Mastering Cybersecurity Identity Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Cybersecurity identity management ensures only the right people and devices can access your company’s systems and data, forming a key part of your digital defense.
At its core, this framework:
- Identifies users and devices.
- Authenticates their identity.
- Authorizes their access.
- Manages their permissions over time.
- Audits their activities for security and compliance.
Think of it as the digital bouncer for your organization. In a world of remote work and evolving cyber threats, knowing who is accessing what is more critical than ever. Without strong identity management, your sensitive information is vulnerable, as threat actors often target user credentials to breach networks.
Cybersecurity identity management builds a robust defense around users and their access points, ensuring every digital interaction is verified and controlled. This guide covers everything you need to know to protect your organization with smart identity management.
Simple cybersecurity identity management word guide:
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM) and What Are Its Core Components?

Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies for managing digital identities and controlling access to critical information. It acts as the secure backbone of your digital environment.
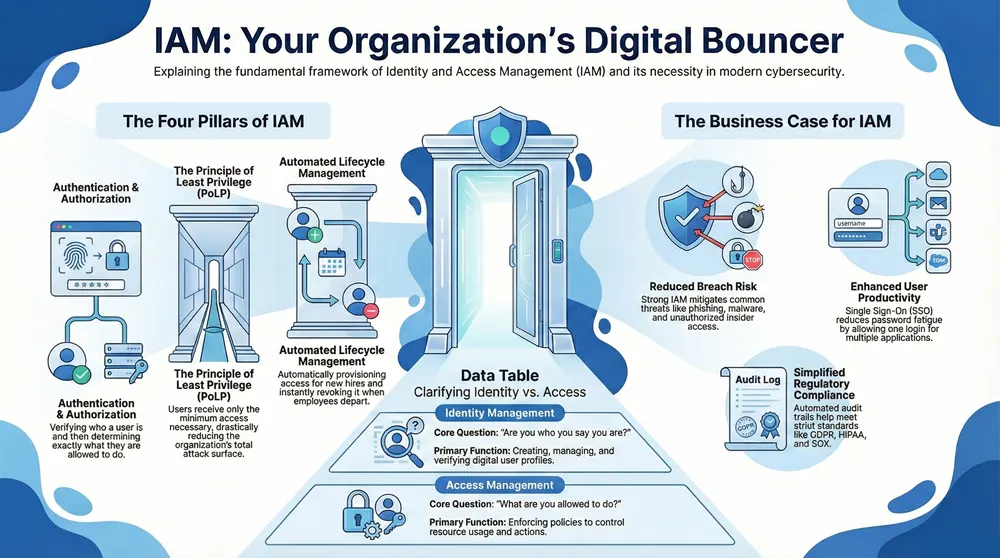
IAM assigns a unique digital identity to every person, device, or application needing access. This identity profile is used to manage access throughout the user’s entire lifecycle, from onboarding to their departure. A core guiding principle is the principle of least privilege (PoLP), which dictates that users should only have the minimum access necessary to perform their job duties. This simple rule drastically reduces your organization’s attack surface.
Defining Identity vs. Access Management
Though related, identity and access management are two distinct parts of IAM:
Identity management focuses on who you are. It involves creating, managing, and verifying user identity data, such as usernames and security credentials. The goal is to maintain a reliable digital identity for every user and device, answering the question, “Are you who you say you are?”
Access management determines what you can do. After a user is authenticated (their identity is proven), access management enforces authorization policies to control which resources they can use and what actions they can perform. It answers the question, “Now that I know who you are, what are you allowed to do?”
Together, they create a powerful security shield for your computer systems, cloud applications, and business assets. For more tips, see our guide on Ways to Secure a Computer Network.
Core Components of a Cybersecurity Identity Management Framework
A strong cybersecurity identity management framework is built on several key components:
- Identity Provisioning & Deprovisioning: Automates the creation, modification, and deletion of user accounts and access rights. This ensures new hires get access quickly and former employees have their access revoked immediately.
- Authentication Services: Confirms a user’s identity. This ranges from simple passwords to advanced methods like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), biometrics, and Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Authorization Controls: Dictates what resources an authenticated user can access. This is often managed through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) or more granular Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC).
- Centralized Directory Services: A central repository for all digital identities and their attributes, simplifying management and ensuring data consistency.
- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA): Ensures access rights align with company policies and regulations through regular reviews, certifications, and enforcement of principles like segregation of duties.
- Reporting and Auditing: Logs all user activities and access events. These audit trails are vital for detecting suspicious behavior, investigating incidents, and proving compliance.
Why IAM is a Cornerstone of Modern Cybersecurity
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity identity management (IAM) is more than an IT function—it’s a business necessity and the cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. It directly addresses common cyberattack vectors while ensuring business operations run smoothly and securely.
Hackers frequently target user credentials through phishing, malware, or ransomware because it’s an easy way to bypass defenses. Without strong IAM, your organization faces a high risk of data breaches, reputational damage, and financial penalties.
IAM is also critical for mitigating insider threats, whether malicious or accidental. By enforcing the principle of least privilege and monitoring access, IAM prevents employees from accessing data they shouldn’t, reducing the risk of data leaks or accidental deletions.
With the rise of remote and hybrid work, employees need secure access to company resources from various locations and devices. Cybersecurity identity management enables this by establishing strict controls that grant safe access to authorized users while blocking outsiders, balancing security with business productivity.
The Benefits of a Strong IAM System
A robust cybersecurity identity management system offers significant advantages:
- Reduced risk of data breaches: By tightly controlling access to networks and data, IAM dramatically improves your overall security posture.
- Improved user experience: Features like Single Sign-On (SSO) allow users to access multiple apps with one login, reducing password fatigue and boosting productivity.
- Centralized control: Automation gives IT teams precise, centralized control over user access, reducing manual workloads.
- Operational efficiency: Automated provisioning and deprovisioning save time and ensure access rights are always aligned with current roles.
- Improved collaboration: Secure, controlled access to shared resources enables seamless collaboration between employees, partners, and vendors.
- Improved compliance and governance: Detailed audit trails simplify compliance with regulations and internal policies. For more tips, check out our 5 Cloud Security Tips for Business Owners.
The Risks of Neglecting IAM
Failing to implement a strong IAM system exposes your organization to severe risks:
- Compromised credentials and unauthorized access: Weak IAM makes stolen credentials an easy entry point for hackers, a leading cause of data breaches.
- High risk of data breaches: Poorly managed access leaves sensitive data and critical systems vulnerable to exposure.
- Reputational damage: A security incident can severely damage customer trust and market standing, with long-lasting effects.
- Financial penalties: Non-compliance with data protection regulations can lead to hefty fines and legal consequences.
- Increased manual work for IT: A lack of automation burdens IT staff with routine tasks, pulling them from critical security initiatives.
- Exposure to insider threats: Without granular controls, employees with excessive access pose a significant risk, intentionally or not. For guidance, see our Tips to Reduce Risks After a Security Breach.
How Cybersecurity Identity Management Works in Practice
Cybersecurity identity management is a dynamic process that ensures every person and device follows the rules for accessing sensitive information. It operates in a continuous cycle of provisioning, authenticating, authorizing, and monitoring access.
For example, when a new employee joins, the IAM system automatically creates their digital identity and provisions the necessary access for their role based on the “principle of least privilege.” If their role changes, the system adjusts their permissions accordingly, granting new access and revoking old privileges. When an employee leaves, the system immediately de-provisions all their accounts, closing potential security gaps.
IAM also manages device identities. Whether it’s a company laptop, a personal phone under a BYOD policy, or an IoT sensor, the system ensures only approved and secure devices can connect to your network. This constant, automated management keeps all access privileges current, accurate, and secure.
Key Technologies and Standards
Modern IAM relies on several key technologies and standards:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, improving convenience and security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds a layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, making it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): A specialized subset of IAM focused on securing and monitoring the powerful accounts of IT administrators and other privileged users.
- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA): Manages the identity lifecycle and access rights to ensure they align with policies and regulations.
- Federated Identity Management: Enables users to use one set of credentials across different organizations, crucial for cloud and partner collaboration. This is supported by standards like SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect (OIDC). Other key standards include SCIM for automating user data exchange and LDAP for directory services. For more on frameworks, see The NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
Common Implementation Challenges
Implementing an IAM system can present several challenges:
- Integrating with legacy systems: Older systems often lack modern APIs, making integration with new IAM solutions complex and costly.
- Scalability: The IAM solution must be able to scale to support a growing number of users, devices, and services.
- Defining clear policies: Creating granular access policies that balance security with user productivity is a complex task.
- User adoption: Employees may resist new security procedures. Clear communication and training are essential for a smooth transition.
- Lack of in-house expertise: Implementing and managing IAM requires specialized skills that many organizations lack.
- Balancing security with productivity: The ultimate goal is to improve security without hindering daily operations. For BYOD insights, see our guide on How to Make the Most Out of Your BYOD Policy.
IAM’s Role in Compliance and Future Trends
Cybersecurity identity management is not just about security; it’s also a critical tool for regulatory compliance. A well-designed IAM system helps your organization prove accountability and meet data protection requirements.
IAM solutions provide detailed audit trails that log all access attempts and user activities, which are essential for auditors. Regular access reviews ensure that permissions align with current roles and policies, preventing “access creep” and enforcing the principle of least privilege. This proactive approach to data protection is vital for navigating today’s strict regulatory landscape.
How IAM Contributes to Regulatory Compliance
IAM is fundamental to meeting various regulatory requirements:
- GDPR: Helps enforce data access controls and provides the audit trails needed to demonstrate compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation.
- HIPAA: Protects sensitive patient data (ePHI) by ensuring only authorized personnel can access it, as required by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
- SOX: Enforces segregation of duties and controls access to financial systems to meet the internal control requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
- PCI DSS: Secures cardholder data with strong authentication and access controls mandated by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
IAM’s automated reporting simplifies compliance audits and helps enforce security policies consistently, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated fines. For more context, read our guide on What is: Risk Management?.
The Future of Cybersecurity Identity Management
The field of cybersecurity identity management is constantly evolving. Here are some key future trends:
- Identity Fabrics: This approach aims to unify disparate identity systems into a single, manageable layer, providing a holistic view and control over all human and machine identities.
- AI and Machine Learning (ML): AI will revolutionize IAM by detecting anomalous behavior, automating risk analysis, and streamlining access decisions. Learn more about What is: AI in Daily Life?.
- Passwordless Authentication: This trend is gaining momentum, replacing traditional passwords with more secure and user-friendly methods like biometrics and FIDO passkeys to eliminate phishing risks.
- Decentralized Identity: Using technologies like blockchain, this model gives individuals control over their own digital identity, allowing them to share verified credentials selectively.
- Advanced Biometrics: Convenient and secure methods like facial and fingerprint recognition are becoming increasingly common for identity verification.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cybersecurity Identity Management
It’s normal to have questions about a topic as vital as cybersecurity identity management. Here are answers to some of the most common ones.
What are the four pillars of IAM?
The four pillars of IAM form a comprehensive framework for securing digital identities:
Administration: Managing the identity lifecycle, including creating, updating, and deleting user accounts.
Authentication: Verifying a user's identity through methods like passwords, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), or biometrics.
Authorization: Determining what resources and data a verified user is allowed to access based on policies.
Auditing: Monitoring and recording user activities to detect threats, investigate incidents, and ensure compliance.
What is the difference between IAM and Privileged Access Management (PAM)?
Cybersecurity identity management (IAM) applies broadly to all users and identities in an organization, managing their access to everyday resources. Its goal is to ensure standard users have the correct access to do their jobs.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a specialized subset of IAM that focuses exclusively on securing and monitoring "privileged accounts." These are the powerful administrator accounts with extensive access to critical systems. PAM applies extra layers of security to these high-risk accounts to prevent catastrophic breaches.
Why is IAM critical for cloud computing?
With cloud computing, the traditional network perimeter has dissolved. Data and applications are distributed across the internet, making identity the new security perimeter.
Cybersecurity identity management is critical in this borderless environment because it ensures every user, device, and application connecting to your cloud resources is verified and authorized. It provides the essential digital boundary needed to protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access in a cloud or hybrid environment. Relying on simple passwords alone is no longer sufficient.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity identity management is essential for keeping your business safe. It acts as your first and most crucial line of defense by defining, authenticating, authorizing, and auditing every access point.
A strong IAM system reduces breach risks, improves operational efficiency, simplifies compliance, and improves the user experience. Neglecting it, however, exposes your business to devastating data breaches, financial penalties, and reputational damage. The stakes are simply too high to overlook.
At 1-800 Office Solutions, we understand the complexities of IAM. As your strategic IT partner, we provide the expertise and continuous vigilance needed to build a comprehensive security strategy. Our goal is to fortify your digital doors, allowing your operations to run securely and productively.
Don’t let identity be the weak link in your security chain. Investing in cybersecurity identity management safeguards your assets and reputation. Let’s work together to achieve a robust security posture that balances protection with productivity. Ready to fortify your defenses? Strengthen your defenses with Managed Cybersecurity Services from 1-800 Office Solutions.











