locked down to prevent interception and fraud.
This is where encryption is an absolute must. Sending financial data over an unencrypted line—be it a traditional phone line or an unsecured Fax-over-IP connection—is a clear violation of PCI DSS. Secure cloud fax services using end-to-end TLS encryption are vital, as they scramble the data and make it unreadable to anyone who might be listening in.
Storage is equally important. An MFP that saves faxes with cardholder data onto an unencrypted internal hard drive is a ticking time bomb. A breach of that single device could expose reams of sensitive financial information and lead to massive fines.
Why Secure Faxing Still Matters
Even with modern communication tools, faxing holds its ground, especially in highly regulated fields. Its persistence is tied directly to compliance pressures. The healthcare industry, in particular, has driven the development of specialized, compliant fax systems built to provide administrative, technical, and physical security. These platforms help ensure the right number is dialed and that only authorized staff can access incoming faxes, hitting key HIPAA requirements head-on. You can discover more about the persistence of faxing in regulated fields on Etherfax.net.
Ultimately, secure faxing must be a core part of your risk management strategy. It isn’t a forgotten IT task; it’s a fundamental business process that allows you to operate legally and maintain client trust. By implementing strong access controls, detailed logging, and solid encryption, you’re not just avoiding penalties—you’re demonstrating a serious commitment to protecting sensitive data.
Answering Your Top Fax Security Questions
Digging into the nuances of fax machine security always brings up important questions. To provide clarity, here are straightforward answers to the most common queries from businesses working to protect their sensitive information.
Are Cloud Fax Services More Secure Than Traditional Fax Machines?
Yes, without a doubt. A reputable cloud fax service is significantly more secure than a physical machine. These services were built to fix the exact security holes that traditional faxing leaves open.
Modern cloud platforms use end-to-end encryption, meaning your data is scrambled from the moment it leaves your computer until the recipient opens it. It’s protected in transit and at rest in professionally managed data centers with robust security protocols. Plus, you get a detailed audit trail of every fax—essential for compliance.
A traditional fax machine is a sitting duck. An analog line can be physically wiretapped with no digital record of the breach. Worse, a modern multifunction printer (MFP) on your network is a potential backdoor for cyberattacks like the 'Faxploit' vulnerability. Moving to a secure cloud service outsources this complex security headache to experts, making it a much safer choice.
How Can We Prove Secure Faxing For HIPAA Compliance?
Proving HIPAA compliance is all about documentation. You need to show that you have the proper administrative, physical, and technical safeguards in place. For faxing Protected Health Information (PHI), your system must create detailed audit logs for every transmission. These logs need to show who sent what, to whom, when, and whether it was successful.
Secure cloud fax platforms excel here, as they typically generate these comprehensive logs automatically. But technology is only half the solution. You also need documented internal policies for handling PHI, a strict rule about using cover sheets with clear confidentiality notices, and a reliable process for verifying every recipient fax number before sending.
The most critical element? Your fax provider must be willing to sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). This is a legally binding contract that makes them just as responsible as you are for protecting PHI under HIPAA. The combination of technical logs, internal policies, and a signed BAA constitutes your proof of compliance.
What Is The Most Critical First Step To Improve Our Fax Security?
If you use a networked multifunction printer (MFP) for faxing, the single most impactful action you can take right now is to isolate it from your main network. The best way to do this is by placing the device on its own dedicated network segment, often called a VLAN.
Once it's walled off, lock it down with a tight set of firewall rules that only allow the bare minimum traffic needed for it to function. Think of it as creating a digital moat. This strategy provides immediate containment. If an attacker exploits a firmware bug on the MFP, this segmentation stops them from jumping over to your critical servers or sensitive data.
While changing default admin passwords and keeping firmware updated are crucial, network isolation is the most robust defense against a device-level hack turning into a full-blown company-wide disaster. It turns your printer into a secure island instead of a bridge into your core infrastructure.
Can a Fax Machine Be Hacked Through a Phone Line?
Absolutely. This is not a hypothetical threat; it's a documented reality. The 'Faxploit' vulnerability proved that an attacker can completely take over a networked fax machine simply by sending a specially crafted image file over a standard telephone line.
The malicious file exploits bugs in how the device’s firmware processes image data. This can cause a buffer overflow, which allows the attacker to run their own code on the machine, giving them total control.
From that point, the compromised fax machine becomes a beachhead inside your network—a launchpad for attacking everything else connected to it. This real-world attack proves that even devices not directly connected to the internet can be dangerous entry points. It is a stark reminder that comprehensive fax machine security for every device is a must.
Strengthening your fax security is no longer optional—it’s a critical component of any modern, defense-in-depth cybersecurity strategy. At 1-800 Office Solutions, our managed IT and security services are designed to protect every endpoint in your organization, from multifunction printers to cloud servers.
Don’t leave your network exposed through an overlooked device. Contact us today to secure your business operations and get a comprehensive security assessment.











