10 Penetration Testing Best Practices for 2025
AI Overview:
This blog outlines ten proven penetration testing best practices that help organizations move beyond compliance-driven assessments to proactive risk management. It explains how to define clear scope and rules of engagement, apply standardized frameworks, prioritize vulnerabilities by business impact, protect sensitive test data, and integrate testing into a continuous security lifecycle. By following these practices, organizations can reduce risk, improve remediation effectiveness, meet compliance requirements, and strengthen long-term security resilience.
Effective penetration testing best practices are essential to identify security gaps before attackers exploit them. Companies relying on ad-hoc or outdated assessments risk wasting resources and leaving critical vulnerabilities unaddressed. This article outlines ten proven penetration testing best practices to strengthen your security posture, meet compliance requirements, and deliver actionable insights that safeguard business assets.
By following these expert-backed strategies, you transform penetration testing from a compliance checkbox into a proactive risk management tool. You will learn how to:
- Define clear scope, rules of engagement, and communication protocols.
- Leverage standardized frameworks and methodologies for repeatable results.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on business impact and technical severity.
- Integrate testing into a continuous security improvement lifecycle.
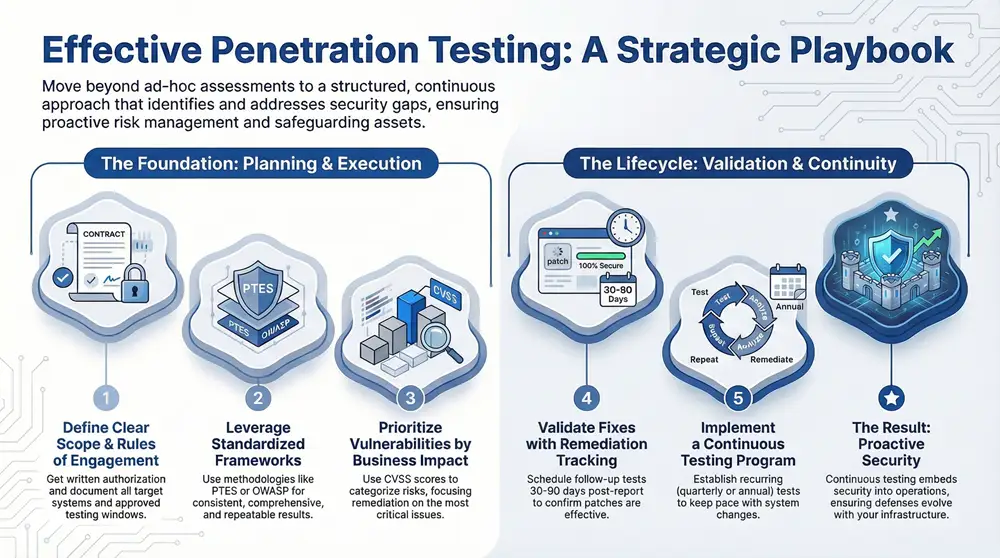
1. Establish Clear Scope and Rules of Engagement
Defining scope and Rules of Engagement (RoE) before testing begins ensures that the engagement is legal, controlled, and aligned with stakeholder expectations. Document target IP addresses, domain names, applications, and physical locations while explicitly listing systems that are off-limits to avoid unintended disruptions.
The RoE specifies approved techniques (e.g., social engineering, DoS simulations), testing windows, and communication channels. Common frameworks like PTES and NIST SP 800-115 emphasize this phase to align legal authorization and technical planning.

Key Takeaway: A detailed scope and RoE document is your “get out of jail free” card, turning what would otherwise be illegal hacking into a sanctioned, controlled security assessment.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Get Written Authorization: Obtain a signed approval from a C-level executive or designated authority.
- Be Hyper-Specific: List exact IPs (
192.168.1.100) and URLs (https://app.yourcompany.com). - Define Testing Windows: Limit testing to off-peak hours (e.g., 10:00 PM–6:00 AM EST).
- Establish Communication Plan: Identify primary contacts and escalation paths.
- Document Everything: Any scope changes require written addenda and approvals.
2. Conduct Pre-Engagement Information Gathering
Passive reconnaissance (OSINT) builds a complete map of the target’s digital footprint, enabling focused, efficient tests. Uncover exposed devices with Shodan, find API keys in public code, and profile personnel via LinkedIn to plan effective social engineering scenarios.
Document IP ranges, domain names, subdomains, and technologies in use. Distinguish passive reconnaissance from active scanning until the RoE permits deeper probing.
Key Takeaway: Passive reconnaissance is a force multiplier, honing in on the most likely points of failure and increasing test efficiency.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Leverage OSINT Tools: Use Shodan, Recon-ng, and Google Dorking.
- Map Digital Footprint: Record cloud assets, server software, and CMS versions.
- Identify Key Personnel: Note email formats and job titles for phishing simulations.
- Scour Public Repositories: Search GitHub/GitLab for hardcoded credentials.
- Maintain Clear Boundaries: Stick to passive methods until authorized.
Case Study: A retail chain discovered exposed S3 buckets via OSINT and secured them before a major holiday season, preventing potential data leakage affecting millions of customer records.
3. Use Standardized Testing Frameworks and Methodologies
Standard frameworks like PTES, NIST SP 800-115, and the OWASP Testing Guide provide a systematic, repeatable process for penetration tests. They cover intelligence gathering, threat modeling, exploitation, and reporting, ensuring comprehensive coverage and compliance alignment.
Adopting a methodology transforms penetration testing into a science, guaranteeing consistent quality and defensible results for auditors and stakeholders.
Key Takeaway: Frameworks ensure a baseline level of rigour, making engagement results consistent, comparable, and actionable.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Select a Relevant Framework: OWASP for web apps, PTES for networks.
- Customize for Your Needs: Adapt baseline processes to your environment (see black box vs white box testing).
- Train Your Team: Ensure all testers are proficient with the chosen methodology.
- Reference in RoE: Align client expectations by citing the framework.
- Document Deviations: Record and justify any process changes for transparency.
4. Document and Report Vulnerabilities Using Severity-Based Prioritization
Transform technical findings into a business-focused roadmap by categorizing vulnerabilities with CVSS scores and impact tiers (Critical, High, Medium, Low). This approach helps executives prioritize remediation based on real risk.

Include a non-technical executive summary and a detailed technical section with step-by-step remediation guidance. Use consistent templates to streamline stakeholder review and compliance reporting.
Key Takeaway: Severity-based reporting bridges technical details with business risk, driving focused remediation on the most critical issues.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Standardize with CVSS: Assign scores (0.0–10.0) for uniform assessment.
- Create Dual-Audience Reports: Non-technical summary plus technical deep dive.
- Contextualize Risk: Explain business impact (e.g., “SQL injection on customer portal could expose PII”).
- Provide Clear Remediation Steps: Include code snippets or configuration commands.
- Use Consistent Templates: Ensure stakeholders know exactly where to find key information (see effective vulnerability risk assessment).
5. Maintain Confidentiality and Secure Handling of Test Data
Penetration tests uncover highly sensitive information. Secure storage, transfer, and destruction of test data are non-negotiable to maintain trust and comply with regulations like GDPR and FedRAMP.
Establish encryption, access controls, NDA enforcement, and data sanitization policies. Familiarize your team with core data security concepts to prevent the test from becoming a source of breach.
Key Takeaway: Treat test data with the same protection as your most critical business assets to uphold ethics and legal compliance.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Encrypted Storage & Transfer: Use BitLocker/VeraCrypt and SFTP or secure portals.
- Need-to-Know Access: Limit data access to authorized personnel only.
- Data Destruction Policies: Wipe test data within 30–90 days post-engagement.
- Sanitize Reports: Produce high-level summaries omitting sensitive details for broader audiences.
- Manage Credentials Securely: Store discovered credentials in an encrypted password manager.
6. Perform Capability Assessment and Team Qualification
The quality of a penetration test depends on the testers’ skills and integrity. Vet teams for industry certifications (OSCP, CEH, GPEN), real-world experience, and professional reputation to ensure ethical, effective assessments.
Review redacted sample reports and verify certifications via issuing bodies. Confirm the team’s expertise matches your technology stack and compliance needs.
Key Takeaway: Skilled ethical hackers using the right tools deliver deeper insights than automated scanners alone.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Verify Certifications: Confirm OSCP, GPEN, GWAPT status through official channels.
- Request Redacted Reports: Assess reporting style and analysis depth.
- Match Expertise to Scope: Ensure experience with mobile apps, cloud environments, or other specialized targets.
- Check Professional Reputation: Look for published research or CVE contributions.
- Require Ongoing Development: Verify how the team stays current with emerging threats.
7. Establish Clear Communication Protocols and Escalation Procedures
A formal communication plan with defined escalation paths ensures critical findings receive immediate attention and prevents operational surprises. Define update cadences, “critical finding” triggers, and 24/7 contact trees.
Use centralized tracking (Jira or security portals) and keep detailed logs for compliance and post-mortem analysis.
Key Takeaway: Structured communication builds trust, ensures rapid mitigation, and transforms the test into a collaborative security initiative.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Schedule Status Calls: Daily or weekly syncs to align progress and roadblocks.
- Define “Critical” Findings: Agree on vulnerabilities requiring immediate escalation.
- Establish a 24/7 Contact Tree: Share emergency contact details for both teams.
- Use Centralized Tracking: Log all findings and communications in a shared system.
- Document Communications: Maintain an audit trail of decisions and notifications (see security vulnerability response).
8. Test in Controlled Phases to Minimize Business Disruption
Phasing the test into approved maintenance windows and non-production environments reduces operational risk. Schedule intensive scans and simulated attacks during low-traffic periods to protect live systems.
Coordinate with IT and business units, prepare rollback procedures, and monitor performance metrics to quickly address unexpected issues.
Key Takeaway: Phased testing intelligently manages risk, allowing comprehensive assessments without disrupting critical operations.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Use Maintenance Windows: Align with pre-approved downtime schedules.
- Test Non-Production First: Validate attack vectors on staging or UAT.
- Coordinate Across Teams: Maintain constant dialogue with IT and business leaders.
- Prepare Rollback Plans: Document steps to restore services if needed.
- Monitor Performance: Watch key metrics for anomalies during tests.
9. Conduct Post-Testing Validation and Remediation Tracking
Re-testing and tracking closes the feedback loop, confirming patches are effective and identifying recurring issues. A formal validation engagement 30–90 days post-test ensures vulnerabilities are fully remediated.
Define service-level agreements (SLAs) for fix timelines, track remediation progress in dashboards, and document repeat findings to address systemic weaknesses.
Key Takeaway: Skipping post-test validation risks operating under a false sense of security. Confirm fixes with targeted re-tests.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Schedule Re-Testing: Plan follow-up tests 30–90 days after reporting.
- Establish Remediation SLAs: Set timelines based on severity (Critical: 7 days; High: 30; Medium: 90).
- Verify Specific Fixes: Re-run the original exploit to confirm remediation.
- Track Repeat Vulnerabilities: Identify trends to improve developer training.
- Create a Remediation Dashboard: Report metrics like time-to-fix and remediation rates.
10. Implement Continuous and Recurring Penetration Testing Programs
Regular tests keep pace with dynamic environments. Quarterly or biannual penetration testing best practices, integrated with SDLC milestones, provide ongoing assurance of your security posture.
Complement manual tests with automated scans between engagements, and monitor trends in remediation metrics to demonstrate program ROI to stakeholders.
Key Takeaway: Continuous testing embeds security into your operations, ensuring defenses evolve alongside your infrastructure.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Establish a Baseline: Conduct an annual, comprehensive test.
- Increase Frequency by Risk: Schedule quarterly or monthly focused assessments.
- Integrate with SDLC: Time tests with development sprints and releases.
- Supplement with Automation: Run automated scans between manual tests.
- Track Remediation Metrics: Measure “time to remediate” and recurrence rates.
Case Study: A SaaS provider adopted quarterly penetration tests and continuous scanning, cutting vulnerability recurrence by 30% and accelerating patch cycles by 40%.
From Best Practices to Business Resilience
Transitioning from a checklist of penetration testing best practices to a robust security posture requires embedding these strategies into daily operations. Define clear scope and RoE, adopt standardized methodologies, prioritize findings, test in phases, and validate remediations continuously. This structured approach fosters a security-driven culture, reduces breach costs, and builds long-term resilience.
Call to Action
Partner with 1-800 Office Solutions to integrate industry-leading penetration testing best practices into your managed security program. Visit 1-800 Office Solutions to request a consultation and discover how our experts turn testing insights into lasting business value.