VPNs Uncovered: What They Are and How They Work
AI Overview:
This blog explains the vpn meaning as a secure, encrypted tunnel that hides your IP address and protects your data online. It covers how VPNs work—through encryption, tunneling, and IP masking—and why they’re essential for privacy, secure remote work, and protecting business data.
You’ll learn the basics of VPN types, key protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard, top benefits for individuals and companies, and the limitations to keep in mind. The article also clarifies that VPNs boost security but should be paired with MFA, antivirus, and strong cybersecurity practices.
In short, VPNs are now a core tool for safe browsing, secure access, and modern business operations.
Understanding VPN Meaning in Today’s Digital Workplace
The vpn meaning centers on creating a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) acts as a protective tunnel, shielding your online activities from prying eyes by routing your traffic through a remote server.
Quick VPN Definition:
- Virtual: Software-based, not physical cables
- Private: Encrypted and hidden from others
- Network: Connects devices securely across the internet
What VPNs Do:
- Encrypt your internet traffic
- Hide your real IP address
- Protect data on public Wi-Fi
- Enable secure remote work access
For businesses, VPNs are a critical line of defense. With cybercrime expected to cause $10.5 trillion in damages annually by 2025, implementing proper VPN solutions has shifted from optional to mandatory for protecting digital assets.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about VPNs, from basic concepts to implementation strategies.
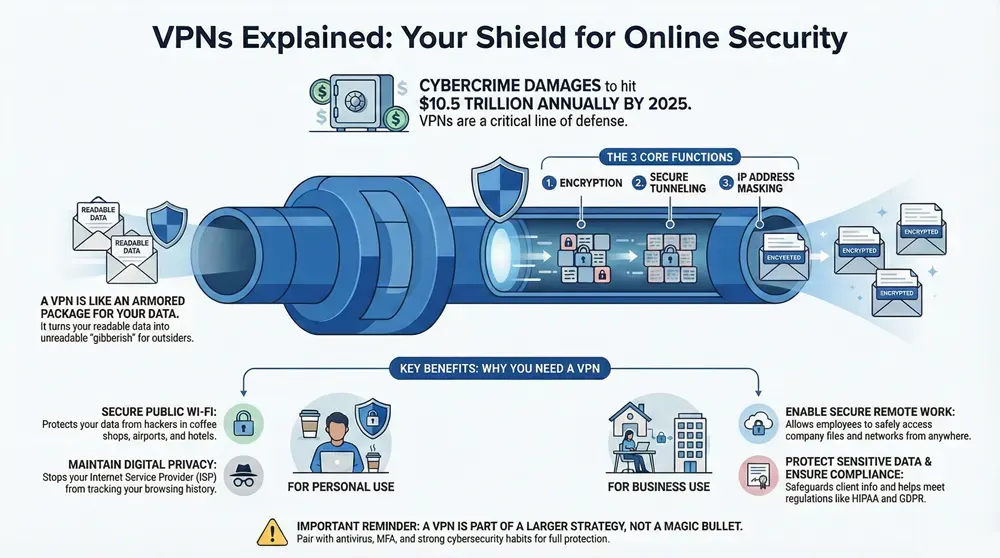
Simple vpn meaning word guide:
What is a VPN? The Core Definition and Meaning Explained
When you hear someone mention vpn meaning, they’re referring to a Virtual Private Network. It creates a secure, encrypted bridge between your device and the internet through a remote server. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines a VPN as a “private network that uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect remote sites or users.” This turns the public internet into a secure, private communication channel.
The global VPN market is projected to reach $76.6 billion by 2030, with a 15.4% annual growth rate, and 41% of American and UK users already use a VPN weekly. This highlights its shift from a niche tool to essential infrastructure. Understanding the vpn meaning is clearer when we break down the acronym:
The “Virtual” Aspect
The “Virtual” part means the connection is software-based, with no physical cable connecting your device to a corporate server. This software creates an “overlay network” on top of the existing internet, like speaking in a secret code in a crowded room. This virtual setup offers incredible flexibility, allowing an employee in a Tampa coffee shop to securely access company files in Jacksonville as if they were in the office.
The “Private” Aspect
This is where the security magic happens. When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted—scrambled into an unreadable format. This prevents your Internet Service Provider (ISP) from seeing your activity, stops hackers on public Wi-Fi from stealing your data, and makes government surveillance more difficult. While regular internet traffic is like a postcard anyone can read, VPN traffic is like a sealed, armored package.
The “Network” Aspect
The network component connects your device to a VPN server, which acts as your representative on the internet. Websites see the VPN server’s IP address and location, not yours. If you’re in Atlanta but connect to a server in New York, websites will think you’re browsing from New York. This capability enables user-to-network connections (remote employees accessing company resources) and network-to-network connections (securely linking two office locations).
How a VPN Works to Protect Your Data and Privacy
Think of a VPN as a digital bodyguard. Without one, your data travels openly online. Understanding the vpn meaning reveals how it functions to provide essential security for personal and business use.
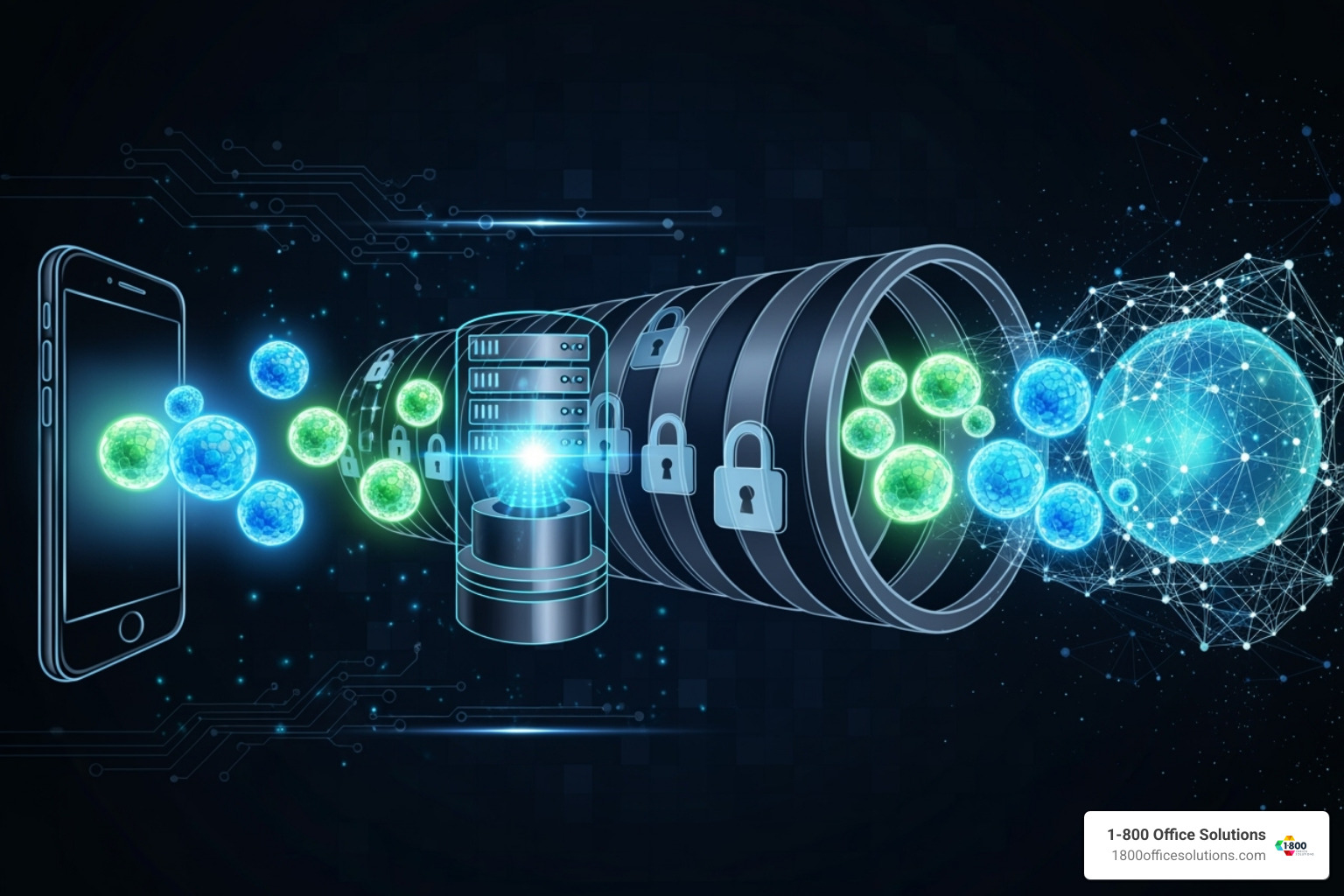

The process works through data tunneling and encapsulation. Imagine sending a confidential document. A VPN seals it in a steel lockbox (encryption), places that box in a secure container (encapsulation), and sends it via a private courier (the tunnel) to a trusted location (the VPN server).
Your identity is protected through IP address masking. The VPN server becomes your stand-in, so websites see its IP address, not yours. This enables geo-spoofing, allowing you to access content as if you’re in London while sitting in Tampa, or bypass regional blocks on business tools.
The Role of Encryption
Encryption transforms readable data into digital gibberish, making it unreadable to outsiders. The gold standard is AES 256-bit encryption, the same military-grade protection used by governments. It would take longer than the age of the universe to crack this encryption by brute force, providing serious data security.
This robust encryption is critical for securing data in transit, protecting everything from login credentials to sensitive client information. It’s also vital for preventing data sniffing on public Wi-Fi. With a VPN, you can safely use a coffee shop or airport network without worrying about cybercriminals intercepting your data.
The VPN Tunneling Process
The VPN tunneling process creates a secure, encrypted highway for your data. When you connect, your device and the VPN server perform a secure handshake to verify each other’s identity. Then, your internet data is wrapped in layers of encryption in a process called encapsulating data packets.
This routing traffic through the encrypted tunnel means your ISP only sees scrambled data going to the VPN server, effectively hiding your activity from your ISP. They can’t track, log, or sell information about your online activities.
This process also protects against identity theft by making it nearly impossible for criminals to intercept your credentials. When securing online transactions, the encrypted tunnel ensures your financial data remains safe from digital pickpockets. For businesses, this tunneling is the backbone of secure remote work, allowing employees to access company resources from anywhere with office-level security.
Primary Benefits of Using a VPN for Individuals and Businesses
The widespread adoption of VPNs is a direct response to our vulnerable digital world. Whether for personal privacy or corporate security, the practical vpn meaning shows why this technology is essential.

A VPN transforms vulnerable moments—like checking email at a coffee shop or accessing company files from home—into secure connections. Key benefits include improved security, privacy protection, and safe remote access. VPNs also help bypass censorship, access geo-restricted content, and prevent online tracking.
The Personal vpn meaning: Enhancing Online Privacy
For individuals, a VPN means reclaiming control over your digital privacy. It puts you back in charge of your data.
- Securing public Wi-Fi: An encrypted tunnel makes your activities invisible to hackers on shared networks in places like coffee shops or airports.
- Stopping ISP tracking: A VPN prevents your Internet Service Provider from monitoring and selling your browsing history to advertisers.
- Avoiding price discrimination: By changing your virtual location, you can sometimes find better prices on flights, hotels, and online goods.
- Streaming international content: Connect to a server in another country to access streaming libraries and content exclusive to that region.
- Protecting personal identity: Masking your IP address makes it much harder for cybercriminals to target you for identity theft.
- Safe online banking: An encrypted connection ensures your financial details remain secure, especially when banking on the go.
The Business vpn meaning: Securing Corporate Resources
For businesses with offices from Miami to Grand Rapids, Michigan, VPNs are a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. The vpn meaning for a business is about operational necessity.
- Secure remote work: A VPN creates a secure bridge for employees, whether in Charlotte or Atlanta, to access company files. Our IT services include VPN implementation to make remote work safe.
- Protecting sensitive data: Encryption is vital for maintaining client trust and protecting intellectual property, whether it’s medical records in Philadelphia or financial data in Tampa.
- Facilitating remote access: Team members can securely connect to company networks, shared drives, and internal software from anywhere.
- Compliance: VPNs help businesses meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR by ensuring data confidentiality and providing secure access trails.
- Preventing corporate espionage: By securing communications and data, VPNs add a crucial layer of protection against competitors and malicious actors.
For comprehensive protection, explore how VPNs integrate into broader security strategies with our cybersecurity services.
Types of VPNs, Protocols, and Key Features
Not all VPNs are the same. They vary by type, security protocols, and features, making it crucial to choose the right solution for your needs.
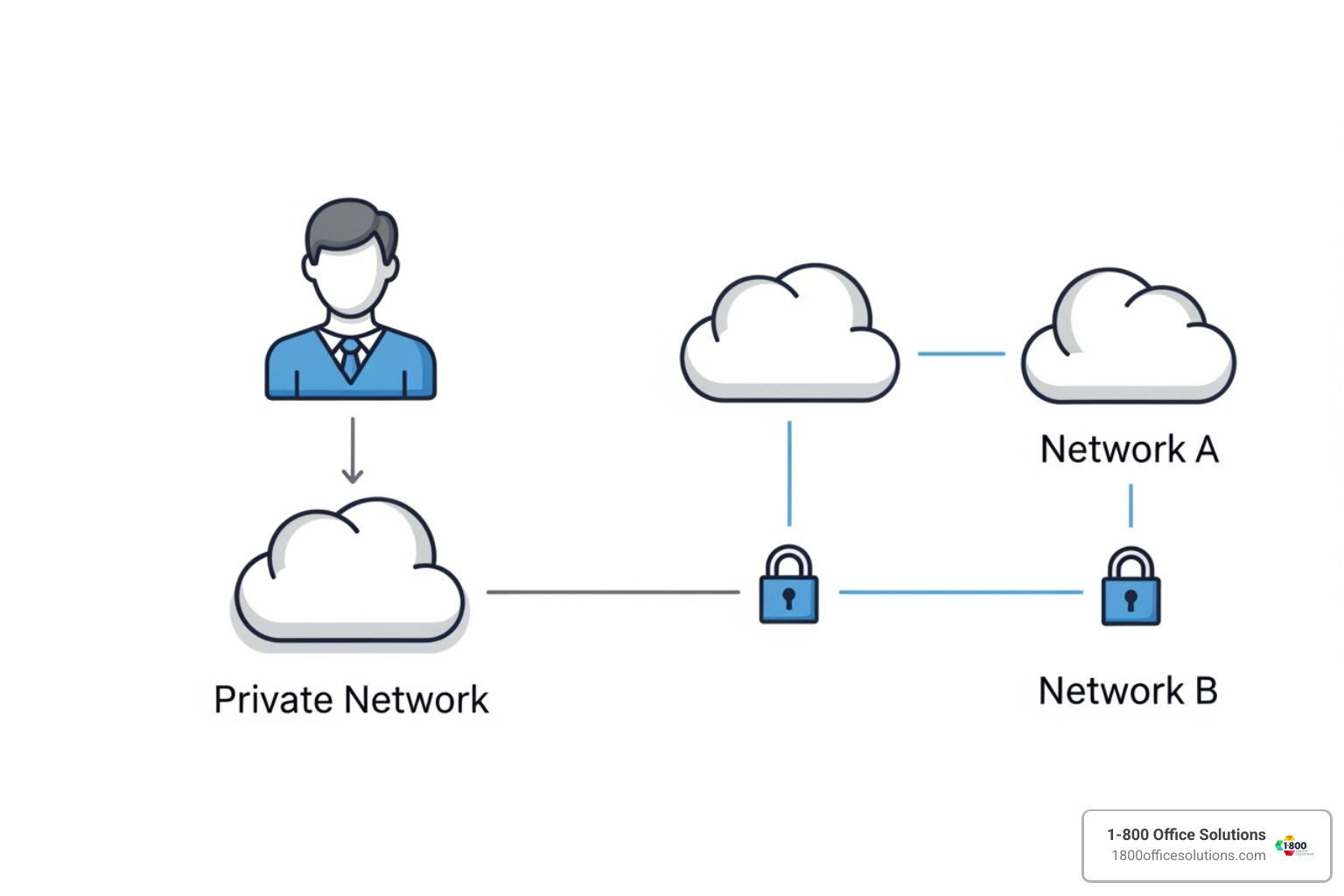
Common Types of VPNs and Their Use Cases
VPNs are categorized by their architecture and purpose.
- Remote Access VPNs: The most common type, allowing individual users (like remote employees) to connect securely to a private network over the internet.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Connect entire networks in different locations, creating a secure bridge between offices. For example, a company can link its Chicago and Philadelphia offices to share resources securely.
- Individual vs. Business VPNs: Individual VPNs focus on personal privacy and bypassing geo-restrictions. Business VPNs offer centralized management, advanced security, and compliance features for organizations.
- Mobile VPNs: Designed for mobile devices, these maintain a secure connection as users switch between Wi-Fi and cellular networks, ideal for field workers or law enforcement.
Key Security Protocols Explained
Protocols are the rules governing how a VPN encrypts data and creates a secure tunnel. They offer different balances of speed and security.
- OpenVPN: The industry gold standard. It’s open-source, highly secure, and versatile, making it a top choice for data protection.
- IKEv2/IPsec: Excellent for mobile devices due to its stability when switching networks. It offers strong security and good speeds.
- WireGuard: A modern, fast, and efficient protocol. Its streamlined code provides top-tier performance and security with less battery drain.
- L2TP/IPsec: Offers good security but can be slower. It’s widely supported but may have issues with some firewalls.
- SSTP: Works well on Windows and can bypass most firewalls, but its Microsoft-centric design makes it less flexible.
Features to Look for in a Good VPN Service
- Kill Switch: Automatically cuts your internet connection if the VPN drops, preventing data leaks.
- No-Logs Policy: Ensures the provider does not store or sell your activity data. Look for services with independent audits, as no-logs policies can be very hard to prove.
- Server Locations: A large network provides more options for bypassing geo-restrictions and improving connection speeds.
- Connection Speed: A quality VPN minimizes speed loss, which is crucial for video conferencing and large file transfers.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized account access.
- Split Tunneling: Allows you to route some traffic through the VPN and some through your regular internet connection, optimizing performance.
- Ease of Use: An intuitive interface ensures consistent use across your team.
Potential Limitations and Drawbacks
- Slower Internet Speeds: Encryption and routing through a remote server can reduce connection speed.
- Blocked by Some Services: Streaming platforms and other websites may detect and block VPN traffic.
- Complex Configuration: Business-grade VPNs can require technical expertise to set up securely.
- Legal Restrictions: Some countries regulate or ban VPN use. Always check local laws.
- False Sense of Security: A VPN doesn’t protect against malware or phishing. It should be part of a broader security strategy.
- Cost of Premium Services: Free VPNs often have limitations and privacy risks. Reliable services require a subscription.
Frequently Asked Questions about VPNs
Understanding the practical vpn meaning is easier once you have answers to common questions. Here are the key concerns we address when helping businesses implement secure remote access.
What is the main purpose of a VPN?
The main purpose of a VPN is to create a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet. This protects your data from being intercepted on insecure networks, like public Wi-Fi. For businesses, this means employees can securely access company files and applications from anywhere, protecting sensitive information from cyber threats, surveillance, and data brokers.
Can you be tracked if you use a VPN?
A VPN makes tracking much more difficult, but it does not make you completely anonymous. It hides your real IP address and encrypts your traffic, preventing your ISP and websites from seeing your location and activity. However, websites can still use other methods like cookies and browser fingerprinting to identify you. A VPN is a powerful privacy tool, but it should be used as part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, not as a standalone solution.
Is using a VPN legal?
Yes, using a VPN is completely legal in the United States and most other countries. Businesses across North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and New York use VPNs daily for legitimate security purposes. However, any activity that is illegal without a VPN remains illegal when using one. Some countries, like China and Russia, have restrictions or bans on VPNs, so it's important to research local laws if operating internationally. Additionally, some streaming services prohibit VPN use in their terms of service, which could lead to an account suspension.
Conclusion: Integrating VPNs into Your Security Strategy
Understanding the vpn meaning is no longer optional in our digital world. A VPN is an essential tool that creates an encrypted tunnel over public networks, masking your IP address and shielding your sensitive data. For individuals, it means privacy and freedom online. For businesses, it’s the backbone of modern operations.
VPNs make secure remote work a reality, allowing a team member in Grand Rapids, Michigan, to safely access the same files as someone in your Charlotte, North Carolina office. This secure connectivity is what enables seamless, protected operations across any distance.
However, VPNs are not a magic bullet. They are powerful tools that work best as part of a layered security strategy. We always recommend pairing a VPN with robust antivirus software, multi-factor authentication, and comprehensive cybersecurity protocols to create a truly resilient defense.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we’ve seen how the right security infrastructure can empower a business. A managed VPN service is the foundation for growth, innovation, and peace of mind. For businesses ready to operate confidently in a connected world, a VPN is a critical component of any serious cybersecurity plan.
Secure your business with a Virtual Private Network (VPN) Service











