The Ins and Outs of What a Server Does in a Network
What does a server do in a network? Simply put, servers are the backbone of any network, handling everything from data storage to application hosting. They’re like the busy bees of the tech world, working tirelessly to ensure efficiency and smooth operation. Within a network, servers manage resources, store vast amounts of data, and host essential services to keep everything running seamlessly.
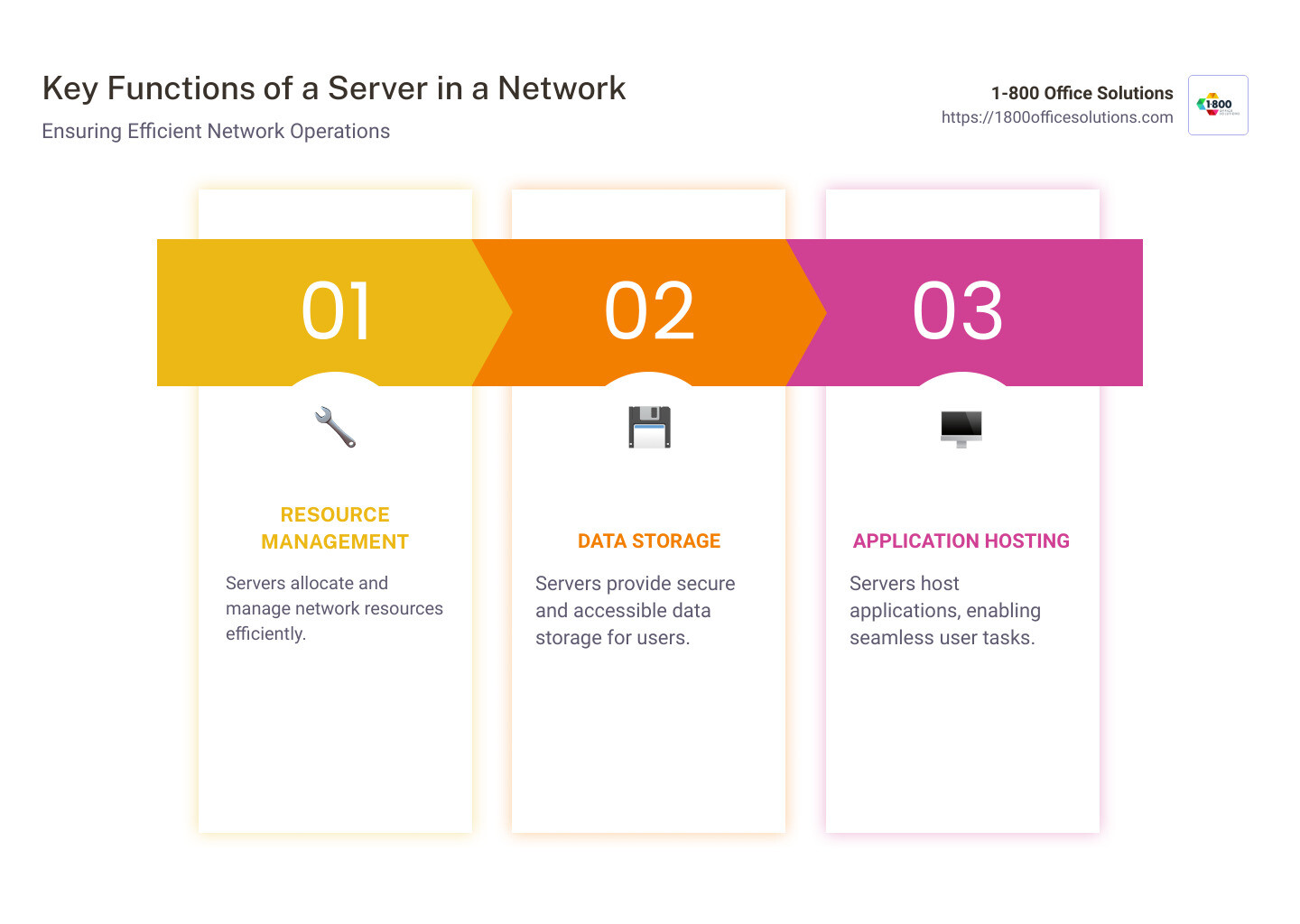
- Resource Management: Servers allocate resources to various devices connected to the network.
- Data Storage: They provide secure storage and easy access to data for users.
- Application Hosting: Servers host applications and services, enabling users to perform tasks efficiently.
From enhancing collaboration to ensuring reliability, servers play a crucial role in the client-server model, which is foundational to modern network infrastructure. In this model, servers act as the providers of resources and services, while clients are the devices that request and consume these services.
Relevant articles related to what does a server do in a network:
What Does a Server Do in a Network?
Servers are the unsung heroes, working tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure everything runs smoothly. They handle a variety of tasks that are essential for the seamless operation of a network. Let’s break down the key roles of a server:
Resource Management
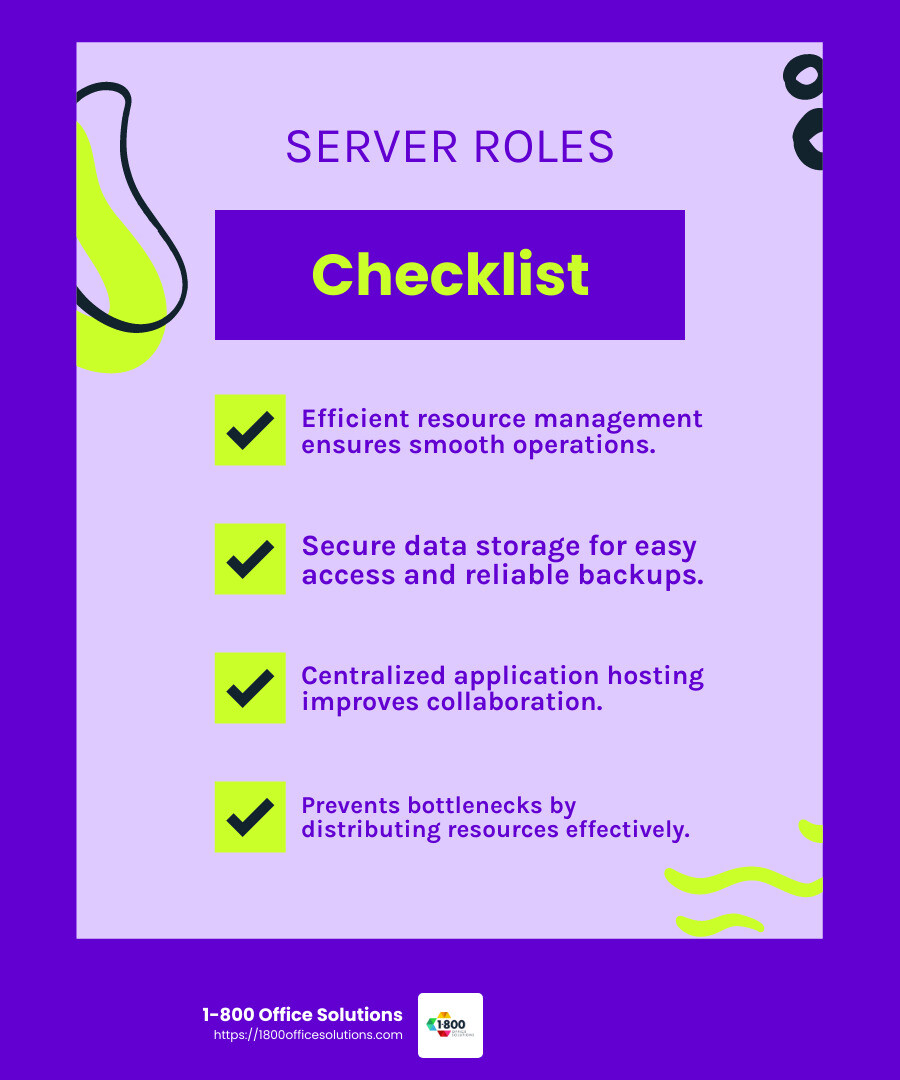
Servers are like traffic controllers for your network resources. They allocate and manage resources such as files, applications, and even processing power. This ensures each device on the network gets what it needs to function optimally. By efficiently distributing resources, servers help prevent bottlenecks and maintain smooth network operations.
Data Storage
Think of servers as vast libraries, storing and organizing data for easy access. They provide a secure space for data storage, ensuring that users can retrieve information quickly and safely. Servers also play a crucial role in data backup and recovery, protecting your data from loss and ensuring it can be restored if needed.
Application Hosting
Servers are the powerhouses behind application hosting. They run and manage applications that users access across the network. This means you can use software without having to install it on every single device. By centralizing applications on servers, businesses can streamline workflows and facilitate collaboration.
What does a server do in a network? It manages resources, stores data, and hosts applications, acting as the backbone of any digital infrastructure. Without servers, modern networks would struggle to function efficiently. They enable businesses to operate smoothly, supporting everything from day-to-day tasks to complex operations.
Next, we’ll explore the key components of a server and how they contribute to its powerful capabilities.
Key Components of a Server
Servers are the backbone of any network, and their power comes from several key components. Let’s explore what makes these machines tick.
Processor
The processor, or CPU, is the brain of the server. It’s responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. Modern servers often use powerful processors with multiple cores, like Intel Xeon, to handle thousands of tasks simultaneously. This allows servers to manage large workloads efficiently, ensuring quick responses to user requests.
RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory)
is the short-term memory of the server. It temporarily stores data that the processor needs to access quickly. The more RAM a server has, the better it can handle multiple tasks at once. This is crucial for servers, as they often deal with numerous user requests and applications running simultaneously. High RAM capacity ensures smooth and fast performance.
Storage
Servers need ample storage to hold operating system files, applications, databases, and user data. They use a combination of traditional hard drives and modern solid-state drives (SSDs) to store this information. SSDs are faster and more reliable, making them ideal for servers that require quick data access. Additionally, many servers use RAID configurations to improve data redundancy and fault tolerance, ensuring data remains safe even if a drive fails.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the amount of data a server can transmit over a network at any given time. High bandwidth is essential for servers because it allows them to serve multiple clients simultaneously without delays. Whether it’s a web server delivering web pages or a file server sharing large files, adequate bandwidth ensures efficient data flow and prevents network congestion.

In summary, the key components of a server—processor, RAM, storage, and bandwidth—work together to provide the power and efficiency needed to support modern networks. These elements ensure that servers can handle complex tasks, deliver fast responses, and maintain reliable operations.
Next, we’ll look at the different types of servers and their specific roles in a network.
Types of Servers
In a network, different types of servers have unique roles that help keep everything running smoothly. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
Web Servers
Web servers are like the librarians of the internet. They store and deliver web pages to users when they type a URL into their browser. Popular web servers include Apache and Nginx. They ensure that when you click a link, the right content appears on your screen quickly.
Mail Servers
Imagine a post office for emails—that’s what mail servers are. They receive, store, and send emails for users. Instead of each computer needing its own mail system, a mail server handles all the email traffic. This setup keeps communication smooth and organized.
Application Servers
Application servers run software applications that users access over a network. They take the heavy lifting off individual computers by running complex tasks centrally. This means users don’t need powerful machines to use resource-intensive applications.
Database Servers
Database servers are the vaults where data is stored and managed. They allow multiple users to access and modify data simultaneously. Oracle and MySQL are examples of database servers that help businesses keep their data organized and accessible.
DNS Servers
DNS servers act like phone books for the internet. They translate human-friendly domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other. Without DNS servers, finding websites would be much more complicated.
Proxy Servers
Proxy servers are intermediaries between users and the internet. They help improve privacy by masking user IP addresses and can also cache web pages to improve load times. They’re often used to control internet usage and improve security.
DHCP Servers
DHCP servers automatically assign IP addresses to devices on a network. This dynamic assignment helps prevent conflicts and makes network management easier. Imagine them as traffic controllers ensuring every device gets a unique address.
File Servers
File servers store and share files across a network. They allow users to access documents, images, and other files without needing a copy on every device. This centralized storage simplifies file management and backup processes.
Gaming Servers
Gaming servers connect players from around the world, providing a platform for multiplayer games. They manage game data and synchronize player actions, ensuring a seamless gaming experience. Popular games like Minecraft and Fortnite rely heavily on these servers.
Print Servers
Print servers manage print jobs from multiple users. Instead of connecting a printer to each computer, a print server queues and processes print requests. This setup reduces hardware costs and simplifies printer management.
Each server type plays a crucial role in ensuring that networks function efficiently, providing specific services to meet various needs. By understanding these roles, we can appreciate how servers keep our digital world connected and functional.
Next, we’ll explore how these servers contribute to network efficiency and why they’re essential for modern businesses.
How Servers Improve Network Efficiency
Servers are the backbone of any network, and understanding what a server does in a network can reveal why they’re so vital. They provide several benefits that improve a network’s overall performance and reliability.
Scalability
As businesses grow, so does their need for more resources. Servers offer scalability by allowing networks to expand without replacing existing hardware. This means adding more users or applications is seamless and doesn’t disrupt operations. Whether it’s more disk space or faster speeds, servers can handle increased demand with ease.
High Processing Power
Servers are like the powerhouses of a network. They provide high processing power, enabling them to handle many tasks at once. This means networks can run complex applications and manage multiple users without slowing down. For example, application servers take on heavy computing tasks, freeing up individual computers for other work.
Reliability
A network’s reliability is crucial for business operations. Servers ensure reliability by minimizing downtime. If one device fails, backup servers can take over, keeping the network running smoothly. This setup ensures that critical systems are always online, which is essential for maintaining business continuity.
Collaboration
Servers improve collaboration by allowing users to access shared resources and applications. For instance, file servers enable multiple users to access and edit documents simultaneously, fostering teamwork and productivity. This setup is especially beneficial in remote work environments, where team members need to collaborate from different locations.
Cost Savings
By centralizing resources, servers help businesses achieve cost savings. They reduce the need for individual devices to perform complex tasks, which means less wear and tear and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, using servers for centralized tasks like printing or file storage can reduce hardware expenses.
Cybersecurity
Protecting data is more important than ever. Servers play a crucial role in cybersecurity by managing and monitoring access to network resources. They can verify IP addresses and block suspicious activity, protecting against threats like malware and DDoS attacks. This level of security is vital for safeguarding sensitive business information.
These features make servers indispensable for modern networks, ensuring they run efficiently and securely. In the next section, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about servers in a network, providing further insights into their purpose and roles.
Frequently Asked Questions about Servers in a Network
What is the purpose of a server in networking?
Servers are like the traffic directors of a network. They manage data access and ensure that resources and services are available to all the computers connected to the network. Imagine you’re at a library. The server is like the librarian who knows exactly where every book is and helps you find what you need. In a network, servers do the same by providing service provision—making sure that the right data reaches the right user at the right time.
What are the three roles of a server?
Servers have three main roles:
- Data Sharing: Servers store and share data among users. Think of it as a central filing cabinet where everyone can access and update shared documents without needing to keep separate copies.
- Resource Distribution: Just like a teacher distributing worksheets to students, servers allocate resources like internet access and applications to users. This ensures everyone gets what they need to work efficiently.
- Workload Management: Servers balance the workload by handling complex tasks themselves, freeing up individual computers for other activities. It’s like having a team leader who takes on the tough jobs so the rest of the team can focus on their tasks.
How do servers ensure network security?
Security is a top priority for servers. They use firewalls and antivirus software to protect the network. Firewalls act as barriers, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules, like a security guard checking IDs at a building entrance. Antivirus software scans for and removes malicious software, keeping the network safe from threats. Together, these tools help servers maintain a secure environment, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring that only authorized users can access the network’s resources.
Conclusion
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we understand that effective network management is crucial for the smooth operation of any business. Servers play a vital role in this process by acting as the backbone of your network infrastructure. They ensure that data flows smoothly, resources are distributed efficiently, and business operations run without a hitch.
Our team is dedicated to helping businesses leverage the full potential of their servers. Whether it’s setting up new servers, managing existing networks, or enhancing cybersecurity measures, we offer comprehensive managed IT services custom to your needs. By partnering with us, you can focus on what you do best—growing your business—while we take care of the technical details.
Ready to optimize your network and improve your business operations? Visit our Managed IT Services in Charlotte page to learn more about how we can help you achieve your goals.
In today’s business world, staying ahead means having a reliable and efficient network. Let us help you build and maintain the network infrastructure you need to succeed.











